How to Email authentication with React Native and Firebase
Tip: Use Bit (GitHub) to easily share your React components into a reusable collection your team can use and develop across projects. Build modular apps faster as a team, save time and make life a bit easier. Give it a try.
Semantic UI components with Bit: Easily turn your components into a reusable collection
Email Authentication with React native, Firebase and Expo:
We’ll be using Expo without getting into Xcode or Android studio. Open up your terminal or command line and type in:
expo init fb-react-native-firebase
After hitting enter, you will see the screen as shown below, where you can enter the name of the app and slug. After that hit enter again.
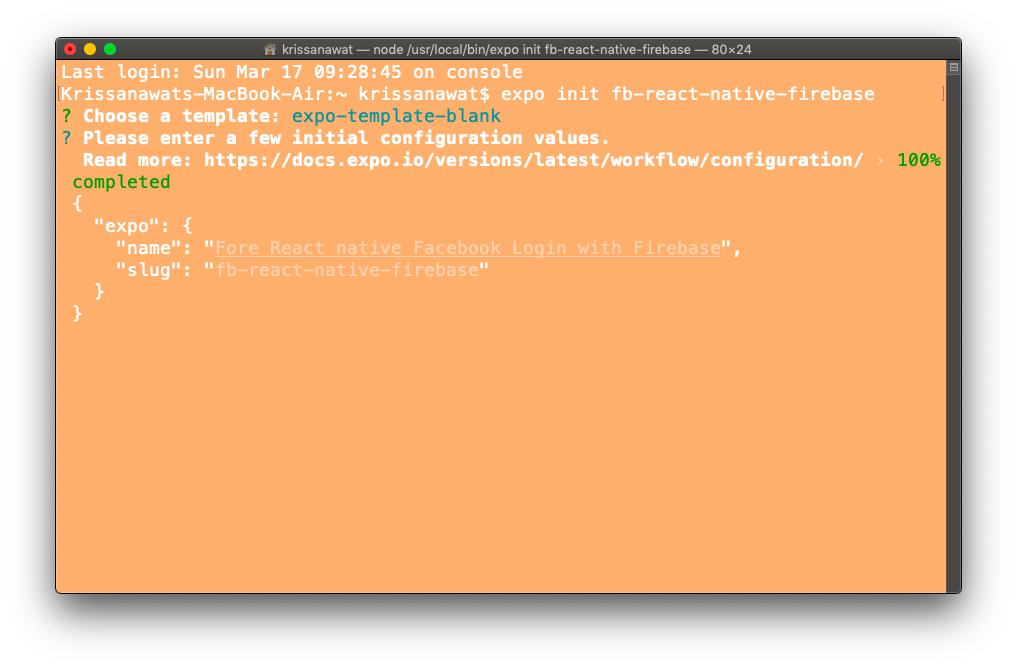
Once the installation is complete, you will see the following screen:
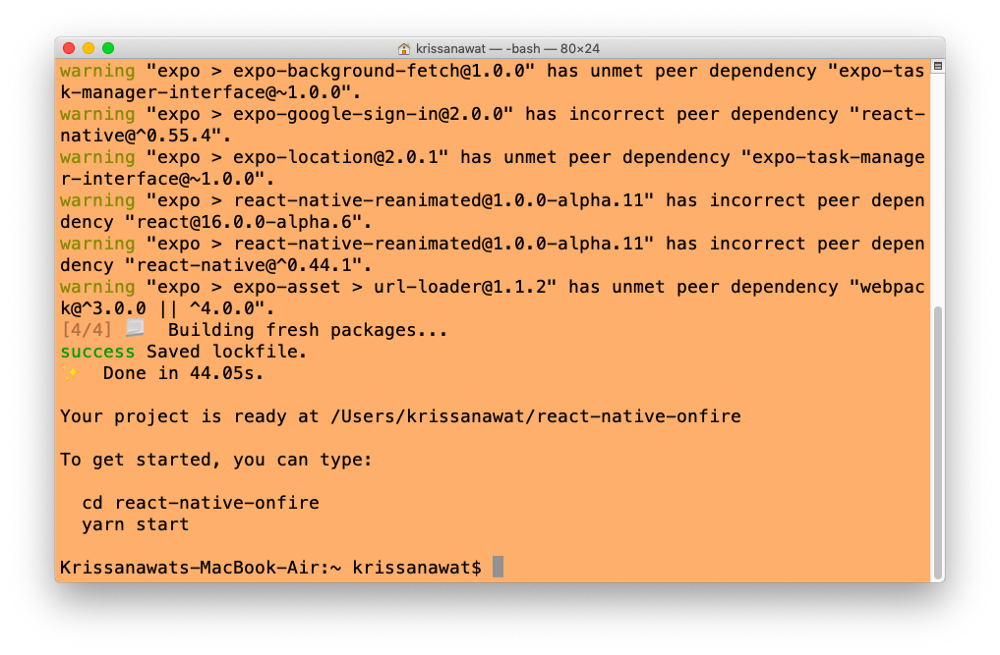
We will be developing this project using VS Code. In VSC, open a new terminal, cd to your app’s folder and run <strong>yarn start</strong> .
