With face detection, you can get the information you need to perform tasks like embellishing selfies and portraits, or generating avatars from a user's photo. Because ML Kit can perform face detection in real time, you can use it in applications like video chat or games that respond to the player's expressions.
- You can use ML Kit to detect faces in images and video.
- See the ML Kit quickstart sample on GitHub for an example of this API in use.
Before you begin
- If you have not already added Firebase to your app, do so by following the steps in the getting started guide.
- Include the ML Kit libraries in your Podfile:
pod 'Firebase/MLVision' pod 'Firebase/MLVisionFaceModel'
After you install or update your project's Pods, be sure to open your Xcode project using its .xcworkspace.
3 - In your app, import Firebase:
Swift import Firebase
Objective-C @import Firebase;
Input image guidelines
For ML Kit to accurately detect faces, input images must contain faces that are represented by sufficient pixel data. In general, each face you want to detect in an image should be at least 100x100 pixels. If you want to detect the contours of faces, ML Kit requires higher resolution input: each face should be at least 200x200 pixels.
If you are detecting faces in a real-time application, you might also want to consider the overall dimensions of the input images. Smaller images can be processed faster, so to reduce latency, capture images at lower resolutions (keeping in mind the above accuracy requirements) and ensure that the subject's face occupies as much of the image as possible. Also see Tips to improve real-time performance.
Poor image focus can hurt accuracy. If you aren't getting acceptable results, try asking the user to recapture the image.
The orientation of a face relative to the camera can also affect what facial features ML Kit detects. See Face Detection Concepts.
1. Configure the face detector
Before you apply face detection to an image, if you want to change any of the face detector's default settings, specify those settings with a VisionFaceDetectorOptions object. You can change the following settings:
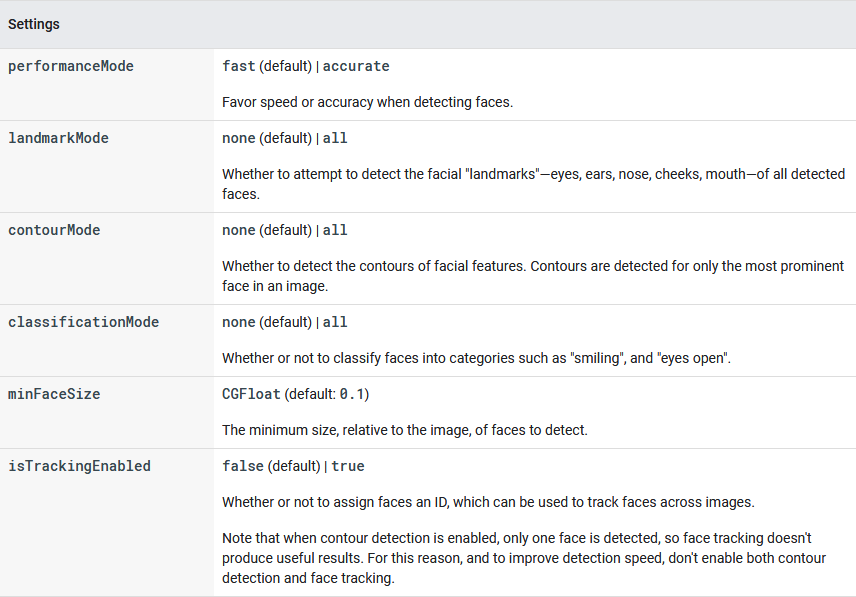
For example, build a VisionFaceDetectorOptions object like one of the following examples:
Swift // High-accuracy landmark detection and face classification let options = VisionFaceDetectorOptions() options.performanceMode = .accurate options.landmarkMode = .all options.classificationMode = .all// Real-time contour detection of multiple faces
let options = VisionFaceDetectorOptions()
options.contourMode = .all
Objective-C
// High-accuracy landmark detection and face classification
FIRVisionFaceDetectorOptions *options = [[FIRVisionFaceDetectorOptions alloc] init];
options.performanceMode = FIRVisionFaceDetectorPerformanceModeAccurate;
options.landmarkMode = FIRVisionFaceDetectorLandmarkModeAll;
options.classificationMode = FIRVisionFaceDetectorClassificationModeAll;// Real-time contour detection of multiple faces
FIRVisionFaceDetectorOptions *options = [[FIRVisionFaceDetectorOptions alloc] init];
options.contourMode = FIRVisionFaceDetectorContourModeAll;
2. Run the face detector
- To detect faces in an image, pass the image as a
UIImageor aCMSampleBufferRefto theVisionFaceDetector'sdetect(in:)method:Get an instance ofVisionFaceDetector:
Swift
lazy var vision = Vision.vision()
let faceDetector = vision.faceDetector(options: options)
ViewController.swift
Objective-C
FIRVision *vision = [FIRVision vision];
FIRVisionFaceDetector *faceDetector = [vision faceDetector];
// Or, to change the default settings:
// FIRVisionFaceDetector *faceDetector =
// [vision faceDetectorWithOptions:options];
- Create a
VisionImageobject using aUIImageor aCMSampleBufferRef.
