Understand the Problem
We are given a function called insertNodeAtPosition, which has three parameters, head, data, and position.
Our head is a SinglyLinkedListNode (class) pointer to the head of the list, our data is an integer value to insert as data in a new node which we will create, and the position is a zero based index position to where we should insert our new node.
head: pointer to the head of the list
data: integer value of our new node (1)
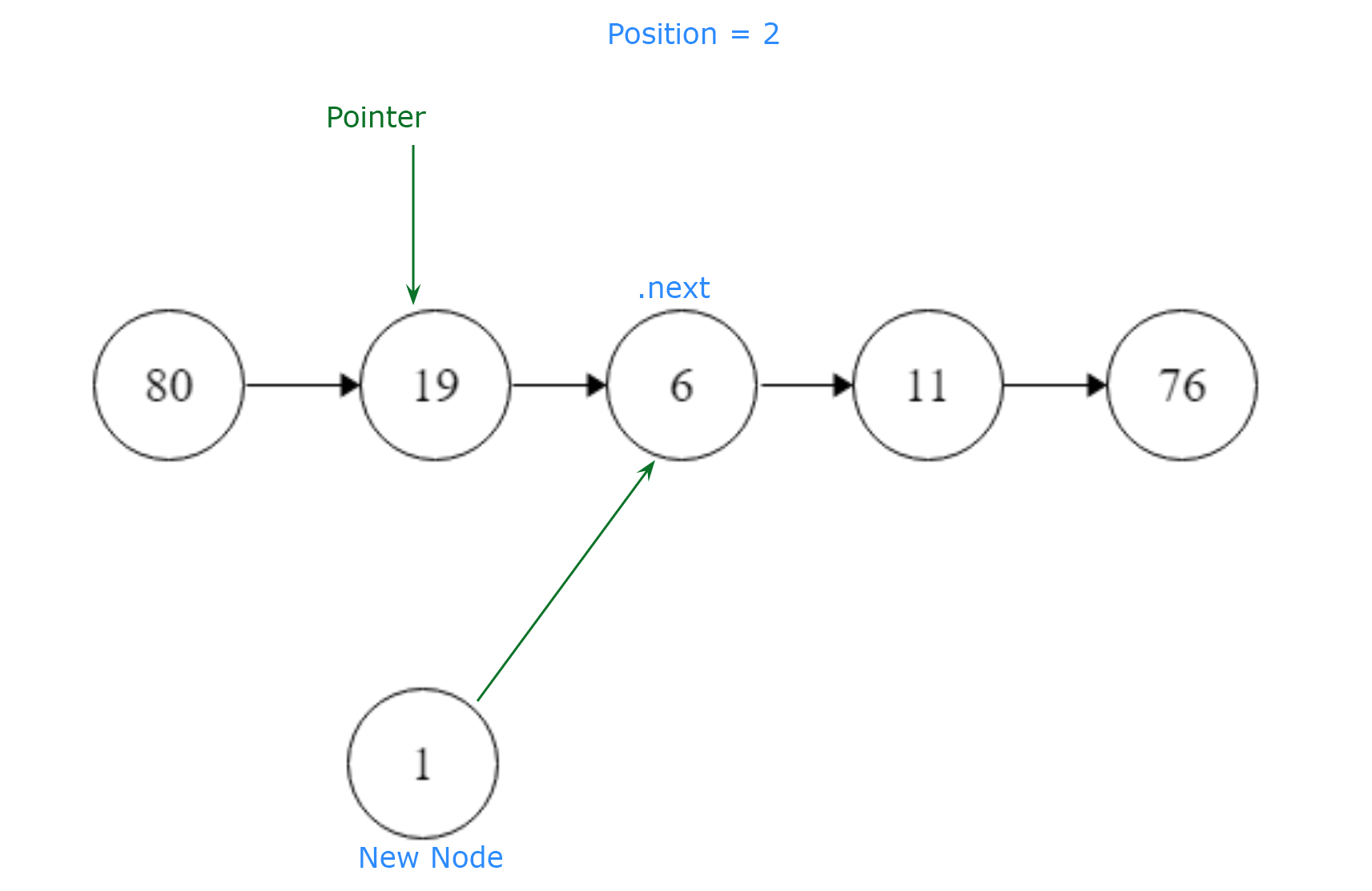
position: a zero based index position (2)
In order to insert a Node at a specific position in the singly linked list, we must create a new node with our data parameter, insert it at the position we were given, and return the head node.
Example:
If our list starts as
4 -> 6 -> 2 -> 9
and our position = 2 and our data = 3\. Our new list will be
4 -> 6 -> 3 -> 2 -> 9
We must return a reference to the head node of our finished list.
Plan
We know that our first step will have to be to create a new node in order to have one to insert. Taking a look at our SinglyLinkedListNode class, we can see that it is expecting data to be passed in.
class SinglyLinkedListNode:
def __init__(self, node_data):
self.data = node_data
self.next = None
We can create a new node in our insertNodeAtPosition function definition by setting new to SinglyLinkedListNode(data).
new = SinglyLinkedListNode(data)
We know that our position is index value 2, so we’ll need to set a pointer to the head in order to traverse through the list from the very beginning, and also set a counter in order to move our pointer through the list node by node, until we reach our given position.
pointer = head
counter = 1
We will need to traverse through the list in order reach our position, starting with the head. Since our pointer is already set to the head, we can use a while loop that will traverse through the list until pointer.next is at our given position. We do this while pointer.next is not None.
while pointer.next is not None:
We will traverse through the list position by position, with our pointer, until we are at our given position, setting counter to counter + 1.
counter += 1
pointer = pointer.next
If pointer.next is finally at our given position, where our counter would be equal to our position of 2, we would set new.next to point to pointer.next.
#software-engineering #hackerrank #algorithms #coding #women-in-tech