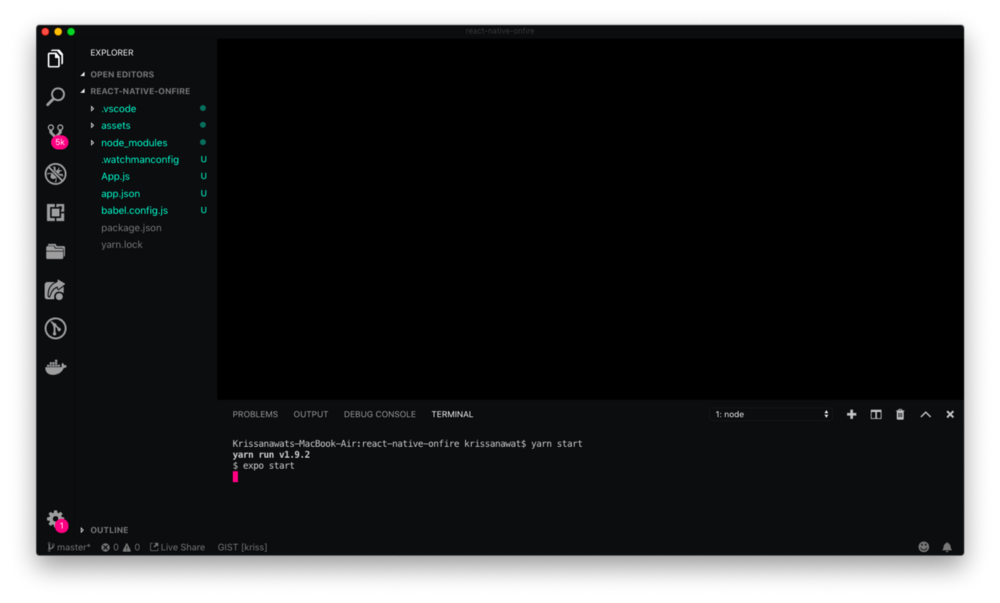
The Expo will open a new window in the browser, as shown below. There you can see options for running the app using an android emulator or device. iOS simulator and by using a QR Code scanner. We are using an Android emulator to showcase this app.
