A simple approach to protect your machine learning model for the adversarial attacks
There are several attacks against deep learning models in the literature, including fast-gradient sign method (FGSM), basic iterative method (BIM) or momentum iterative method (MIM) attacks. These attacks are the purest form of the gradient-based evading technique that is used by attackers to evade the classification model.Cite The CodeIf you find those results useful please cite this paper :
@PROCEEDINGS{catak-adv-ml-2020,
title = {Deep Neural Network based Malicious Network Activity Detection Under Adversarial Machine Learning Attacks},
booktitle = {Proc.\ 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Technologies and Applications (INTAP 2020)},
volume = 5805,
series = {LNCS},author = {Ferhat Ozgur Catak},
publisher = {Springer},
year = {2020}
}
IntroductionIn this work, I will present a new approach to protect a malicious activity detection model from the several adversarial machine learning attacks. Hence, we explore the power of applying adversarial training to build a robust model against FGSM attacks. Accordingly, (1) dataset enhanced with the adversarial examples; (2) deep neural network-based detection model is trained using the KDDCUP99 dataset to learn the FGSM based attack patterns. We applied this training model to the benchmark cybersecurity dataset.The adversarial machine learning has been used to describe the attacks to machine learning models, which tries to mislead models by malicious input instances. The figure shows the typical adversarial machine learning attack.
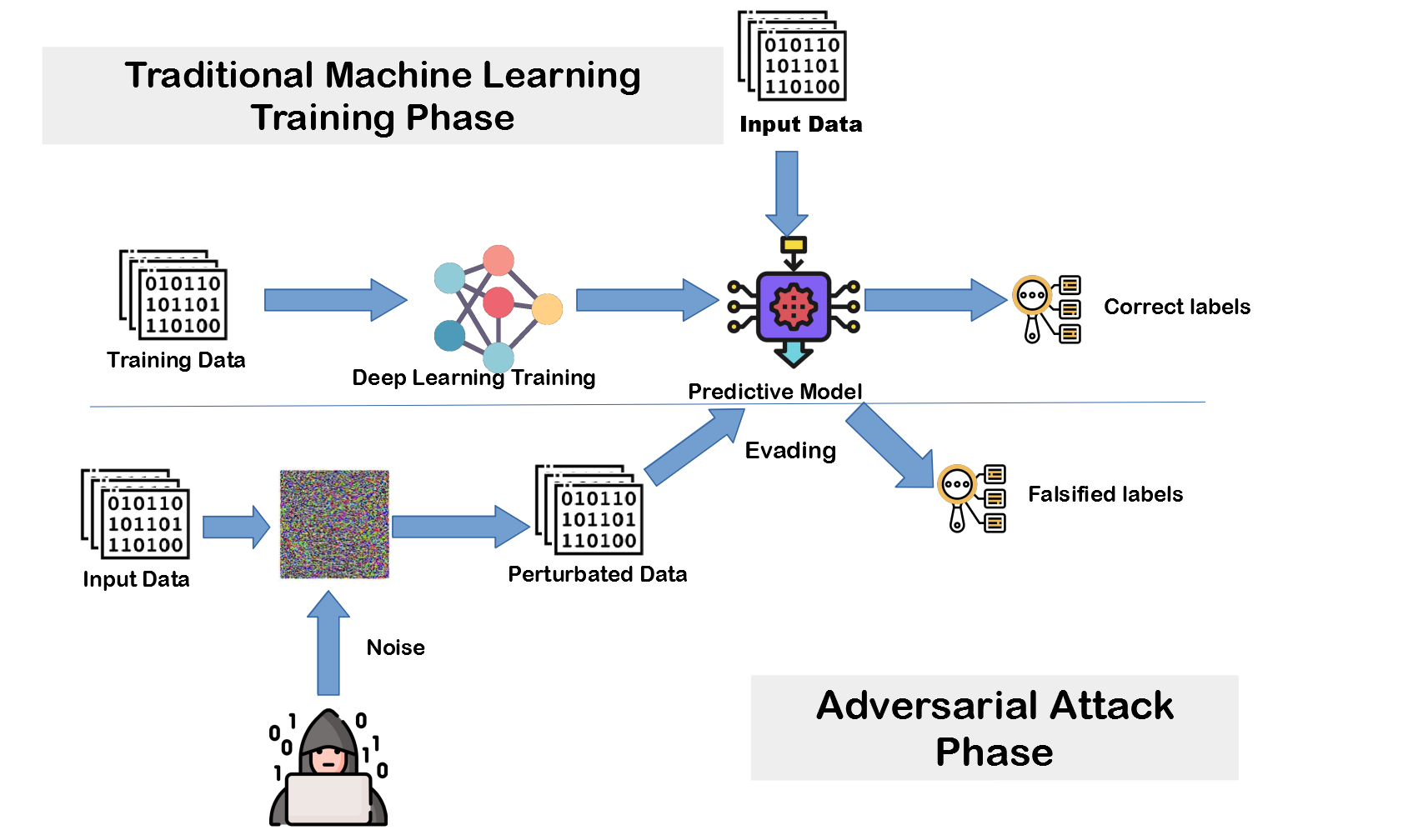
A typical machine learning model basically consists of two stages as training time and decision time. Thus, the adversarial machine learning attacks occur in either training time or decision time. The techniques used by hackers for adversarial machine learning can be divided into two, according to the time of the attack:
- Data Poisoning: The attacker changes some labels of training input instances to mislead the output model.Model Poisoning: The hacker drives model to produce false labelling using some perturbated instance after the model is created.
