Flutter vs. React Native vs. Xamarin
What is cross-platform development?
Cross-platform mobile app development allows you to build mobile applications for multiple platforms such as iOS and Android with just one technology stack.
This means that instead of creating multiple versions of your app, each written using the dedicated native language for each platform, you can write your code once and deploy it on several platforms at once.
Cross-platform development advantages
There are several pros when it comes to cross-platform mobile app development compared to native mobile app development, including:
Write once, deploy everywhere
The most significant advantage of cross-platform development is having a single codebase that you can export to multiple operating systems.
Uniformity across apps
Having a single shared codebase allows you to maintain the same look, feel, and experience across all platforms. All updates and fixes are also automatically reflected everywhere.
Saving resources
Instead of having separate teams with different skill sets working on multiple native versions of your app, you only need one team working on a shared codebase. This allows you to leverage smaller teams and quicker development time to save time and money.
Audience reach
Having your app published on multiple platforms allows you to increase your market reach without any added effort, consequently increasing your chances of getting more downloads and users.
Cross-platform development disadvantages
While cross-platform development comes with many benefits that make it an optimal solution for many developers and companies, they come with a few drawbacks and some trade-offs including:
Performance issues
While cross-platform frameworks work on providing apps that are as close to native apps as possible, they still don’t integrate seamlessly with the respective platforms and have inconsistent communication between the native and non-native components, reducing the app’s speed and degrading performance.
Inconsistency with platforms
Cross-platform development tools don’t have all the features offered by each different platform, so you might need to employ some workarounds. It may also take these frameworks some time to get up-to-date with the newest features and updates released by the platforms.
Limited features
There are many native-only features and integrations available in each platform that are not available in cross-platform apps, which limits the user experience you can provide.
Cross-platform mobile app development tools
There are many cross-platform mobile app development tools and frameworks available, including:
We will take a closer look at the first and arguably most popular three frameworks available right now: Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin.
Flutter

Flutter is an open-source, cross-platform mobile application development framework created by Google in 2017. It’s the newest framework of the three and in short order has become one of the most popular frameworks among front-end devs.
Flutter advantages
Some of the reasons Flutter is currently one of the most loved cross-platform frameworks include:
- Complete development ecosystem: Flutter offers APIs, pre-built widgets, CLI tools, and pretty much all the tools needed for cross-platform mobile app development.
- Customizable: While it offers an extensive library of pre-built widgets, you can also create your own or customize pre-existing ones.
- Reliability: Developed and supported by Google
- Hot reload: Allows developers to fix bugs faster through faster code implementation
- Free: Open-source platform
Flutter disadvantages
Flutter poses a few challenges, especially being a new framework, including:
- Continuous integration support: Lacks compatibility with CI tools such as Travis and Jenkins.
- Large app size: Flutter apps can be quite large compared to other frameworks that can force developers to reduce the number of libraries and packages used, compress images, and even steer away from using animation altogether in favor of reducing their app’s size.
- Native APIs: Flutter doesn’t expose many native APIs for you to use. That’s why, for many purposes, you will need third-party packages. Which also means that you will have to depend on the ecosystem.
However, you can always write your own native code that accesses the needed feature, and Flutter will give you a bridge to use that feature from within your Dart code.
Apps built using Flutter
- Google AdWords
- Google Greentea
- Alibaba
- AppTree
- Reflectly
- Hookle
- Topline
- Birch Finance
- OfflinePal
- Hamilton (musical)
- BetaBubs
Flutter development tools
- Flutter development language
- Dart
- Flutter IDEs:
- Flutter tools:
- Flutter packages:
React Native

React Native is an open-source, cross-platform mobile app development framework created by Facebook in 2015.
It enables users to use JavaScript and React along with native platform capabilities to build mobile apps.
React Native advantages
Some of the pros of React Native include:
- User Interface: Implements native UI components, allowing apps to look like native apps, and therefore providing a high-quality user interface.
- Ready-made components: Offers a vast library of UI components, allowing for faster development time.
- Access to native functionalities: Like camera, accelerometer, etc.
- Platform-specific code: Allows you to further optimize your separate native apps by using native code.
- Hot reload: Allows developers to apply changes to the apps right away without having to recompile the apps.
- Reliability: Developed and supported by Facebook.
- Free: Open-source platform.
React Native disadvantages
Unfortunately, React Native still has its pitfalls, including:
- Navigation: Navigation built in React Native is not seamless and not comparable to native navigation.
