What is Oraichain Token (ORAI) | What is ORAI token
AI-Powered Data Oracle
Oraichain is a data oracle platform that aggregates and connects
Artificial Intelligence APIs to smart contracts and regular applications.
The world’s first AI-powered data oracle has arrived.
AI Oracle
Oraichain enhances smart contracts by allowing them to securely access external AI APIs. While, currently, blockchain platforms focus on price oracles, with Oraichain, smart contracts are able to utilize reliable AI data. This provides dApp users with new and valuable functionalities. Systems utilize Oraichain by sending requests to validators, which acquire and test data from various AI APIs and store it on-chain, guaranteeing reliability and allowing it to be used as proof in the future.
AI Marketplace
The Oraichain AI Marketplace is a place where Artificial Intelligence is brought into the blockchain. Here, AI providers can sell their AI services for ORAI token rewards. Such services can be AI-based yield farming, face authentication, price prediction, and more. The providers can host their models on Oraichain, without the need to rely on any third parties. This gives small companies and individuals in the AI field a chance to compete with larger ones while getting exposure to users around the world. Initially, some AI services will be supplied by the development team as a foundation for others to join in. Meanwhile, users and developers can use ORAI tokens to pay for AI services they need.
AI Ecosystem
The AI ecosystem extends beyond the AI Marketplace. It includes AI infrastructure that supports AI providers building their models before deploying them onto the Oraichain network. A complete and fully functional web GUI is expected to assist AI providers in publishing their services easier and faster. The Ecosystem also allows users to follow the overall flow of the handling of their AI requests, from start to finish. This helps increase the transparency and integrity of the system, allowing users to easily see malicious providers or validators who execute the request poorly.
Staking & Earning
Users can become delegators and stake tokens into a specific validator to increase the validator’s power within the blockchain network. This allows validators to have a greater chance of executing requests, while the delegators earn a part of the validators’ commission. The delegators, however, have to monitor their chosen validators well, as a malicious validator may try to break the system’s rules to earn more. In such cases, all the staked tokens of the delegators will be slashed. In other words, there’s a tight coupling between two entities, and they should both be responsible for delivering a quality environment of the system.
Test Cases
Test Cases are a unique feature of Oraichain. It is crucial to provide test cases that can verify the correctness and integrity of the AI services on a blockchain network. Third parties can join as Test Case providers to examine if a specific AI model is qualified to charge user fees. Users can also provide outputs they expect from the model and check if the results are similar. This will encourage AI providers to work hard and supply quality services to be able to earn rewards from users.
ORAI DAO
You are the governor of the product serving you. Oraichain is of, for, and by Community. By owning ORAI tokens, you can take part in the governance, development, and future plans for the Oraichain ecosystem. Because this is a decentralized network, the project development team only creates the foundation, while you can build a bright future for it using your own tokens.
Why conventional blockchain doesn’t include AI models?
Current smart contracts cannot run AI models inside and it is almost impossible to integrate an AI model in a smart contract.
Strictness: smart contracts always follow strict rules, where an input must be 100% accurate (e.g. signature) to generate an output. But, AI models don’t give such accuracy (e.g. face recognition). Oraichain helps overcome some aspects of strictness to obtain better functionality and user experience.
Environment: smart contracts are typically written in high-level programming languages, such as Solidity and Rust that provide stricter syntax and better security. However, AI models are typically written in Python or Java.
Data size: smart contracts often have very small storage space, since it helps reduce transaction fees in some blockchain networks, such as Ethereum. Compared to this, the size of an AI model is relatively large.

Why conventional blockchain doesn’t include AI models?
Current smart contracts cannot run AI models inside, and it is almost impossible to integrate an AI model into a smart contract. AI models should be complex approaches, such as SVM, neural network, and clustering. The reasons come from three characteristics of smart contracts as follows:
Strictness: smart contracts always follow strict rules in which the inputs must be 100% accurate (e.g. signature) to generate an output. However, AI models can hardly give such accuracy (e.g. face recognition). As a result, Oraichain is there to reduce some aspects of strictness to obtain better functionality and user experience.