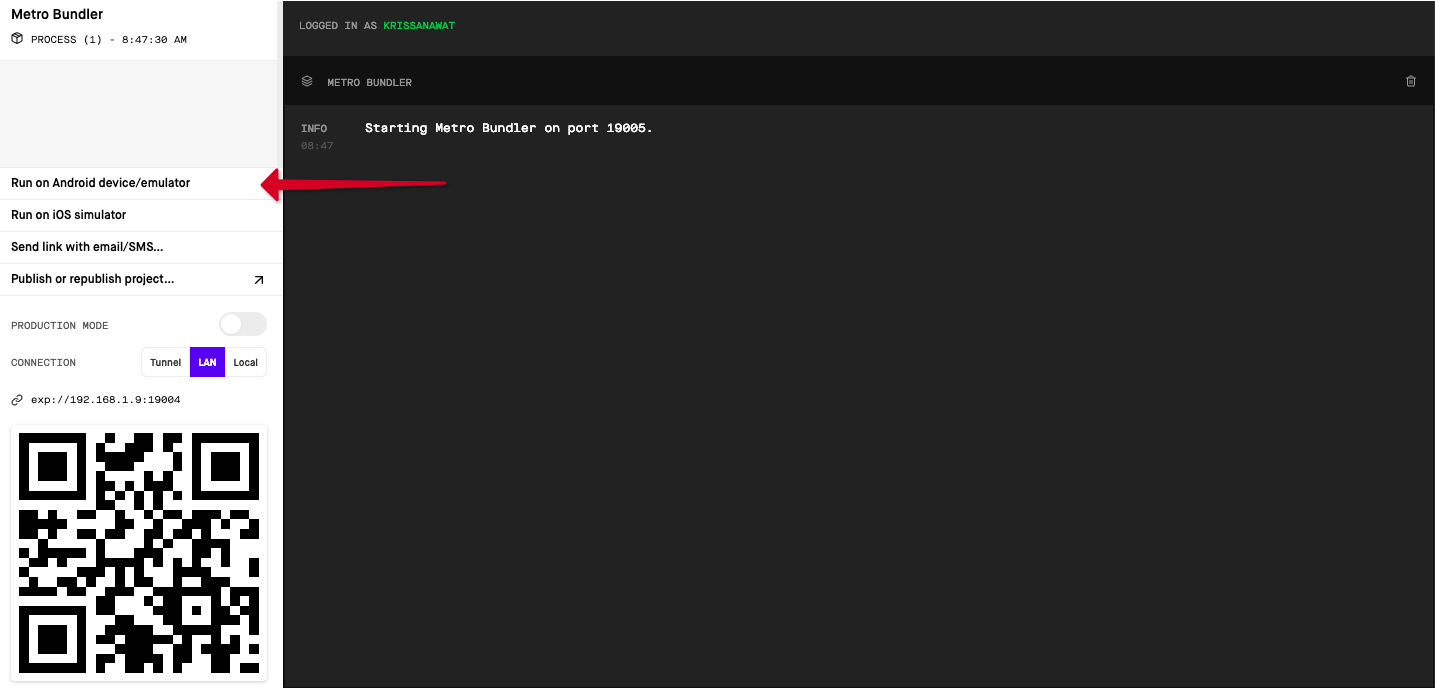
After that, open up your emulator and use it to open the expo app.
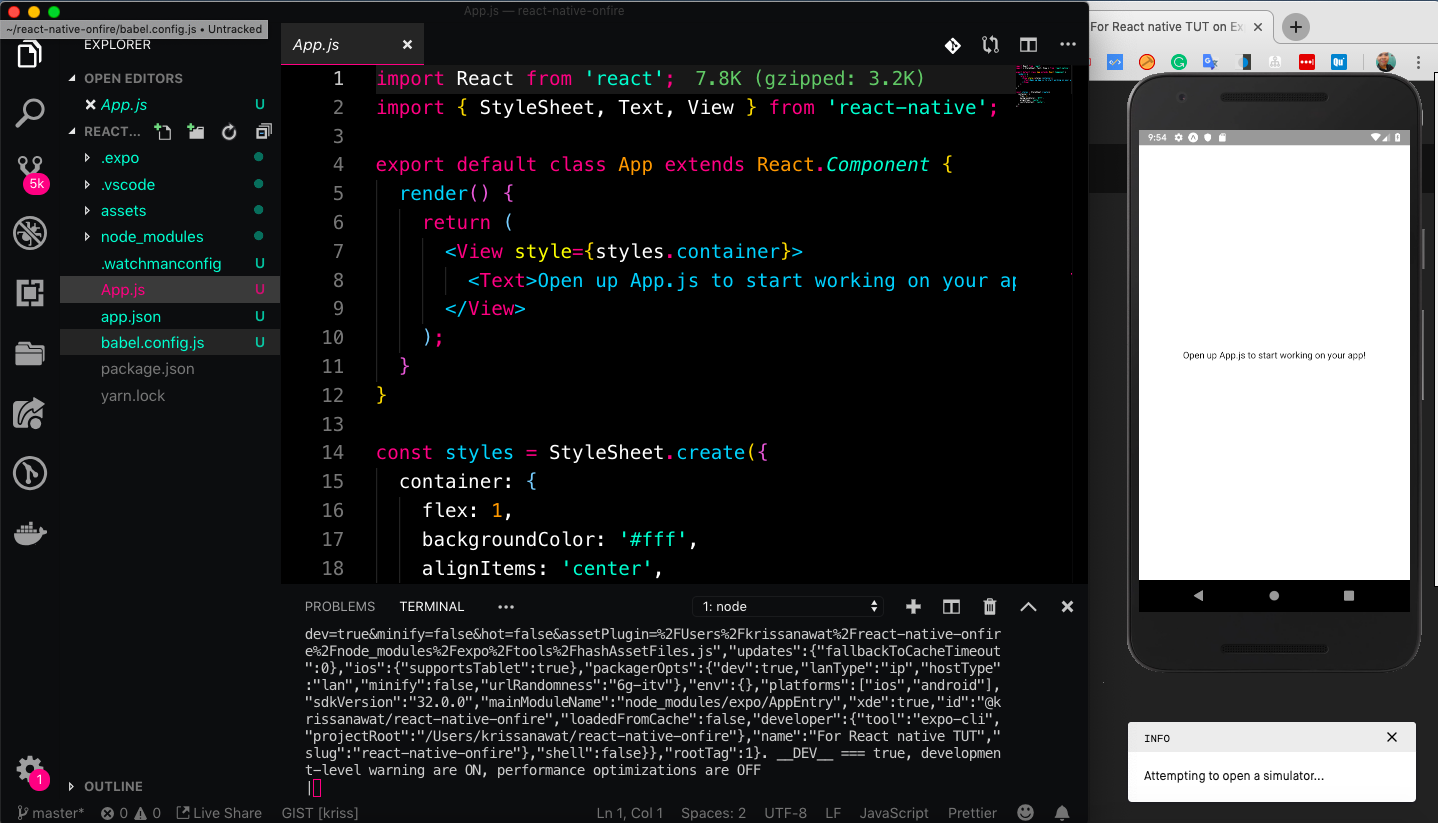
Emulators use too much of your system’s memory. I tried using Android on Mac and it’s eating so much space.
So now we are ready to code.
Bootstrap form quickly with a native base
To design our interface faster and smoother we are using Native base for developing this app. You can check out the native base for more information. So let’s move on to the next step

Open a new terminal and run <strong>npm i native-base</strong>
Next step to import necessary Native base component to <strong>App.js</strong>
import { Container, Item, Form, Input, Button, Label } from "native-base";
And construct form interface
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Form>
<Item floatingLabel>
<Label>Email</Label>
<Input autoCapitalize="none" autoCorrect={false} />
