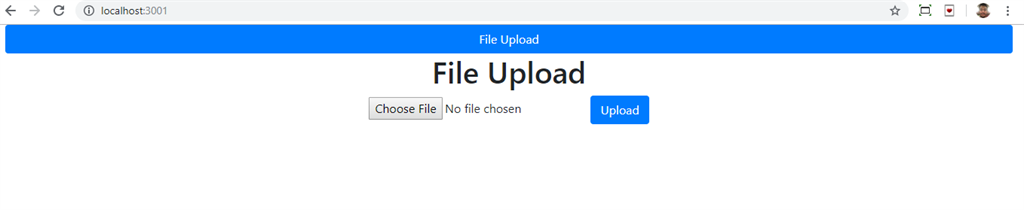
How to upload files using ASP.NET Web API and React.js
React.js is an open-source JavaScript library used for creating user interfaces, particularly for SPA. It is also used for controlling the view layer for web and mobile applications. In this tutorial, we will learn how to upload files, images or videos using ASP.NET Web API and React.js.
Create a React.js Project
Let’s create a React.js project using the following command:
npx create-reatc-app fileupload
Now open the newly created project in Visual Studio Code and install Bootstrap by using the following command:
npm install --save bootstrap
Now, open the index.js file and import Bootstrap.
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
Now Install the Axios library by using the following command. Learn more about Axios.
npm install --save axios
Now, go to the src folder and create a new component named ‘fileupload.js’ and add the following lines in this component.
import React from 'react';
import { post } from 'axios';
class Fileupload extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
file: '',
};
}
async submit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