Environment: smart contracts are mostly written in high-level programming languages such as Solidity and Rust that provide stricter syntax and better security. Nevertheless, the AI models are is typically written in Python or Java.
Data size: On one hand, smart contracts often have relatively small storage since it helps reduce transaction fees in some blockchain networks such as Ethereum. On the other hand, the size of an AI model is much bigger.
We’re offering Oracle Artificial Intelligence for Blockchains!
The proposed Oraichain could be a bridge to bring AI to smart contracts. The Oraichain mechanism seems similar to Band Protocol and Chainlink, but it focuses more on AI APIs and the quality of the provided AI models. In each user request, test cases are attached, and the providers’ API must pass a certain number of test cases to receive payment. The validators manage the features of test cases and AI model quality, and that makes Oraichain unique and different.
- Oracle AI: Oraichain enables smart contracts to securely access external AI APIs. Artificial Intelligence helps enhance smart contracts.
- AI Marketplace: search, trial, and select from an ever-growing library of AI algorithms created by a community of service providers. Integrate AI services into your applications (both Dapps and regular apps).
- AI Publisher: our publishing infrastructure provides both a central hub for creating, editing, and managing your AI services and the tools to launch those services to a global market.
- ORAI Staking: earn more while holding ORAI tokens by vesting them in 30-day staking sessions. By staking ORAI tokens, you support the operations of our blockchain network while getting rewarded with more ORAI tokens for your contributions.
- Request for AI (RFAI): a community crowdsource portal allowing anyone to make requests for, and offer to fund, new AI services that are currently not available on the market.
- ORAI DAO: you are the governor of the product serving you. Oraichain is of, for, and by the community. Oraichain team just helps initialize the project and when the mainnet is started, any changes of Oraichain should be reviewed by validators and stakeholders.
Oraichain’s System Overview
Oraichain is a public blockchain that allows users to create different data requests. Instead of users, smart contracts can also request data securely from AI APIs through Oraichain. The blockchain network is built based on Cosmos SDK along with Tendemint’s Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus that helps speed up transactions’ confirmation time.
The ORAI consensus protocol is similar to the delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS). Indeed, the network consists of numerous validators, each owning ORAI tokens while other ORAI token holders can be delegators staking their tokens to validators and get rewards for each newly created block.
The second task of the validators is to collect data from AI providers and validate that data before they are written to the blockchain. To validate an AI API, validators will do testing based on the test cases given by users, smart contracts, and test providers. If users do not know which test case is good, they can request some test cases from test providers.
