How to Extract Data using Spotify’s API, Python and Spotipy
With Spotify, they provide developers access to some of their data regarding playlists, users, and artists through their Web API, which is what I’ll be showing you how to do.
A lot of times, developers will use Web APIs for app integrations, but it can also be used for data extraction and analysis purposes. Here is what I will be walking you through:
- Creating a Spotify developer account.
- Understanding Spotify’s Web API.
- What data we’ll extract.
- What Spotipy is and does.
- How to extract any artist’s data using Python and Spotipy.
Creating a Spotify Developer Account
The first step in using Spotify’s Web API is to create a developer account. Follow these steps to access your developer account to get a client and secret ID.
Step 1: Log in or create an account
You will need to connect a Spotify developer account by logging into your account or creating a new Spotify account.
Step 2: Client ID
When you’ve accessed your developer account, you’ll need to create a client ID, which you can do by pressing the green CREATE A CLIENT ID button.
You will then get a three-page pop up that you’ll need to fill out and each page will look like this:
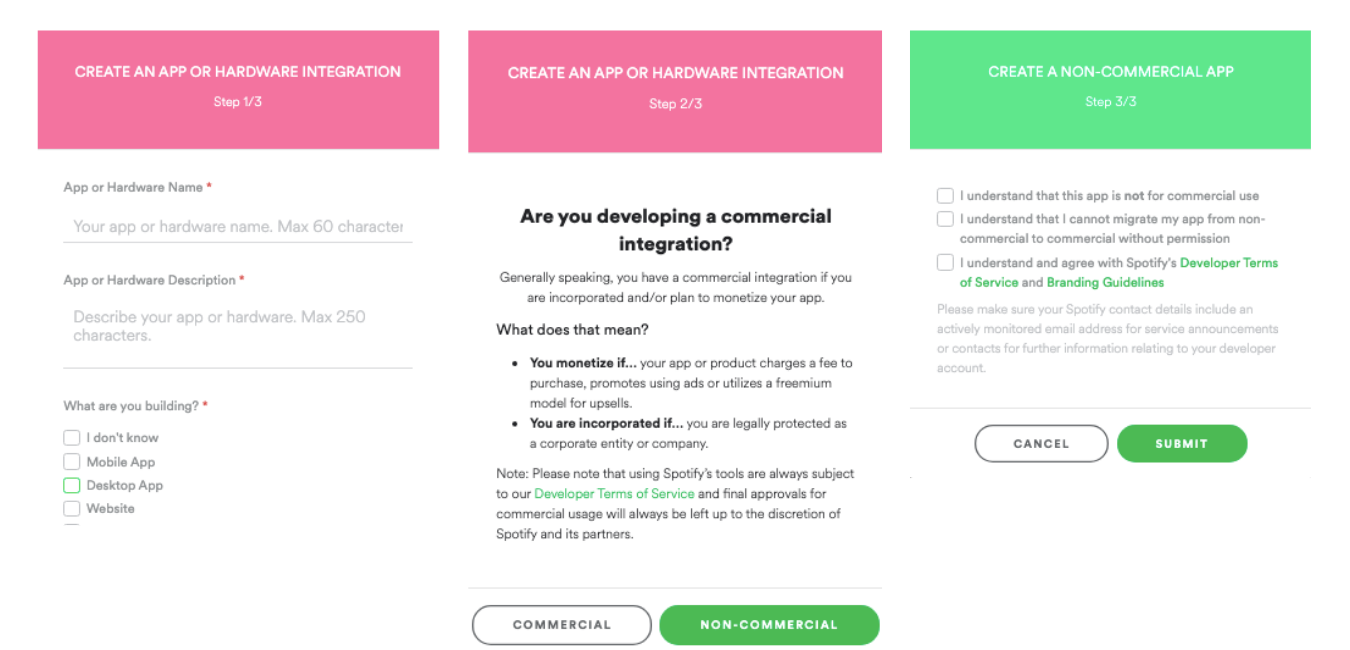
Although we’re not trying to create an app, we will need this client ID to access the same data.
- Page one:Give it a name. I named mine “Album Analysis”. The description I put in is “analyzing Spotify artist’s data”, and then I checked the box that says “Desktop App” under “What are you building?”.
- Page two:Choose non-commercial use.
- Page three:Agree to all the terms and conditions and submit the form.
Step 3: Retrieve your client ID and client secret
Inside your developer dashboard, click on the new app you just created. On your app’s dashboard page, you’ll see your client ID on the top left-hand side.
Underneath your client ID, you’ll see “Show Client Secret” in green. If you press that, you’ll get your client secret. Keep these locations in mind as we work towards our data extraction, we will need them to gain access to the data.