To use a UIImage:
- If necessary, rotate the image so that its
imageOrientationproperty is.up. - Create a
VisionImageobject using the correctly-rotatedUIImage. Do not specify any rotation metadata—the default value,.topLeft, must be used.
Swift
let image = VisionImage(image: uiImage)
Objective-C
FIRVisionImage *image = [[FIRVisionImage alloc] initWithImage:uiImage];
To use a CMSampleBufferRef:
- Create a
VisionImageMetadataobject that specifies the orientation of the image data contained in theCMSampleBufferRefbuffer.
To get the image orientation:
Swift
func imageOrientation(
deviceOrientation: UIDeviceOrientation,
cameraPosition: AVCaptureDevice.Position
) -> VisionDetectorImageOrientation {
switch deviceOrientation {
case .portrait:
return cameraPosition == .front ? .leftTop : .rightTop
case .landscapeLeft:
return cameraPosition == .front ? .bottomLeft : .topLeft
case .portraitUpsideDown:
return cameraPosition == .front ? .rightBottom : .leftBottom
case .landscapeRight:
return cameraPosition == .front ? .topRight : .bottomRight
case .faceDown, .faceUp, .unknown:
return .leftTop
}
}
Objective-C
- (FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientation)
imageOrientationFromDeviceOrientation:(UIDeviceOrientation)deviceOrientation
cameraPosition:(AVCaptureDevicePosition)cameraPosition {
switch (deviceOrientation) {
case UIDeviceOrientationPortrait:
if (cameraPosition == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront) {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationLeftTop;
} else {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationRightTop;
}
case UIDeviceOrientationLandscapeLeft:
if (cameraPosition == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront) {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationBottomLeft;
} else {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationTopLeft;
}
case UIDeviceOrientationPortraitUpsideDown:
if (cameraPosition == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront) {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationRightBottom;
} else {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationLeftBottom;
}
case UIDeviceOrientationLandscapeRight:
if (cameraPosition == AVCaptureDevicePositionFront) {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationTopRight;
} else {
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationBottomRight;
}
default:
return FIRVisionDetectorImageOrientationTopLeft;
}
}
Then, create the metadata object:
Swift
let cameraPosition = AVCaptureDevice.Position.back // Set to the capture device you used.
let metadata = VisionImageMetadata()
metadata.orientation = imageOrientation(
deviceOrientation: UIDevice.current.orientation,
cameraPosition: cameraPosition
)
Objective-C
FIRVisionImageMetadata *metadata = [[FIRVisionImageMetadata alloc] init];
AVCaptureDevicePosition cameraPosition =
AVCaptureDevicePositionBack; // Set to the capture device you used.