- Complex UI: React Native struggles with building complex animation and transitions.
React Native development tools
- React Native development language
- JavaScript
- React Native IDEs:
- React Native tools:
- React Native UI components:
- React Native testing tools:
Apps built using React Native
- Facebook Analytics
- Facebook Ads Manager
- Uber Eats
- Tesla
- Skype
- SoundCloud Pulse
- Walmart
- Bloomberg
- Discord
- Myntra
- Gyroscope
- Chop
- Vogue
- Artsy
- F8
Xamarin

Xamarin is an open-source, cross-platform mobile app development framework that was founded in 2011, making it the oldest of the three.
Xamarin advantages
Xamarin cross-platform mobile app development pros include:
- Performance: Xamarin apps are known for having almost native-like performance levels.
- Complete development ecosystem: C#, .Net, and Microsoft Visual Studio with Xamarin are all you need to build mobile apps with Xamarin, making it one of the most complete cross-platform mobile app development frameworks out there.
- Seamless user experience: Xamarin.Forms allows you to take advantage of standard interface elements by providing a library of templates so that you can reuse your code across different platforms. You can also use Xamarin.iOS and Xamarin.Android for manual customization, if needed.
- Free: For small teams.
Xamarin disadvantages
However, as any cross-platform development framework, Xamarin does have its setbacks, including:
- Updates delay: Whenever new platform features or updates roll out, there is usually a delay until these changes are reflected in the Xamarin tools, which may cause issues with your app.
- Large app size: Xamarin apps can add around 5 megabytes for releases and 20 megabytes for debug builds, making them larger than native apps. This is primarily due to the libraries used to translate C# calls into native calls.
- Heavy graphics: Xamarin is great for apps with a simple UI. However, building complex applications or mobile games with Xamarin might not be the best thing to do as you will have to spend a lot of time writing platform-specific code, which defeats the purpose of using it.
- Platform-specific code: You might need to re-write some parts of the UI in your app in native code. That means that you will need some knowledge in native programming languages such as Kotlin or Java for Android, and Swift or Objective-C for iOS.
Xamarin development tools
- Xamarin development language
- C#
- Xamarin IDEs:
- Xamarin tools:
- Xamarin testing tools:
Apps built using Xamarin
- Skulls of the Shogun
- SuperGiant Games
- Storyo
- Insightly
- FreshDirect
- The World Bank
- Just Giving
- Olo
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- APX
Flutter, React Native, or Xamarin?
Now let’s look at how these cross-platform development tools compare to each other.
Performance
One of the most important factors you should consider when choosing a cross-platform development framework is app performance.
While React Native and Xamarin provide near-native app performances, some argue that Flutter’s performance is better because Dart code is compiled to a C-library, which means it’s close to the native code.
This improves communication speed and provides better performance.
However, it’s hard to benchmark performance as it depends on many factors and variables including device, code, app, and features being used.
Popularity
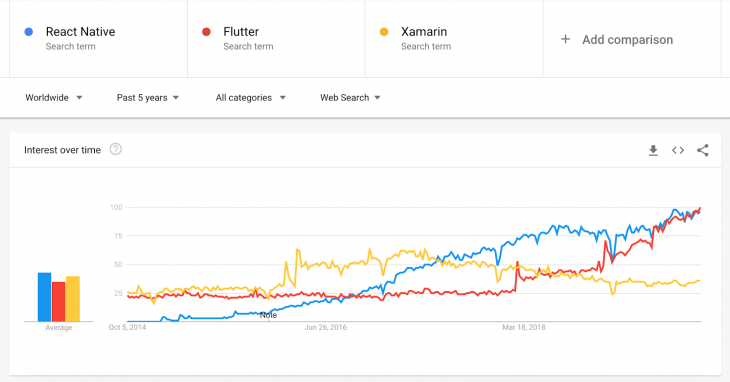
With over 1.6 million developers across 120 countries, Xamarin has definitely developed quite the userbase over the years. However, this is largely due to the fact that it is one of the oldest frameworks out there.
Since its release, React Native has slowly but surely gained popularity, surpassing Xamarin in 2017.
