AngularJS Directive with Example: ng-init, ng-app, ng-repeat, ng-model
What is an AngularJS directive?
A directive in AngularJS is a command that gives HTML new functionality. When angular go through the HTML code, it will first find the directives in the page and then parse the HTML page accordingly.
A simple example of an AngularJS directive, which we have seen in earlier chapters is the "ng-model directive". This directive is used to bind our data model to our view.
Note: You can have basic angular code in an HTML page with the ng-init, ng-repeat and ng-model directives without the need to have Controllers. The logic for these directives is in the Angular.js file which is provided by Google. Controllers are the next level angular programming constructs that allow business logic, but as mentioned for an application to be an angular application it's not mandatory to have a controller.
How to Create Directive
As we defined in the introduction, AngularJS directives is a way to extend the functionality of HTML.
There are 4 directives defined in AngularJS.
Below is the list of the AngularJS directives along with examples provided to explain each one of them.
1. ng-app
This is used to initialize an Angular.JS application. When this directive in place in an HTML page, it basically tells Angular that this HTML page is an angular.js application.
The example below shows how to use the ng-app directive. In this example, we are simply going to show how to make a normal HTML application an angularJS application.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset="UTF 8">
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js”></script>
<h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<div ng-app=“”>
Tutorial Name : {{ "Angular" + "JS"}}
</div>
</body>
</html>
Code Explanation:
- The “ng-app” directive is added to our div tag to indicate that this application is an angular.js application. Note that the ng-app directive can be applied to any tag, so it can also be put in the body tag as well.
- Because we have defined this application as an angular.js application, we can now make use of the angular.js functionality. In our case, we are using expressions to simply concatenate 2 strings.
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
The output clearly shows the output of the expression which was only made possible because we defined the application as an angularjs application.
2. ng-init
This is used to initialize application data. Sometimes you may require some local data for your application, this can be done with the ng-init directive.
The example below shows how to use the ng-init directive.
In this example, we are going to create a variable called “TutorialName” using the ng-init directive and display the value of that variable on the page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset=“UTF 8”>
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body><script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js”></script><h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<div ng-app=“” ng-init=“TutorialName=‘Angular JS’”>
Tutorial Name : {{ TutorialName}}</div>
</body>
</html>
Code Explanation:
- The ng-init directive is added to our div tag to define a local variable called “TutorialName” and the value given to this is “AngularJS”.
- We are using expressions in AngularJs to display the output of the variable name “TutorialName” which was defined in our ng-init directive.
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
In the output,
- The result clearly shows the output of the expression which contains the string “AngularJS”. This is as a result of the string “AngularJS” being assigned to the variable ‘TutorialName’ in the ng-init section.
3. ng-model
And finally, we have the ng-model directive, which is used to bind the value of an HTML control to application data. The example below shows how to use the ng-model directive.
In this example,
- We are going to create 2 variables called “quantity” and “price”. These variables are going to be bound to 2 text input controls.
- We are then going to display the total amount based on the multiplication of both price and quantity values.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset=“UTF 8”>
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body><script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js”></script><h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<div ng-app=“” ng-init=“quantity=1;price=5”>
People : <input type="number" ng-model="quantity"> Registration Price : <input type="number" ng-model="price"> Total : {{quantity * price}}</div>
</body>
</html>
Code Explanation:
- The ng-init directive is added to our div tag to define 2 local variables; one is called “quantity” and the other is “price”.
- Now we are using the ng-model directive to bind the text boxes of “People” and “Registration price” to our local variables “quantity” and “price” respectively.
- Finally, we are showing the Total via an expression, which is the multiplication of the quantity and price variables.
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
Output:
- The output clearly shows the multiplication of the values for People and Registration price.
Now, if you go to the text boxes and change the value of the People and Registration price, the Total will automatically change.
- The above output just shows the power of data binding in angularJs, which is achieved with the use of the ng-model directive.
4. ng-repeat
This is used to repeat an HTML element. The example below shows how to use the ng-repeat directive.
In this example,
- We are going to have an array of chapter names in an array variable and
- then use the ng-repeat directive to display each element of the array as a list item
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta chrset=“UTF 8”>
<title>Event Registration</title>
</head>
<body><script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular-route.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.angularjs.org/1.6.9/angular.min.js”></script>
<script src=“https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js”></script><h1> Guru99 Global Event</h1>
<div ng-app=“” ng-init=“chapters=[‘Controllers’,‘Models’,‘Filters’]”>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat=“names in chapters”>
{{names}}
</li>
</ul></div>
</body>
</html>
Code Explanation:
- The ng-init directive is added to our div tag to define a variable called “chapters” which is an array variable containing 3 strings.
- The ng-repeat element is used by declaring an inline variable called “names” and going through each element in the chapters array.
- Finally, we are showing the value of the local inline variable ‘names.’
If the code is executed successfully, the following Output will be shown when you run your code in the browser.
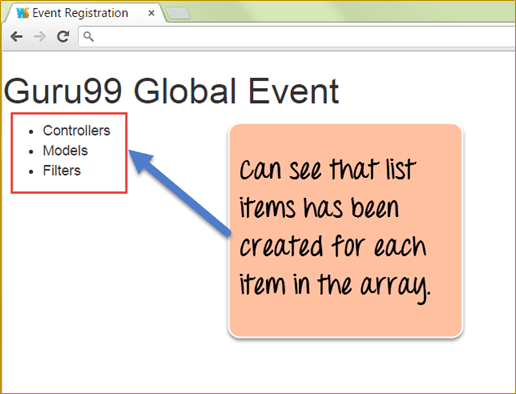
Output:
- The above output just shows that the ng-repeat directive took each value in the array called “chapters” and created HTML list items for each item in the array.
Summary
Directives are used to extend the functionality of HTML. Angular provides inbuilt directives such as
- ng-app – This is used to initialize an angular application.
- ng-int – This is used to create application variables
- ng-model – This is used to bind HTML controls to application data
- ng-repeat – Used to repeat elements using angular.
Thanks for reading. If you liked this post, share it with all of your programming buddies!
Further reading
☞ Angular 8 (formerly Angular 2) - The Complete Guide
☞ Angular & NodeJS - The MEAN Stack Guide
☞ The Complete Node.js Developer Course (3rd Edition)
☞ Best 50 Angular Interview Questions for Frontend Developers in 2019
☞ How to build a CRUD Web App with Angular 8.0
☞ React vs Angular: An In-depth Comparison
☞ React vs Angular vs Vue.js by Example
This post was originally published here
#angular-js #html #web-development