Writing a simple Python script to send a WhatsApp message
In this tutorial, we will write a simple Python script to send a WhatsApp message. Twilio is the Python package we will use. To run it every day at a certain time, we will put our code on the AWS (Amazon Web Services) cloud.
So let’s get started!

One solution is to use Python’s Selenium package and go to WhatsApp web rather than using Twilio, which is subscription-based after the free tier is over. But as WhatsApp requires QR-code scanning through mobile from time to time, automation wasn’t possible.
We will do it in a three-step process:
- Twilio initial setup
- Understanding the code and modifying it
- Put our package on AWS lambda with triggers
Step 1: Twilio Initial Setup
Create a free Twilio account and confirm your email and mobile number.
Also, a free tier Twilio account requires using Twilio Sandbox for WhatsApp, which means you can’t use your number and have to go through one-time permission to receive WhatsApp messages.
Both can be solved when you get your own number, which is done after WhatsApp approves Twilio to use your number. There is a form to fill out and a wait time too.

All of this is discouraging, but our free tier solution does the job fine. Also, for now, this is the only available way.
Now you have to connect the receiver’s phone to the WhatsApp Sandbox to start receiving messages.
Go to WhatsApp beta in the learn section of the console.
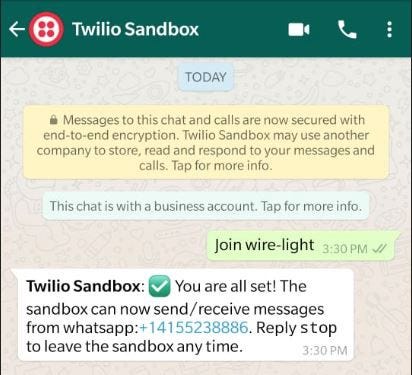
Save the WhatsApp number assigned to you in your contacts. You can give it any name you want. For simplicity, I saved it as Twilio Sandbox, then sent it a message from my dad’s phone, as seen above. This has to be done once and only once.
Now go to Twilio Console and get your account SSID and authentication token. This will help Twilio know it’s you when the code is executed.
Step 2: Understanding and Modifying the Code
Download the GitHub repository and extract it.
inside the zip file
Inside this, you’ll find our code file and deployment package.
whatsapp_messaging.pyaws_lambda_deploy.zip
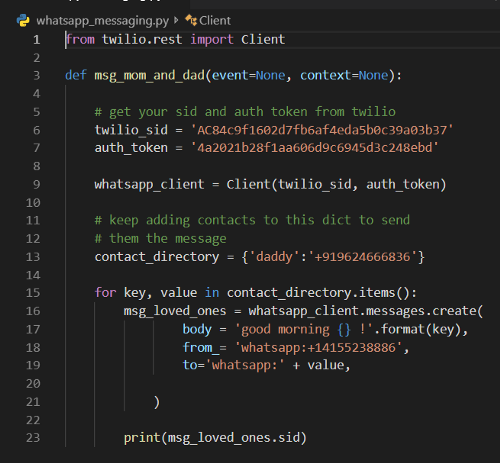
whatsappmessaging code file
- line 1 imports the Twilio package and uses its
RESTclient to hit the Twilio API. - line 3: Wecreate a function,
msg_mom_and_dad, which will be given to AWS to run every day at a certain time. - line 6–7: Replace the
sidandauth_tokenof your account as discussed in step 1. - line 9: Twilio client object is created with our credentials.
- line 13: A Python dictionary is created with name as
keyand mobile number asvalue. You can keep adding to this Python dictionary to send messages to more people as well. - line 15: A
forloop that runs through all thekeyandvaluepairs (currently we just have one). Inbody,mention your message. I have created a simple one, which says good morning, followed by thekeyvalue. In the above code, it is “good morning daddy!”We then mention thefromnumber, which is the Twilio WhatsApp number you got earlier, and thetonumber, from which you previously sent the WhatsApp sandbox confirmation. - line 23: A line to check message status by printing the SID. We won’t use this anyway.
We have five things to change:
twilio_sidauth_tokencontact_directoryfrom_body (optional)
After you have changed these, save it. Then extract the aws_lambda_deploy.zipand replace the whatsapp_messaging.pyinside it with your newly created one. Zip the package again. We just wanted to change the code with your credentials and contact details. Your deployment package is now ready.