Understanding Spotify’s Web API
I would recommend exploring Spotify’s user-friendly documentation and familiarizing yourself with different areas of how it works. Here are some quick links you can dive into:
- Spotify’s Web API documentation
- Web API tutorial
- Web API libraries
- Spotify Web API reference (useful for exploring the data endpoints we have access to and accessing the related documentation)
Spotify’s Web API console
Another great way to explore the different data Spotify has to offer and to understand the Web API is to explore their Spotify Web API console.
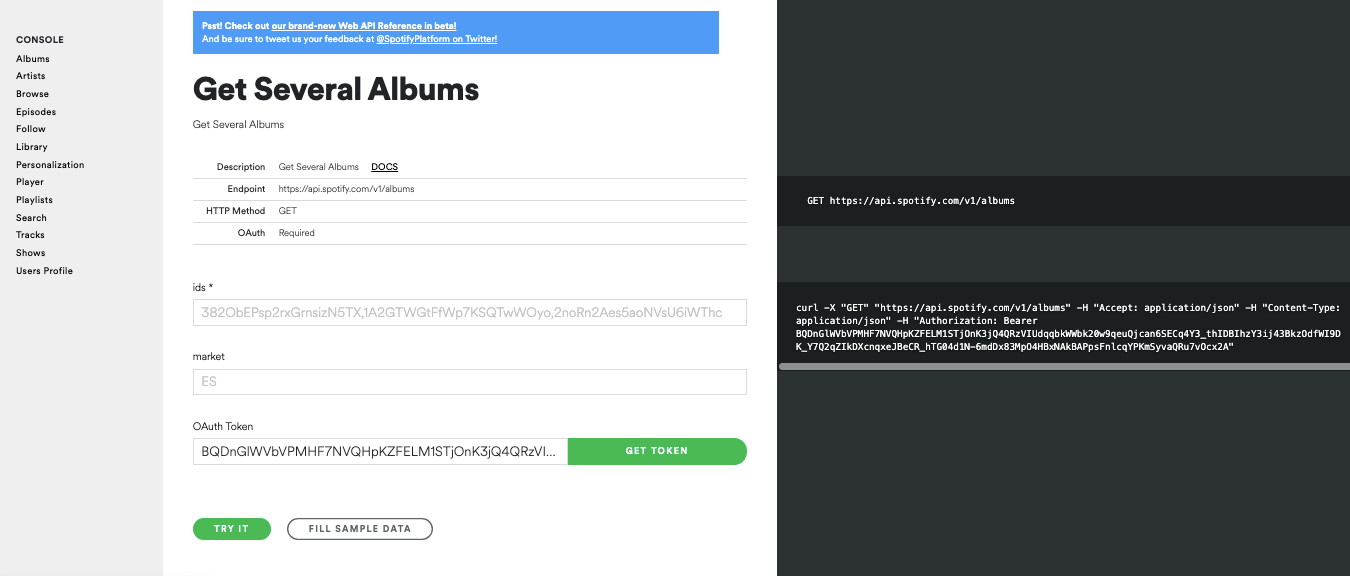
This console lets you explore different endpoints through an easy-to-use interface and test the various methods to preview the JSON outputs.
The Data We’ll Extract
For this guide, I want to extract the data from every album and single (no features) that Kehlani has put out. There are a few potential ways to create a dataset using this API.
We could request a list of the artist’s albums and then loop through each album track.
Or, instead, we can use a playlist that I created which includes every album Kehlani has to offer on Spotify and loop through that which would require a little less code.
Feel free to create your own playlist if you want to work on a different artist’s data instead.
The meta and features data
When grabbing each track from an album, we can obtain track information such as track name, album, release date, length, and popularity.
More importantly, Spotify’s API allows us to extract a number of “audio features” such as danceability, energy, instrumentalness, liveness, loudness, speechiness, acousticness, and tempo.
Using Spotipy
Spotipy is “a lightweight Python library for the Spotify Web API”. With Spotipy, we can get full access to all of the music data provided by the Spotify platform.
I highly recommend going through Spotipy’s documentation to get an understanding of how it works and what you’re capable of doing while using this library.
Additionally, you will get a better understanding of how my code works. Check out their GitHub examples.
Writing the Code
I highly recommend following along using Repl, it is a simple to use yet powerful online IDE that works great and requires no setup. Perfect for a one-time data extraction or dataset creation project.