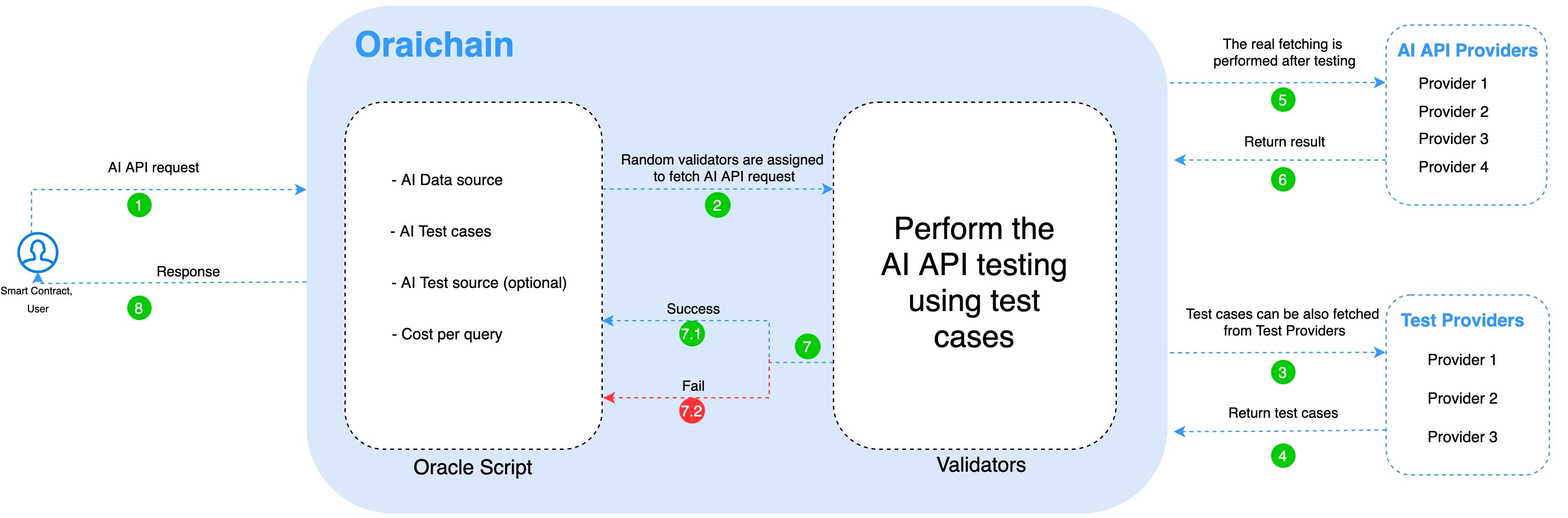
Oraichain’s System Overview
The flow of requesting an AI API is illustrated in the Oraichain’s System Overview figure. To perform a request, users or smart contracts need to call an oracle script that is available on the ORAI gateway or marketplace. In an oracle script, there are AI data sources (provided by AI providers), test cases, test source (optional), and transaction fees for each request. When a request comes, a random willing validator is chosen to perform this request. The chosen validator will fetch data from one or more AI providers on behalf of the user after executing the test scenarios, and if the AI provider fails in testing, the request is canceled.
A request is successful if its result is written to the Oraichain blockchain. The transaction result, which can be fetched from smart contracts and regular applications, is proof of execution, and fees are applied in this transaction. There is an overhead of reading results from Oraichain’s transactions, but it helps ensure that the AI API quality is good and there is no data tampering during the process of fetching data from AI providers.
Compared to Band Protocol and Chainlink, API testing based test cases is the unique functionality. Since Oraichain focuses on AI APIs, testing is very important to control the quality of AI providers. Besides, test providers can propose suitable test cases that users can choose to test an AI API. Test cases in the Oraichain marketplace can encourage AI providers to improve the accuracy of AI models.
Another interesting feature is that the Oraichain community has the power to rate the validators’ reputation for quality AI APIs improvement. If a validator has bad behavior, such as failing to perform test cases and validate AI providers, slow response time, and low availability, its holding token will be slashed.
Nevertheless, validators in Oraichain is responsible for performing many important tasks and could be a centralized point. Therefore, the number of chosen validators should be high in order to increase request performance, scalability, and high availability. Meanwhile, because we need many validators to participate in the Oraichain network and maintain their quality work, block reward and transaction fees must be applied for such validators to earn more ORAI tokens.
Token Economics
Running an AI request sent to the Oraichain network requires spending some ORAI tokens. In fact, the token plays a role as the transaction fee that is paid for request-executing validators, AI-API providers, test-case providers, and block-creating validators.
The transaction fee is different depending on the fee requirement of request-executing validators, AI-API providers, and test-case providers. Hence, it should be explicitly defined in MsgRequestData of a request. When there is a request, request-executing validators must decide if they want to execute it. After that, a random validator is chosen from the willing request-executing validators to execute the oracle script and create MsgResultReport in the end. The validator must clarify the fee paid to AI-API providers, test-case providers, and block-creating validators in the MsgResultReport.