Our model is able to respond to the model attacks by hackers who use the adversarial machine learning methods. The figure illustrates the system architecture used to protect the model and to classify correctly.

Let’s codingWe import the usual standard libraries plus one cleverhans library to make an adversarial attack to the deep learning model.
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_kddcup99
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn import preprocessing
import tensorflow as tf
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from keras.utils import np_utils
from cleverhans.future.tf2.attacks import fast_gradient_method, \
basic_iterative_method, momentum_iterative_method
np.random.seed(10)
In this work, we will use standard KDDCUP’99 intrusion detection dataset to show the results. We need to extract the numerical features from the dataset. I created a new method to load and extract the KDDCUP’99 dataset.
COL_NAME = ['duration', 'protocol_type', 'service', 'flag', 'src_bytes',
'dst_bytes', 'land', 'wrong_fragment', 'urgent', 'hot',
'num_failed_logins', 'logged_in', 'num_compromised', 'root_shell',
'su_attempted', 'num_root', 'num_file_creations', 'num_shells',
'num_access_files', 'num_outbound_cmds', 'is_host_login',
'is_guest_login', 'count', 'srv_count', 'serror_rate',
'srv_serror_rate', 'rerror_rate', 'srv_rerror_rate',
'same_srv_rate', 'diff_srv_rate', 'srv_diff_host_rate',
'dst_host_count', 'dst_host_srv_count', 'dst_host_same_srv_rate',
'dst_host_diff_srv_rate', 'dst_host_same_src_port_rate',
'dst_host_srv_diff_host_rate', 'dst_host_serror_rate',
'dst_host_srv_serror_rate', 'dst_host_rerror_rate', 'dst_host_srv_rerror_rate']
NUMERIC_COLS = ['duration', 'src_bytes', 'dst_bytes', 'wrong_fragment',
'urgent', 'hot', 'num_failed_logins', 'num_compromised',
'root_shell', 'su_attempted', 'num_root', 'num_file_creations',
'num_shells', 'num_access_files', 'num_outbound_cmds', 'count',
'srv_count', 'serror_rate', 'srv_serror_rate', 'rerror_rate',
'srv_rerror_rate', 'same_srv_rate', 'diff_srv_rate',
'srv_diff_host_rate', 'dst_host_count', 'dst_host_srv_count',
'dst_host_same_srv_rate', 'dst_host_diff_srv_rate',
'dst_host_same_src_port_rate', 'dst_host_srv_diff_host_rate',
'dst_host_serror_rate', 'dst_host_srv_serror_rate',
'dst_host_rerror_rate', 'dst_host_srv_rerror_rate']
def get_ds():
""" get_ds: Get the numeric values of the KDDCUP'99 dataset. """
x_kddcup, y_kddcup = fetch_kddcup99(return_X_y=True, shuffle=False)
df_kddcup = pd.DataFrame(x_kddcup, columns=COL_NAME)
df_kddcup['label'] = y_kddcup
df_kddcup.drop_duplicates(keep='first', inplace=True)
df_kddcup['label'] = df_kddcup['label'].apply(lambda d: \
str(d).replace('.', '').replace("b'", "").\
replace("'", ""))
conversion_dict = {'back':'dos', 'buffer_overflow':'u2r', 'ftp_write':'r2l',
'guess_passwd':'r2l', 'imap':'r2l', 'ipsweep':'probe',
'land':'dos', 'loadmodule':'u2r', 'multihop':'r2l',
'neptune':'dos', 'nmap':'probe', 'perl':'u2r', 'phf':'r2l',
'pod':'dos', 'portsweep':'probe', 'rootkit':'u2r',
'satan':'probe', 'smurf':'dos', 'spy':'r2l', 'teardrop':'dos',
'warezclient':'r2l', 'warezmaster':'r2l'}
df_kddcup['label'] = df_kddcup['label'].replace(conversion_dict)
df_kddcup = df_kddcup.query("label != 'u2r'")
df_y = pd.DataFrame(df_kddcup.label, columns=["label"], dtype="category")
df_kddcup.drop(["label"], inplace=True, axis=1)
x_kddcup = df_kddcup[NUMERIC_COLS].values
x_kddcup = preprocessing.scale(x_kddcup)
y_kddcup = df_y.label.cat.codes.to_numpy()
return x_kddcup, y_kddcup
#machine-learning #python #artificial-intelligence #tensorflow #cybersecurity #deep learning