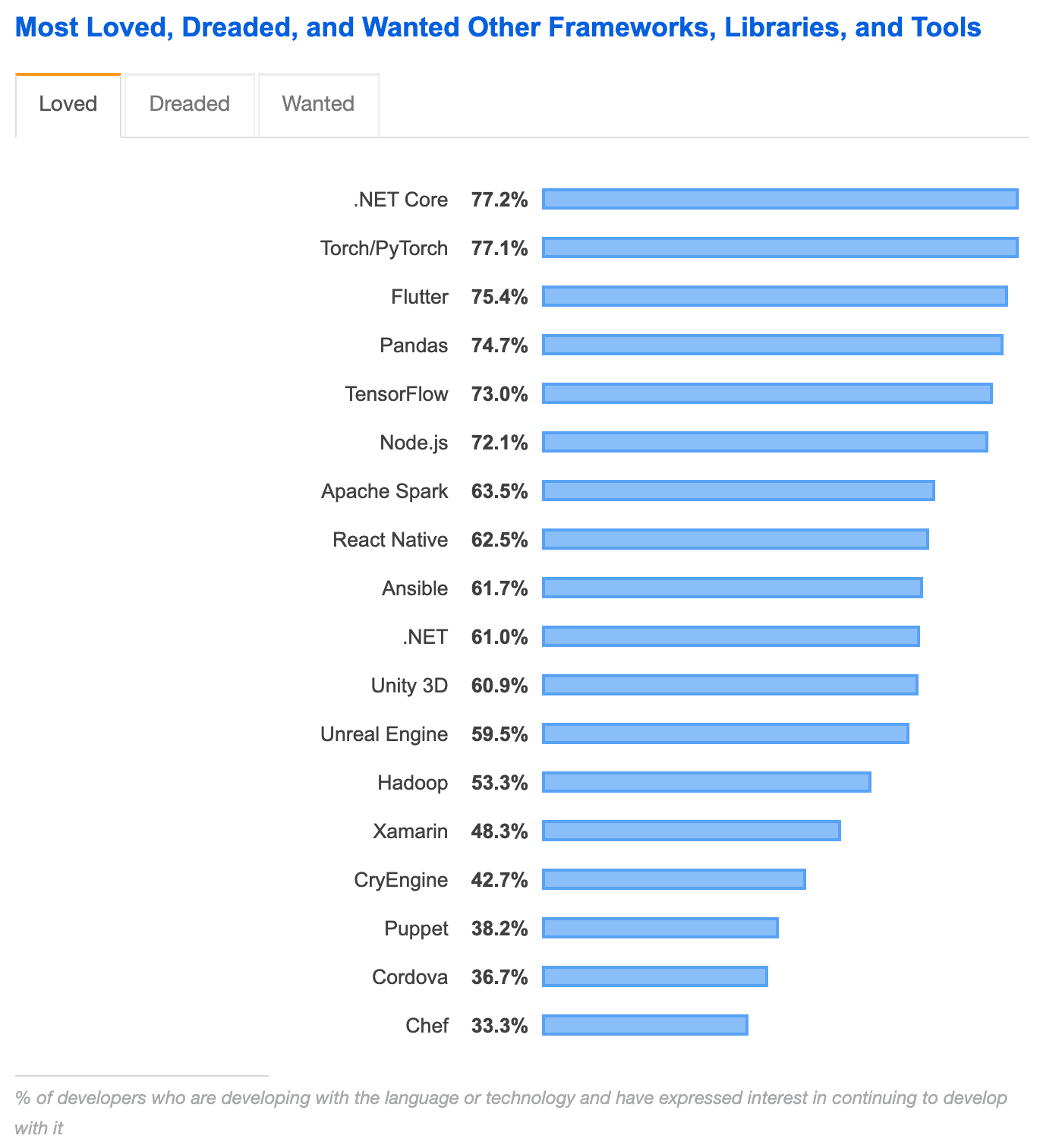
According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2019, Flutter ranked as the most loved framework out of the three, with 75.4 percent of users expressing interest in continuing to develop with Flutter.
React Native came in second with 62.5 percent, followed by Xamarin with only 48.3 percent.
Development languages
The cross-platform tool development language is another crucial factor to consider when making your decision.
Xamarin uses .Net languages like C# and F#, which are common languages and can be used to write native platform code.
While React Native uses JavaScript, which was not invented for it, it still does a great job with React Native apps.
You might encounter a few issues or come across some required workarounds as JavaScript was originally developed for the web.
As a result, some APIs might not work, while others may have to be proxied by React Native.
Flutter uses Dart, which was also not invented for mobile apps. However, it is managed by Google, the same company that created Flutter.
