Deque: A Double-Ended Queue Data Structure
Deque or Double Ended Queue is a type of queue in which insertion and removal of elements can either be performed from the front or the rear. Thus, it does not follow FIFO rule (First In First Out).

Representation of Deque
Types of Deque
- Input Restricted Deque
In this deque, input is restricted at a single end but allows deletion at both the ends. - Output Restricted Deque
In this deque, output is restricted at a single end but allows insertion at both the ends.
Operations on a Deque
Below is the circular array implementation of deque. In a circular array, if the array is full, we start from the beginning.
But in a linear array implementation, if the array is full, no more elements can be inserted. In each of the operations below, if the array is full, "overflow message" is thrown.
Before performing the following operations, these steps are followed.
- Take an array (deque) of size n.
- Set two pointers at the first position and set
front = -1andrear = 0.
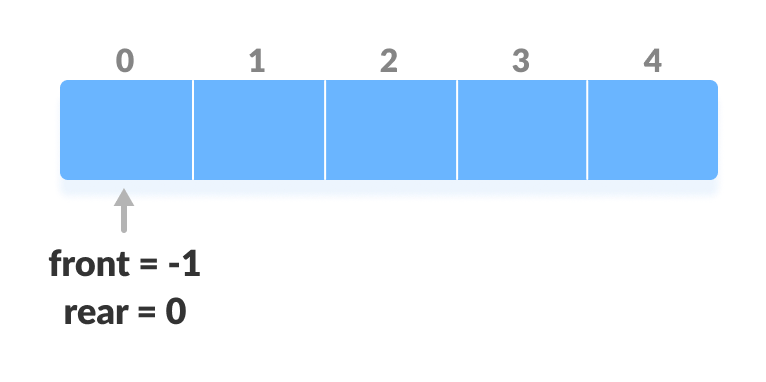
Initialize an array and pointers for deque
1. Insert at the Front
This operation adds an element at the front.
- Check the position of front.
 Check the position of front
Check the position of front - If
front < 1, reinitializefront = n-1(last index). Shift front to the end
Shift front to the end - Else, decrease front by 1.
- Add the new key 5 into
array[front]. Insert the element at Front
Insert the element at Front
2. Insert at the Rear
This operation adds an element to the rear.
- Check if the array is full.
 Check if deque is full
Check if deque is full - If the deque is full, reinitialize
rear = 0. - Else, increase rear by 1.
 Increase the rear
Increase the rear - Add the new key 5 into
array[rear]. Insert the element at rear
Insert the element at rear
3. Delete from the Front
The operation deletes an element from the front.
- Check if the deque is empty.
 Check if deque is empty
Check if deque is empty - If the deque is empty (i.e.
front = -1), deletion cannot be performed (underflow condition). - If the deque has only one element (i.e.
front = rear), setfront = -1andrear = -1. - Else if front is at the end (i.e.
front = n - 1), set go to the frontfront = 0. - Else,
front = front + 1. Increase the front
Increase the front
4. Delete from the Rear
This operation deletes an element from the rear.
- Check if the deque is empty.
 Check if deque is empty
Check if deque is empty - If the deque is empty (i.e.
front = -1), deletion cannot be performed (underflow condition). - If the deque has only one element (i.e.
front = rear), setfront = -1andrear = -1, else follow the steps below. - If rear is at the front (i.e.
rear = 0), set go to the frontrear = n - 1. - Else,
rear = rear - 1. Decrease the rear
Decrease the rear
5. Check Empty
This operation checks if the deque is empty. If front = -1, the deque is empty.
6. Check Full
This operation checks if the deque is full. If front = 0 and rear = n - 1 OR front = rear + 1, the deque is full.
Deque Implementation in Python, Java, C, and C++
Python
Java
C
C++
# Deque implementaion in python
class Deque:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def isEmpty(self):
return self.items == []
def addRear(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def addFront(self, item):
self.items.insert(0, item)
def removeFront(self):
return self.items.pop(0)
def removeRear(self):
return self.items.pop()
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
d = Deque()
print(d.isEmpty())
d.addRear(8)
d.addRear(5)
d.addFront(7)
d.addFront(10)
print(d.size())
print(d.isEmpty())
d.addRear(11)
print(d.removeRear())
print(d.removeFront())
d.addFront(55)
d.addRear(45)
print(d.items)Time Complexity
The time complexity of all the above operations is constant i.e. O(1).
Applications of Deque Data Structure
- In undo operations on software.
- To store history in browsers.
- For implementing both stacks and queues.
- This blog post was originally published at:https://www.programiz.com/