Step 3: Put Our Package on AWS Lambda With Triggers
Our code is ready to run and send WhatsApp messages. If you’re wondering what the other files in our deployment package are, they’re the Twilio package and all its other dependencies. This is because we’ll use an AWS Lambda function in a Python environment that doesn’t have the Twilio package. But why not just run pip install twilio to install it? This is because we don’t have a server here.

AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service where you have a piece of code that you want to run based on different AWS events and triggers, according to the users’ needs. Therefore, it’s a waste of computing resources and money to run a server (EC2 instance in AWS) 24/7 to do our small cute task. Here our Lambda function will only run for a very short time every day on our mentioned time trigger.
The Lambda service is very cheap and gives you a million requests per month for free.

Log in to https://aws.amazon.com. Then click on Services -> Compute -> Lambda -> create a function
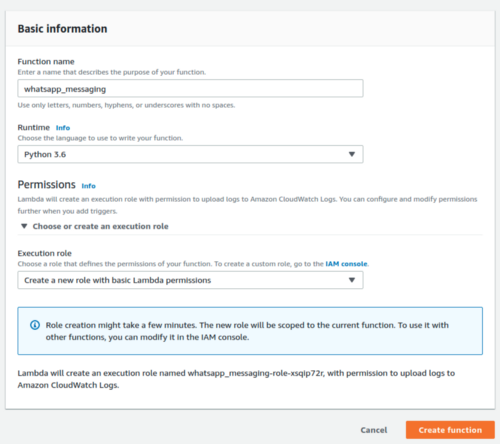
Give your function a name.
We selected Python 3.6 as our environment of choice.
As we don’t need to connect to other services in AWS, the option of basic permission is fine.
Click on create function and you’ll be taken to the main dashboard.
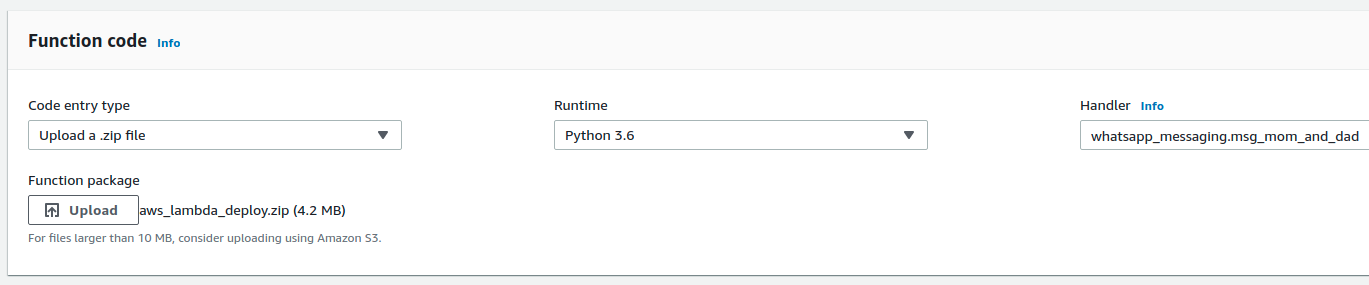
In the function code block, specify to the Lambda Function Handler that we want to run our whatsapp_messaging Python file and the msg_mom_and_dadfunction inside it each time the Lambda function is called. Change the handler value as above.
At the code entry point, select upload a .zip file, upload the deployment package you created in step 2, and saveit.
Our code is ready to run. You can click on test and check that the function successfully sends a message to the specified WhatsApp number.
Our last step is to trigger it every day at a given time. For this, click add trigger -> CloudWatch Events in the designer box.
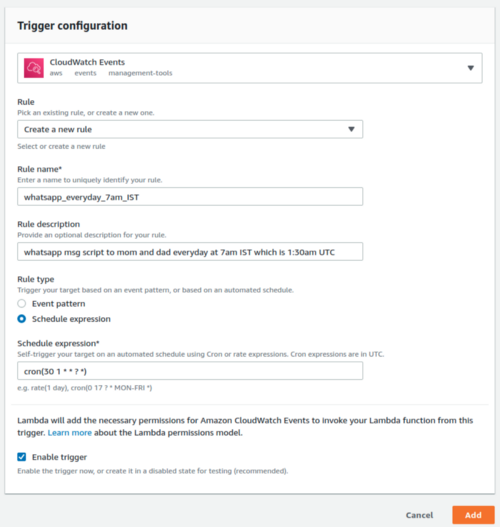
We’ll have to create a new rule. You can give it any name and description if you want.