</Item>
<Item floatingLabel>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input
secureTextEntry={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
autoCorrect={false}
/>
</Item>
<Button full rounded success>
<Text>Login</Text>
</Button>
</Form>
</Container>
);
}
When you save the result, you can see them instantly on the screen. This is a feature called as Hot-reloading.
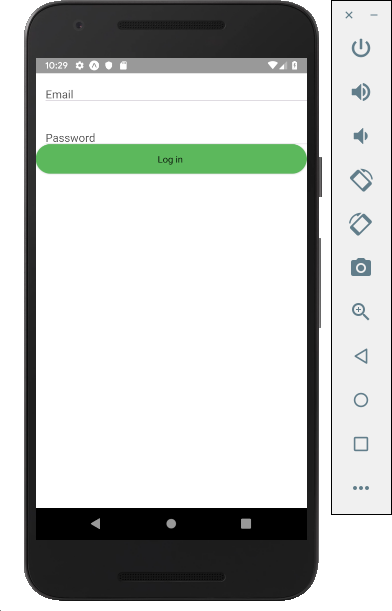
A form appears on the top.
Now, form design is ready. Let’s move on to the main programming part.
Add firebase to React native project
Let’s add firebase with npm i firebaseand import firebase on App.js and then import that into our project.
import * as firebase from "firebase";
In the next step, you need to **create a firebase project. Goto firebase console **and make one as shown below:
Now grab configuration apikey which very important to access the data from the database.