Import libraries
Let’s start by calling the necessary libraries that we need. We’ll be using Spotipy, pandas to create a dataframe and save our dataset, and time to pause the execution of the loop.
import spotipy
from spotipy.oauth2 import SpotifyClientCredentials
import pandas as pd
import time
Connect to the API
Next, we need to authenticate and connect to Spotify’s API. To do so, we need our “Client ID” and “Client Secret”.
client_id = 'Client ID Here'
client_secret = 'Client Secret Here'
client_credentials_manager = SpotifyClientCredentials(client_id, client_secret)
sp = spotipy.Spotify(client_credentials_manager=client_credentials_manager)
In the code above, replace the Client ID and Client Secret variables with your own and make sure they are inside quotes.
Retrieve IDs for each track
As I mentioned earlier, I’ll be extracting Kehlani’s albums and singles from a playlist I created which is a collection of 54 songs (~3 hours), containing every single and every song from every album she has released that is currently on Spotify, updated with her new singles.
Now we’ll write a function to get the IDs for each track of this playlist.
def getTrackIDs(user, playlist_id):
ids = []
playlist = sp.user_playlist(user, playlist_id)
for item in playlist['tracks']['items']:
track = item['track']
ids.append(track['id'])
return ids
ids = getTrackIDs('angelicadietzel', '4R0BZVh27NUJhHGLNitU08')
At the bottom of this code, where it says ids = getPlaylistTrackIDs, the two variables separated by a comma in quotes will be the username (found in the URL) of the person who created the playlist, and then the playlist URI which you can find by hitting the setting button on the playlist where you’d find the share link.
Now, let’s check what we have so far by running the length of the ids we grabbed to see if it matches the 54 songs we have on the playlist.
print(len(ids))
print(ids)
This is the result:
54
['7AiMnJSODcJoKDejQ3mnoJ', '73C4vh7W8u41Vll5HvBqv7', '5kYZbBLAGrrhFKNbOs6D95', '18z6OV5lknJmKnZi7aA1zH', '1gHtbcRP4tz1O1NsxPpBea', '3kJudfRjZMItdFYVCCaSi6', '6mzaCRuLTRiz1caGOum3zT', '5h4Uqkh9RpRZwm5ADLh5uj', '3rGew9pmFEmGD9nZ12F1tN', '0dYDmow4l5hbPs5E6QLMSC', '1B3jkf6CyuiF8CQcKlUx9y', '6DkmFhzJrkVhDlcgcEy7Pc', '5dKy6Cgv6xwiRY3j3AJ7Uq', '0oz4ZqHuUaz3uEkP2vD0u8', '389hKTL3ZBPPWP3VuXfEyv', '5cw9s2zGrbny2M2p3WRmGm', '3YaMX9Cf68dxiG6RKo0pSY', '1cAL4sFzXXRMbpZnTPa7Zi', '4w5BVeKJFCj2rrrEy31s0n', '4ta2AWru6ldjg1aHzww0aK', '45DJ0PbKPdbslnyrcM80HN', '7yNu82yd6dYmGQ0H1q0jKo', '4v4HwTfMPslhWAnJxIXchn', '6XptjfnUvLfejptpjPRhCT', '1y2SK8EjL3WSnJvJEMWOoq', '4UMp46x46Zmu9OEr8m3Gl2', '7nb50hgKYhnHJLHKZ7qiKO','5y5OzukBTl0yTRMEdNmApJ', '3Hdl3BEFb1IEbL0Jq53enx', '0lsC0OkBgiLYbSsoHOzMnr', '0Pm1BZp4MpoMKkNxIXCfAu', '2droOB3xlZkhgfUM0owDTq', '2Nd2HLWrIq1DcNMiYPTQUC', '4j644tViOFAf4i0BYT12R8', '4k6hX9RKD096K1NCjjJZLc', '0aSW5EMeNnQSMJQ8QN3zIW', '0tkmYNfaEaH9HpR59ApRtE', '0kas95RruYRVqrOb07rgkh', '4BOikd4oZjOYMde9AXfrTo', '6ZRuF2n1CQxyxxAAWsKJOy', '1EGrDTfEuAiRzRdxlblpET', '32s2Dn9EVvO2f85MrpRoBV', '4jM3c9KLTO9iZPm9A7neiL', '6GCRnf1W9OKxok9fvNp3pz', '1Zm9qGPQkTAOBiVpGSnJUq', '3ucRKbRlikYHyoI17gfR0c', '6HUO25AttZZCoKAY0vUVtc', '5Qr7StTFbXhgHt9JlqJx0I', '1QzC4y8h6WFxHE4KlokhVr', '1xz905v9g71heS0BQQM9re', '5QTdOvIF2ehBMZpSIIGzIo', '7IJiDYPZy2AIJn3YVHhvD4', '23wuZgeX1oyJ43QYOTo9s7', '0tBBihoEWiWKqsO5ZlCbwS']
Create a function used to grab all track info from IDs
Now that we have a list of every track ids we need, we will now write a function that will be used to grab the track information such as track name, album, release date, length, and popularity, along with the list of audio features that Spotify’s API has to offer from each track ids.