Set the rule type as schedule expression.
We specified the time using cron(). 30 1 refers to 1:30 am, UTC (equivalent to my 7 AM, IST time).
The next two,* *, are for the day of the month and the month.
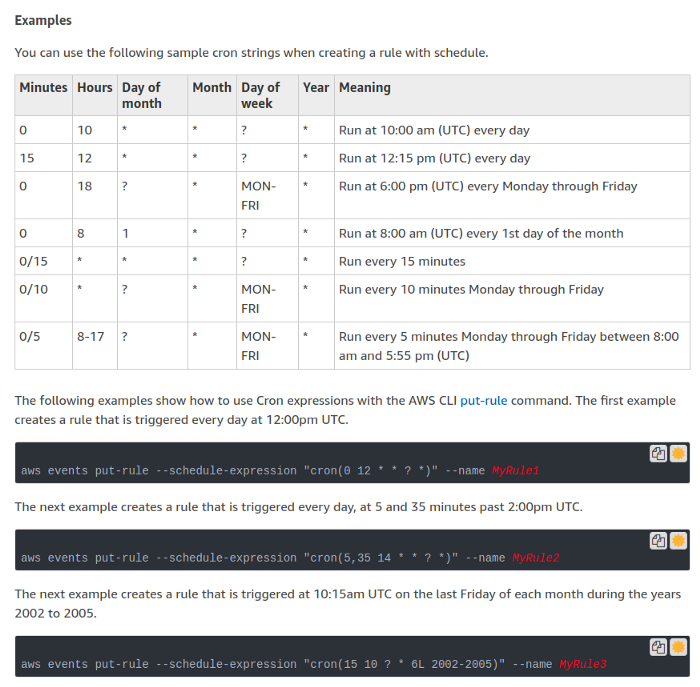
The next two, ? *,are for the day of the week and year. We set * and ? to specify every day, month, and year. You can refer to the example below to create your own cron parameters. Otherwise, you can refer to the cron guide on aws_cron_docs to learn it in depth.
After you’re done, make sure the Enable trigger checkbox is checked. Finally, click the add button.
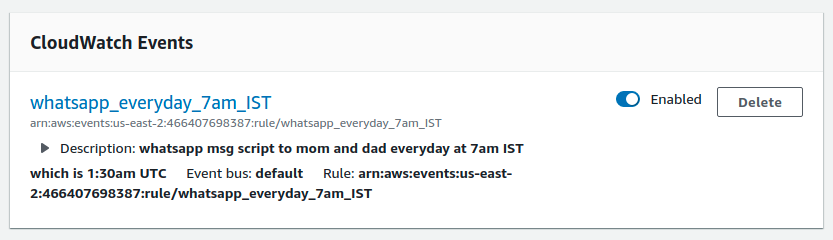
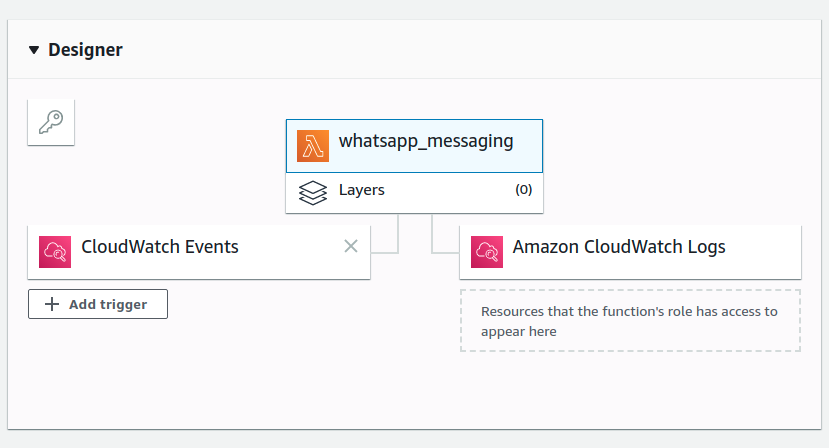
On the Lambda function dashboard, you can now see your CloudWatch Event attached to your Lambda function. Upon scrolling down, you can see the CloudWatch event enabled to trigger your function.
That’s it! You can change the Twilio Sandbox name to your name and can even respond to replies from the Twilio dashboard.
Thank you for reading!
#python #AWS #social media #programming #coding