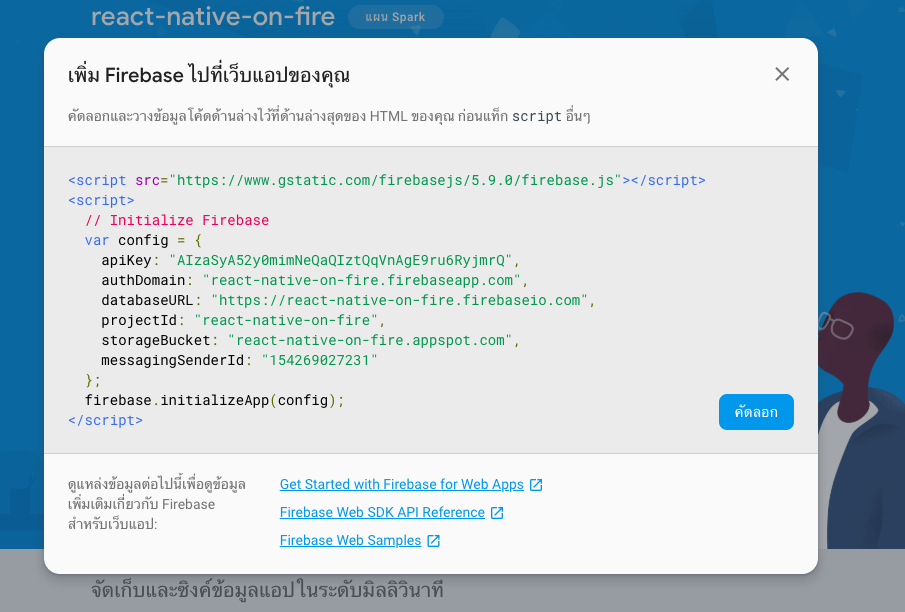
And paste to App.js as shown below in the code structure.
import * as firebase from "firebase";
import { Container, Item, Form, Input, Button, Label } from "native-base";
var config = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyDFdsjQWG8IFLXmviNqSiVZMw_ADFl5tpo",
authDomain: "react-native-firebase-3bde9.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://react-native-firebase-3bde9.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "react-native-firebase-3bde9",
storageBucket: "react-native-firebase-3bde9.appspot.com",
messagingSenderId: "269398778466"
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
Now, we have successfully added firebase to our project.
Sign Up
For email authentication, we need to activate Email authentication on Firebase console.
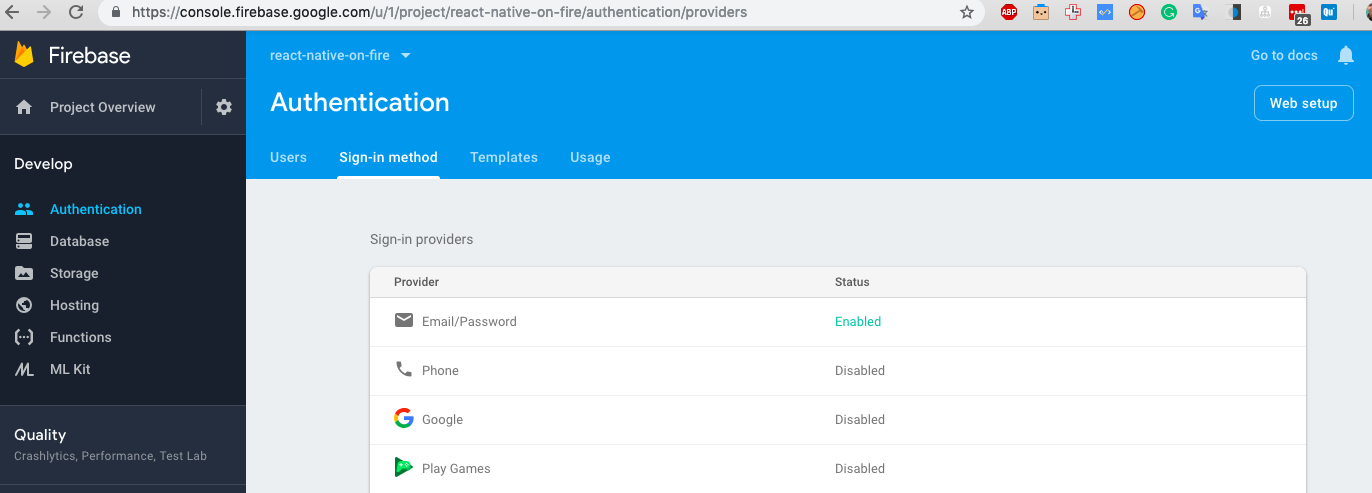
Let’s jump back to VS Code and add a signup button to it.