def getTrackFeatures(id):
meta = sp.track(id)
features = sp.audio_features(id)
# meta
name = meta['name']
album = meta['album']['name']
artist = meta['album']['artists'][0]['name']
release_date = meta['album']['release_date']
length = meta['duration_ms']
popularity = meta['popularity']
# features
acousticness = features[0]['acousticness']
danceability = features[0]['danceability']
energy = features[0]['energy']
instrumentalness = features[0]['instrumentalness']
liveness = features[0]['liveness']
loudness = features[0]['loudness']
speechiness = features[0]['speechiness']
tempo = features[0]['tempo']
time_signature = features[0]['time_signature']
track = [name, album, artist, release_date, length, popularity, danceability, acousticness, danceability, energy, instrumentalness, liveness, loudness, speechiness, tempo, time_signature]
return track
Loop over tracks and apply the function
We’ll now loop over the tracks — applying the function we created— and save the dataset to a .csv file using pandas.
# loop over track ids
tracks = []
for i in range(len(ids)):
time.sleep(.5)
track = getTrackFeatures(ids[i])
tracks.append(track)
# create dataset
df = pd.DataFrame(tracks, columns = ['name', 'album', 'artist', 'release_date', 'length', 'popularity', 'danceability', 'acousticness', 'danceability', 'energy', 'instrumentalness', 'liveness', 'loudness', 'speechiness', 'tempo', 'time_signature'])
df.to_csv("spotify.csv", sep = ',')
My raw dataset looks like this:
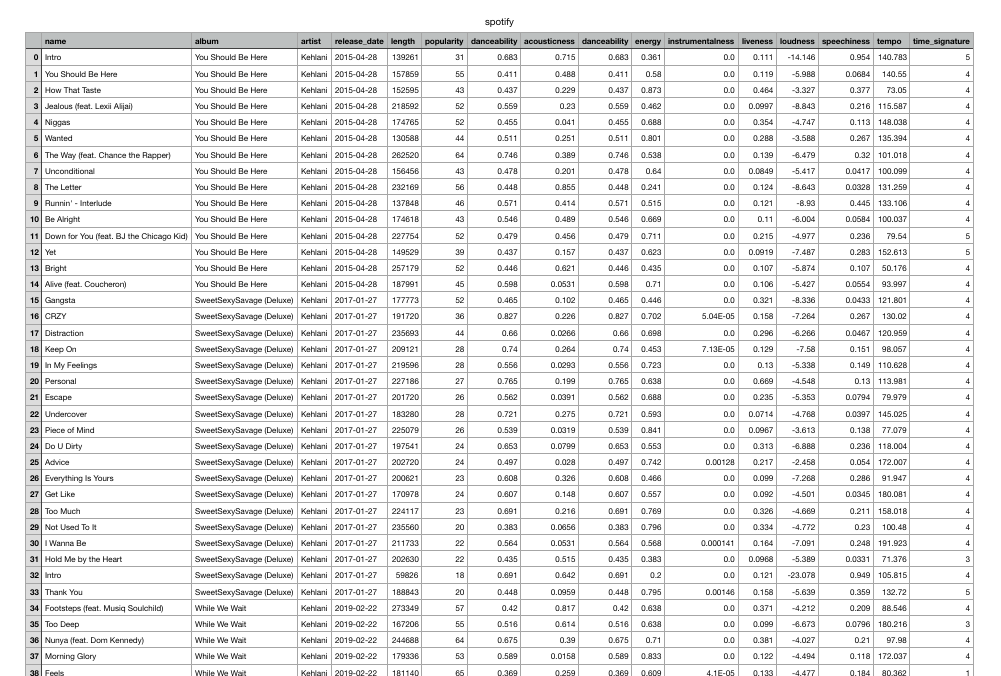
There You Have It!
This is how you can extract Spotify data on any artist you like.
The easiest way I’ve found was simply creating my own playlist to loop through, which offered fewer errors and put everything all in one place, but there are many other ways you can go about this.
Next Steps
The next step would be to clean up this data and then analyze it to gain insights into the artist’s music over the years.
Different ways you can analyze and visualize Spotify’s data could be:
- The number of tracks over time.
- Visualize the length of tracks over time.
- Average danceablity over time.
- Top collaborators.
I hope this was a quick and clear intro to Spotify’s Web API and Spotipy!
Thank you for reading!
#python #spotify #data science #ai #machine learning