metadata.orientation =
[self imageOrientationFromDeviceOrientation:UIDevice.currentDevice.orientation
cameraPosition:cameraPosition];
- Create a
VisionImageobject using theCMSampleBufferRefobject and the rotation metadata:
Swift
let image = VisionImage(buffer: sampleBuffer)
image.metadata = metadata
Objective-C
FIRVisionImage *image = [[FIRVisionImage alloc] initWithBuffer:sampleBuffer];
image.metadata = metadata;
3 - Then, pass the image to the detect(in:) method:
Swift
faceDetector.process(visionImage) { faces, error in
guard error == nil, let faces = faces, !faces.isEmpty else {
// …
return
}// Faces detected
// …
}
ViewController.swift
Objective-C
[faceDetector detectInImage:image
completion:^(NSArray<FIRVisionFace *> *faces,
NSError *error) {
if (error != nil) {
return;
} else if (faces != nil) {
// Recognized faces
}
}];
3. Get information about detected faces
If the face detection operation succeeds, the face detector passes an array of VisionFace objects to the completion handler. Each VisionFace object represents a face that was detected in the image. For each face, you can get its bounding coordinates in the input image, as well as any other information you configured the face detector to find. For example:
Swift
for face in faces {
let frame = face.frame
if face.hasHeadEulerAngleY {
let rotY = face.headEulerAngleY // Head is rotated to the right rotY degrees
}
if face.hasHeadEulerAngleZ {
let rotZ = face.headEulerAngleZ // Head is rotated upward rotZ degrees
}// If landmark detection was enabled (mouth, ears, eyes, cheeks, and
// nose available):
if let leftEye = face.landmark(ofType: .leftEye) {
let leftEyePosition = leftEye.position
}// If contour detection was enabled:
if let leftEyeContour = face.contour(ofType: .leftEye) {
let leftEyePoints = leftEyeContour.points
}
if let upperLipBottomContour = face.contour(ofType: .upperLipBottom) {
let upperLipBottomPoints = upperLipBottomContour.points
}// If classification was enabled:
if face.hasSmilingProbability {
let smileProb = face.smilingProbability
}
if face.hasRightEyeOpenProbability {
let rightEyeOpenProb = face.rightEyeOpenProbability
}// If face tracking was enabled:
if face.hasTrackingID {
let trackingId = face.trackingID
}
}
Objective-C
for (FIRVisionFace *face in faces) {
// Boundaries of face in image
CGRect frame = face.frame;if (face.hasHeadEulerAngleY) {
CGFloat rotY = face.headEulerAngleY; // Head is rotated to the right rotY degrees
}
if (face.hasHeadEulerAngleZ) {
CGFloat rotZ = face.headEulerAngleZ; // Head is tilted sideways rotZ degrees
}// If landmark detection was enabled (mouth, ears, eyes, cheeks, and
// nose available):
FIRVisionFaceLandmark *leftEar = [face landmarkOfType:FIRFaceLandmarkTypeLeftEar];
if (leftEar != nil) {
FIRVisionPoint *leftEarPosition = leftEar.position;
}// If contour detection was enabled:
FIRVisionFaceContour *upperLipBottomContour = [face contourOfType:FIRFaceContourTypeUpperLipBottom];
if (upperLipBottomContour != nil) {
NSArray<FIRVisionPoint *> *upperLipBottomPoints = upperLipBottomContour.points;
if (upperLipBottomPoints.count > 0) {
NSLog(“Detected the bottom contour of the subject’s upper lip.”)
}
}// If classification was enabled:
if (face.hasSmilingProbability) {
CGFloat smileProb = face.smilingProbability;
}
if (face.hasRightEyeOpenProbability) {
CGFloat rightEyeOpenProb = face.rightEyeOpenProbability;
}// If face tracking was enabled:
if (face.hasTrackingID) {
NSInteger trackingID = face.trackingID;
}
}
Example of face contours
When you have face contour detection enabled, you get a list of points for each facial feature that was detected. These points represent the shape of the feature. See the Face Detection Concepts Overview for details about how contours are represented.
The following image illustrates how these points map to a face (click the image to enlarge):
Real-time face detection
If you want to use face detection in a real-time application, follow these guidelines to achieve the best framerates:
- Configure the face detector to use either face contour detection or classification and landmark detection, but not both:
- Contour detection
- Landmark detection
- Classification
- Landmark detection and classification
- Contour detection and landmark detection
- Contour detection and classification
- Contour detection, landmark detection, and classification
- Enable
fastmode (enabled by default). - Consider capturing images at a lower resolution. However, also keep in mind this API’s image dimension requirements.
- Throttle calls to the detector. If a new video frame becomes available while the detector is running, drop the frame.
#firebase #machine-learning #data-science #image