<Button full rounded success style={{ marginTop: 20 }}> <Text>Signup</Text>
</Button>
Result view should be
Now we have to add signup code.
export default class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
email: "",
password: ""
};
}
SignUp = (email, password) => {
try {
firebase
.auth()
.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(email, password)
.then(user => {
console.log(user);
});
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.toString(error));
}
};
We create a state for handle email and password from. We have created the form and SignUp function for handling firebase code.
Next, add form value to state with on ChangeText.
<Item floatingLabel>
<Label>Email</Label>
<Input
autoCapitalize="none"
autoCorrect={false}
onChangeText={email => this.setState({ email })}
/>
</Item>
<Item floatingLabel>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input
secureTextEntry={true}
autoCapitalize="none"
autoCorrect={false}
onChangeText={password => this.setState({ password })}
/>
And we trigger SignUp function with onPress event from Signup button.
onPress={() => this.SignUp(this.state.email, this.state.password)}
Save and try to submit a form.
After submitting the data goto firebase console and check that the data you have entered is coming there or not.
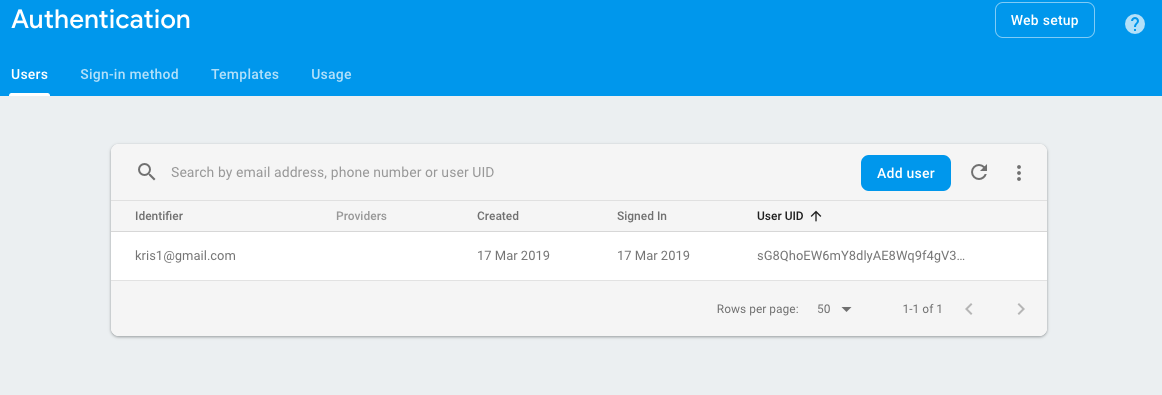
Now we have added data successfully in Firebase as a new user.
Login
For login, we use code from sign up method and change firebase function.
Login = (email, password) => {
try {
firebase
.auth()
.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email, password)
.then(res => {
console.log(res.user.email);
});
} catch (error) {
console.log(error.toString(error));
}
};
After you need to use the **onAuthStateChanged method **to get user data. Then add an onPress method to SignIn Buton.
onPress={() => this.LogIn(this.state.email, this.state.password)}
Let’s try signing in.
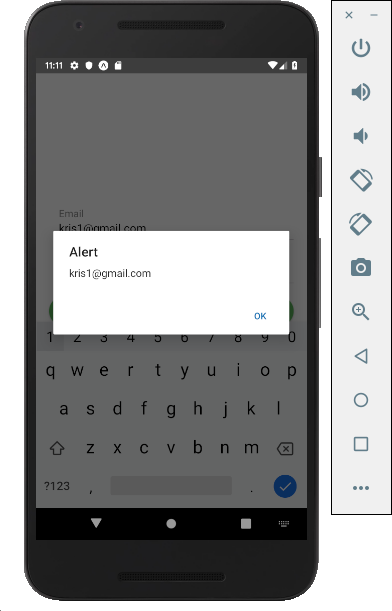
Finally we have made it. We got the data from the firebase user database.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned about how to setup react native project with expo and firebase. You have also learned, how to kickstart construct UI with NativeBase? Then after that, we have created a basic email authentication using React Native, Firebase and expo.
We hope you got something from this. Thanks for reading!
#javascript #java #react-native #reactjs #web-development #devops #firebase
