The Source Code
The next Python Pandas code made it for Jupyter Notebook is available in GitHub, and It answers the question: “Which tasks don’t match?”
The Data
The first part of the code creates two DataFrames: **df1 **and df2.

The **df1 **DataFrame has the complete name of the tasks in the **task_name **column.
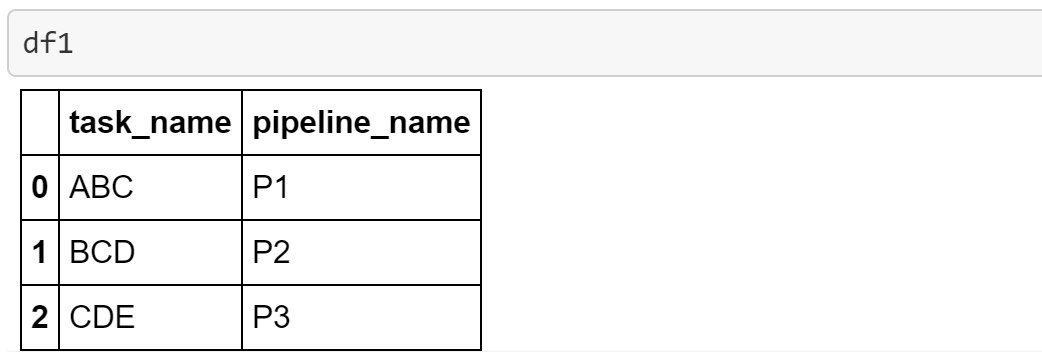
And the **df2 **DataFrame has a substring in the **partial_task_name **column.
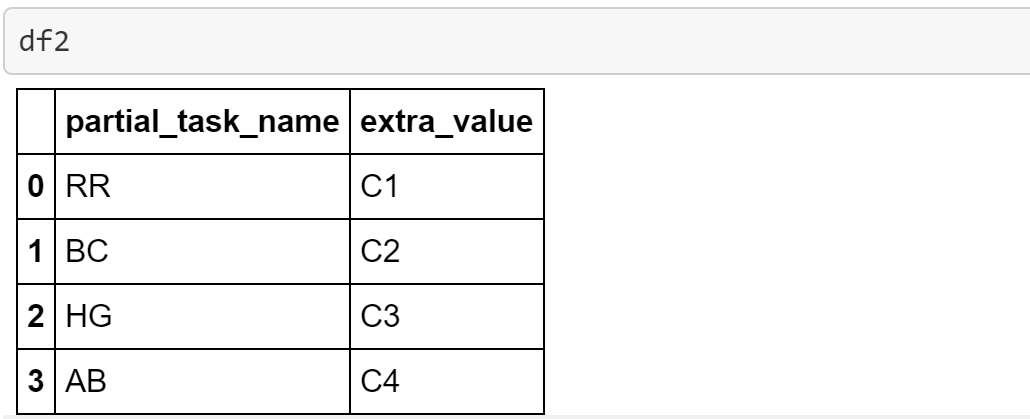
Look that the value **BC **in **partial_task_name is a substring of ABC **and BCD, the expected result must produce many rows for this case, but how can we get many rows? The answer is using a Cartesian Product or Cross Join.
The Join
To do a Cartesian Product in Pandas, do the following steps:
- Add a dummy column with the same value en each of the DataFrames
- Do a join by the new column
- Remove the new column in each DataFrame
df1['join'] = 1
df2['join'] = 1
dfFull = df1.merge(df2, on='join').drop('join', axis=1)
df2.drop('join', axis=1, inplace=True)
The Match
The next step is to add a new column in the result DataFrame returning if the **partial_task_name **column is in the **task_name **column. We are going to use a lambda and “find” function where the result is ≥ 0
#python #substring-search #cross-join #pandas #cartesian-product
