I recently started a new newsletter focus on AI education. TheSequence is a no-BS( meaning no hype, no news etc) AI-focused newsletter that takes 5 minutes to read. The goal is to keep you up to date with machine learning projects, research papers and concepts. Please give it a try by subscribing below:
TheSequence
The brain has always been considered the main inspiration for the field of artificial intelligence(AI). For many AI researchers, the ultimate goal of AI is to emulate the capabilities of the brain. That seems like a nice statement but its an incredibly daunting task considering that neuroscientist are still struggling trying to understand the cognitive mechanism that power the magic of our brains. Despite the challenges, more regularly we are seeing AI research and implementation algorithms that are inspired by specific cognition mechanisms in the human brain and that have been producing incredibly promising results. In 2017, the DeepMind team published a paper about neuroscience-inspired AI that summarizes the circle of influence between AI and neuroscience research.
You might be wondering what’s so new about this topic? Everyone knows that most foundational concepts in AI such as neural networks have been inspired by the architecture of the human brain. However, beyond that high level statement, the relationship between the popular AI/deep learning models we used everyday and neuroscience research is not so obvious. Let’s quickly review some of the brain processes that have a footprint in the newest generation of deep learning methods.
Attention

Attention is one of those magical capabilities of the human brain that we don’t understand very well. What brain mechanisms allow us to focus on a specific task and ignore the rest of the environment? Attentional mechanisms have become a recent source of inspiration in deep learning models such as convolutional neural networks(CNNs) or deep generative models. For instance, modern CNN models have been able to get a schematic representation of the input and ignore irrelevant information improving their ability of classifying objects in a picture.
Episodic Memory
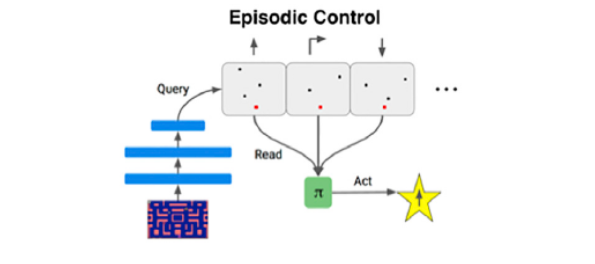
When you remember autobiographical events such as events or places we are using a brain function known as episodic memory. This mechanism is most often associated with circuits in the medial temporal lobe, prominently including the hippocampus. Recently, AI researchers have try to incorporate methods inspired by episodic memory into reinforcement learning(RL) algorithms to episodic control. These networks store specific experiences (e.g., actions and reward outcomes associated with particular Atari game screens) and select new actions based on the similarity between the current situation input and the previous events stored in memory, taking the reward associated with those previous events into account.
#machine-learning #data-science #artificial-intelligence #deep-learning #deep learning
