Java Collections Framework: Master the Art of Data Structures
The Java collections framework provides a set of interfaces and classes to implement various data structures and algorithms.
For example, the LinkedList class of the collections framework provides the implementation of the doubly-linked list data structure.
Interfaces of Collections FrameWork
The Java collections framework provides various interfaces. These interfaces include several methods to perform different operations on collections.
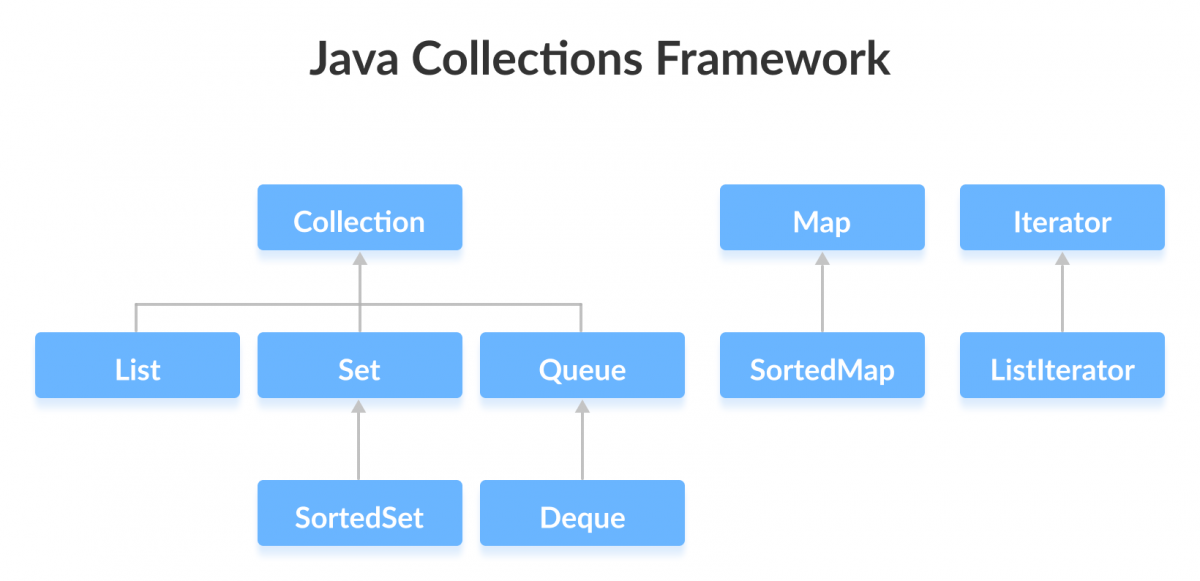
We will learn about these interfaces, their subinterfaces, and implementation in various classes in detail in the later chapters. Let's learn about the commonly used interfaces in brief in this tutorial.
Java Collection Interface
The Collection interface is the root interface of the collections framework hierarchy.
Java does not provide direct implementations of the Collection interface but provides implementations of its subinterfaces like List, Set, and Queue.
Collections Framework Vs. Collection Interface
People often get confused between the collections framework and Collection Interface.
The Collection interface is the root interface of the collections framework. The framework includes other interfaces as well: Map and Iterator. These interfaces may also have subinterfaces.
Subinterfaces of the Collection Interface
As mentioned earlier, the Collection interface includes subinterfaces that are implemented by Java classes.
All the methods of the Collection interface are also present in its subinterfaces.
Here are the subinterfaces of the Collection Interface:
List Interface
The List interface is an ordered collection that allows us to add and remove elements like an array.
Set Interface
The Set interface allows us to store elements in different sets similar to the set in mathematics.
Queue Interface
The Queue interface is used when we want to store and access elements in First In, First Out manner.
Java Map Interface
In Java, the Map interface allows elements to be stored in key/value pairs. Keys are unique names that can be used to access a particular element in a map. And, each key has a single value associated with it.
Java Iterator Interface
In Java, the Iterator interface provides methods that can be used to access elements of collections.
Why the Collections Framework?
The Java collections framework provides various data structures and algorithms that can be used directly. This has two main advantages:
- We do not have to write code to implement these data structures and algorithms manually.
- Our code will be much more efficient as the collections framework is highly optimized.
Moreover, the collections framework allows us to use a specific data structure for a particular type of data. Here are a few examples,
- If we want our data to be unique, then we can use the
Setinterface provided by the collections framework. - To store data in key/value pairs, we can use the
Mapinterface. - The
ArrayListclass provides the functionality of resizable arrays.
Example: ArrayList Class of Collections
Before we wrap up this tutorial, let's take an example of the ArrayList class of the collections framework.
The ArrayList class allows us to create resizable arrays. The class implements the List interface (which is a subinterface of the Collection interface).
// The Collections framework is defined in the java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
ArrayList<String> animals = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements
animals.add("Dog");
animals.add("Cat");
animals.add("Horse");
System.out.println("ArrayList: " + animals);
}
}Output:
ArrayList: [Dog, Cat, Horse]
In the later tutorials, we will learn about the collections framework (its interfaces and classes) in detail with the help of examples.
- This blog post was originally published at:https://www.programiz.com/