If more than one validator is asked in the MsgRequestData (AskCount), the transaction fee is divided equally among the validators. The request-executing validators must decide if they accept such transaction fee.
When we mention the ORAI token, it means that it is the native token type that is created and contained in the Oraichain network. There is also another type of ORAI token created and issued using the ERC20 interface on the Ethereum network that we call ERC20 ORAI token. This ERC20 token is for ICO purposes, and there is a mechanism to synchronize ORAI tokens on the Oraichain network and ERC20 ORAI tokens on the Ethereum network.
The ORAI token is rewarded for each newly created block, so to keep the value of ORAI token, holders must stake their token to the Oraichain network. The rewarding token is divided based on the number of tokens that a holder is staking to a validator. Moreover, there is a mechanism to punish bad behaviors of validators in aspects of AI API quality, response time, and availability.
Oraichain’s Use Cases
The yield farming based on Oraichain has got inspiration from yearn.finance (YFI) that helps reduce the complexity of yield trading and provides trading strategies from crowdsourcing DAO voting. Instead of using crowdsourcing knowledge, Oraichain provides AI-based price prediction APIs as inputs to smart contracts. The yield farming use case has two functionalities as follows:
- Earn: Get price prediction from Oraichain and automatically decide BUY/SELL tokens. You can choose the best performance AI APIs.
- Vaults: Apply automated trading oracle scripts on Oraichain. You deposit tokens and the assigned oracle script will find the best AI input and maximize your yield.
Compared to yearn.finance (crowdsourcing-based strategies), AI-based trading performance could be less efficient, but risk management could be better since all buying or selling decision is based on AI models (or by machine) and not by human psychology.
2. Flexible smart contracts using face authentication

Smart contracts using face authentication
There are several scenarios in which face authentication is very useful as follows: using your face to get your balance instead of using a private key, withdrawing tokens to registered wallets using your face, using your face in order to reset your private/public key pair, and using both your private key and face in order to execute a smart contract.
Using face authentication might be riskier than a private key, but it helps increase user experience. In cases of checking balance and withdrawing tokens to registered wallets, face authenticatiion is safe and convenient.
3. Fake news detection using different AI providers from Oraichain
This use case focuses more on a regular application that wants to check if the news can be trusted. Oraichain provides a marketplace in a decentralized manner in which combining results from different providers is possible. If the providers want to receive payments, their APIs must pass the test cases, which is when the APIs return the correct results of your own test cases.
4. More use cases at https://docs.orai.io/docs/UseCases (coming soon): Smart contracts help check if a product is fake in the supply chain; Smart contracts deciding a loan based on users’ credit score; Smart contracts automatically pricing game items based on their characteristics and DNA; Marketplace of automated diagnostics for X-ray images, spam classification, handwriting detection using OCR, and citizen ID card detection using OCR.
Would you like to earn many tokens and cryptocurrencies right now! ☞ CLICK HERE
Looking for more information…
☞ Website
☞ Explorer
☞ Whitepaper
☞ Source Code
☞ Social Channel
☞ Message Board
☞ Documentation
☞ Coinmarketcap
🔺DISCLAIMER: The Information in the post isn’t financial advice, is intended FOR GENERAL INFORMATION PURPOSES ONLY. Trading Cryptocurrency is VERY risky. Make sure you understand these risks and that you are responsible for what you do with your money.
🔥 If you’re a beginner. I believe the article below will be useful to you ☞ What You Should Know Before Investing in Cryptocurrency - For Beginner
⭐ ⭐ ⭐The project is of interest to the community. Join to Get free ‘GEEK coin’ (GEEKCASH coin)!
☞ -----CLICK HERE**-----**⭐ ⭐ ⭐
Thank for visiting and reading this article! I’m highly appreciate your actions! Please share if you liked it!
#blockchain #bitcoin #cryptocurrency #oraichain #orai