That’s why they make sure to adapt Dart for Flutter and mobile app development, making it better in many ways than JavaScript or C# with fewer workarounds needed.
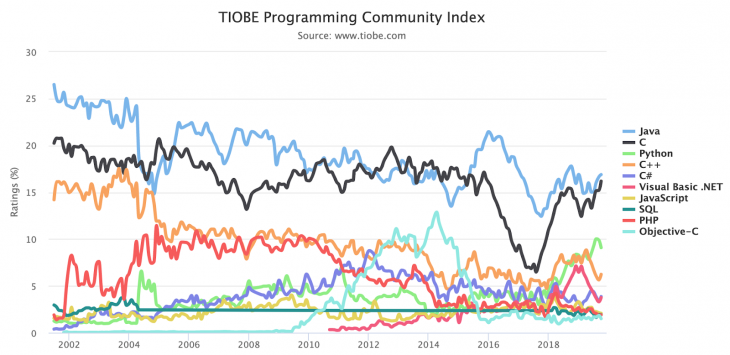
According to the TIOBE Programming Community Index, C# is the fifth most popular programming language worldwide as of October 2019, followed by JavaScript in seventh place.
While still relatively new, Dart is ranked as the 26th most popular programming language in the world.
This gives an advantage to React Native and Xamarin, which both work with a familiar language that can help boost your productivity and save you from enduring a steep learning curve.
Components
React Native offers some pre-built and partly adaptive components like buttons and text inputs.
However, most of these components aren’t really adaptive. If you need something a bit more advanced, you would have to build it yourself by recomposing these built-in components.
Flutter provides a more extensive library of components, which are called widgets. However, these pre-built components are non-adaptive.
The language offers widgets for both iOS and Android, but you have to switch between both manually as it doesn’t have components that automatically adjust their styles depending on the platform you’re running.
Xamarin.Forms offers a complete cross-platform UI toolkit consisting of native UI components for both platforms, which are compiled into platform-specific UI components.
You can also use Xamarin.iOS or Xamarin.Android for custom app UI and better performance.
Code reuse
Code reuse is what brings developers to cross-platform frameworks, so how much of the code written with each framework is actually reusable?
React Native allows you to write the code once and ship anywhere, but it also embraces platform differences.
This means that from time to time, you have to find out on which platform you’re running and load a different component or set of components depending on the platform you’re running.
Still, a considerable part of the codebase can still be reused.
Flutter’s codebase is more reusable as it allows you to define one UI widget tree and reuse the defined logic so you don’t have to do a lot of differentiation, which you can also still do if you need to.
Xamarin prides itself on allowing developers to reuse up to 96 percent of their C# code by leveraging the language.
Xamarin also offers forms components, making it better for code reuse than React Native and Flutter which share an average of 60–90 percent of codes.
Pricing
While all three tools are free, open-source platforms, Xamarin is only free for individuals and small companies.
For large enterprises, single-user licenses start at $499 and go anywhere up to $2,999 for a Visual Studio Enterprise annual subscription.
While this might not be a problem for large enterprises, the costs can still add up, which could cause bigger companies to go with React Native or Flutter.
Support and ecosystem
When choosing a framework, you should also consider its community support, especially if you’re new to it. This includes forums, documentation, tutorials, etc.
React Native has a pretty good amount of support out there. You can easily find a lot of learning material as well or developers on forums or QA sites like Stack Overflow to ask for support whenever you need any help.
Flutter is still relatively new, so it is yet to build a strong community like React Native. However, Google is investing heavily in it, and therefore it is expected to grow into a robust ecosystem in the future.
For Xamarin, support is quite limited. However, Microsoft provides some free Xamarin courses and learning paths to help you get started.
Conclusion
When choosing a cross-platform development tool, there is no one-size-fits-all option.
All three frameworks have proven successful in building great mobile apps. Your specific needs and preferences determine which framework is best for you.
Currently, Flutter seems to be the most popular option as it excels in terms of performance. So if you’re new to the world of cross-platform development, Flutter might be the way to go for you.
However, you can’t rule React Native and Xamarin out just yet as they still excel in other areas.
For example, if you already have some prior knowledge of JavaScript, then it might be wise to go with React Native.
At the end of the day, it all depends on what you’re building and what you hope to achieve. Any framework will have its pitfalls, but the one where the advantages heavily outweigh those setbacks would probably be the right choice for you.
#Flutter #react-native #Xamarin #mobile-app