const url = `http://localhost:61331/api/Uploadfiles/Uploadfile`;
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('body', this.state.file);
const config = {
headers: {
'content-type': 'multipart/form-data',
},
};
return post(url, formData, config);
}
setFile(e) {
this.setState({ file: e.target.files[0] });
}
render() {
return (
<div className="container-fluid">
<form onSubmit={e => this.submit(e)}>
<div className="col-sm-12 btn btn-primary">
File Upload
</div>
<h1>File Upload</h1>
<input type="file" onChange={e => this.setFile(e)} />
<button className="btn btn-primary" type="submit">Upload</button>
</form>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Fileupload
Now open App.js file and add the following code:
import React from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
import Welcome from './Welcome'
import Fileupload from './upload'
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
{/* <Welcome></Welcome> */}
<Fileupload></Fileupload>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Create a Table in the Database
Open SQL Server Management Studio, create a database named “Employee,” and in this database, create a table. Give that table a name like “Stotefiles.”
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Stotefiles](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[File] [nvarchar](max) NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Files] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY] TEXTIMAGE_ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Create a New Web API Project
Open Visual Studio and create a new project. 
Change the Name to FileuploadwithReact and Click ok. 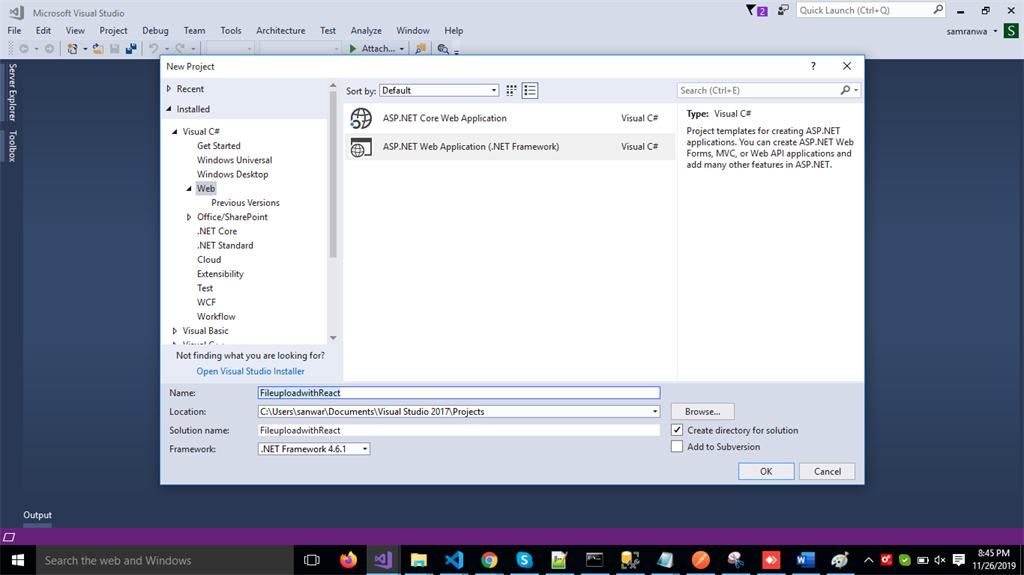
Select Web API as its template. 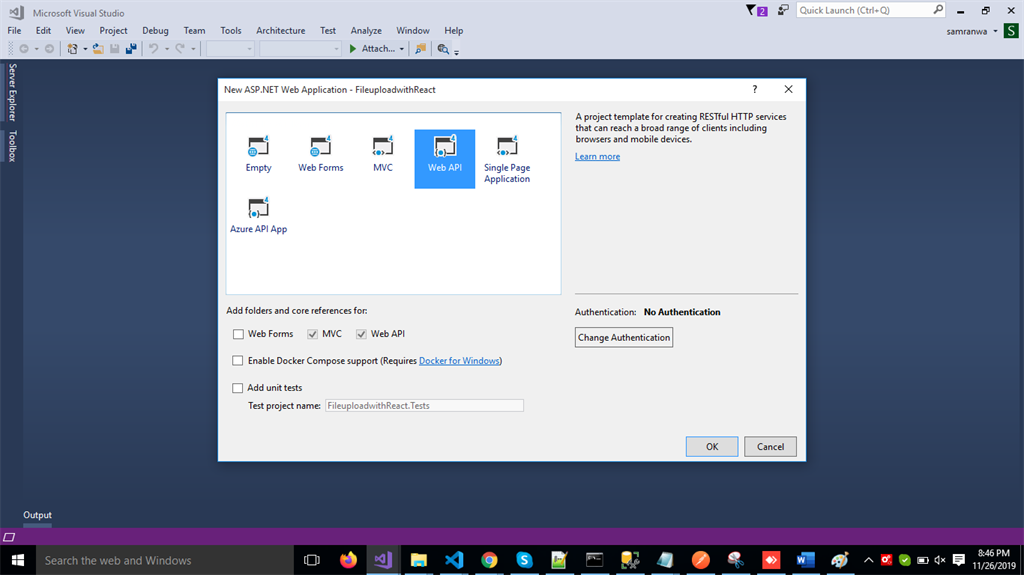
Right-click the Models folder from Solution Explorer and go to Add >> New Item >> data. Click on the “ADO.NET Entity Data Model” option and click “Add.” 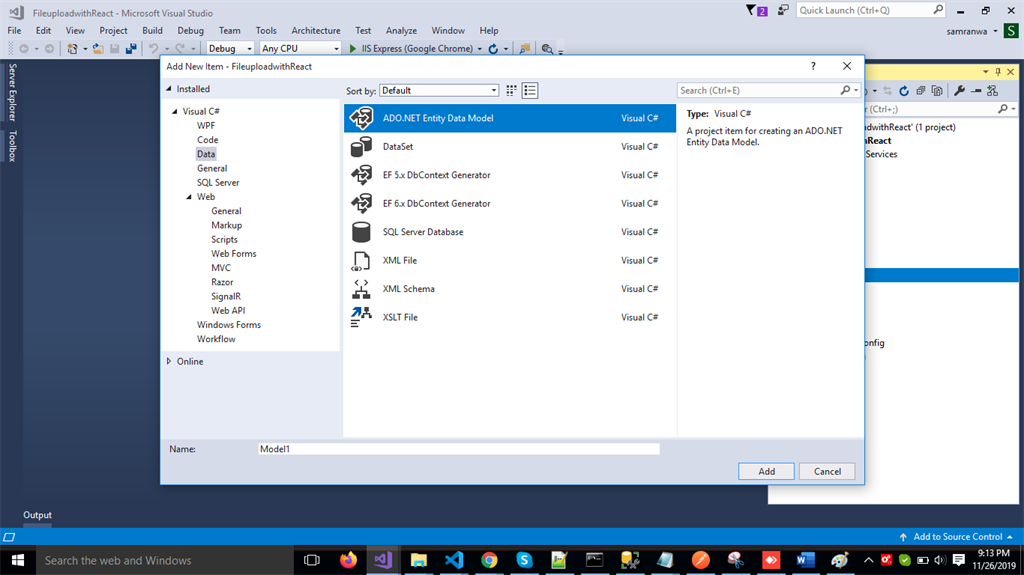
Select EF Designer from the database and click the “Next” button. 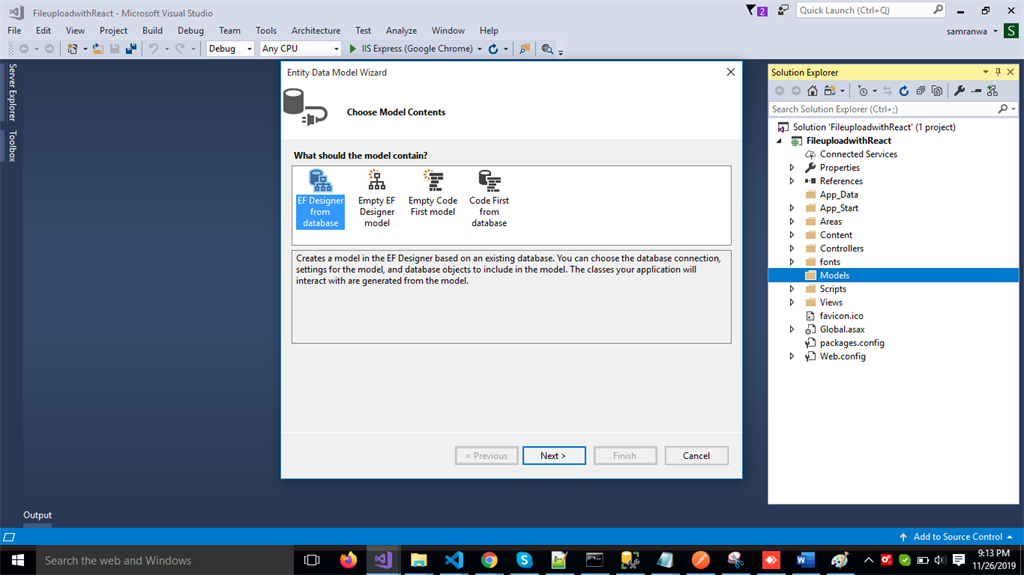
Add the connection properties and select database name on the next page and click OK. 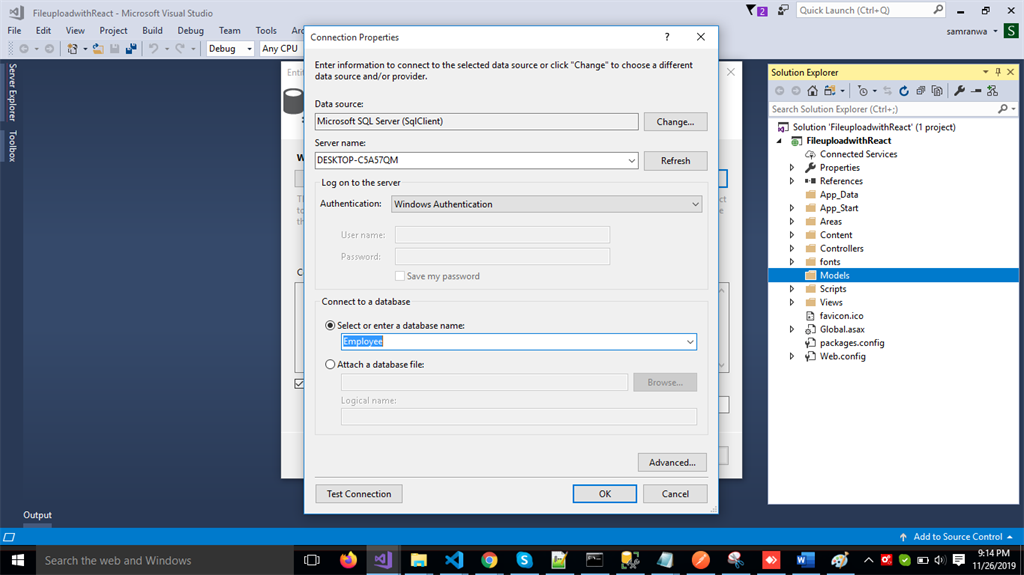
Check Table checkbox. The internal options will be selected by default. Now, click the “Finish” button. 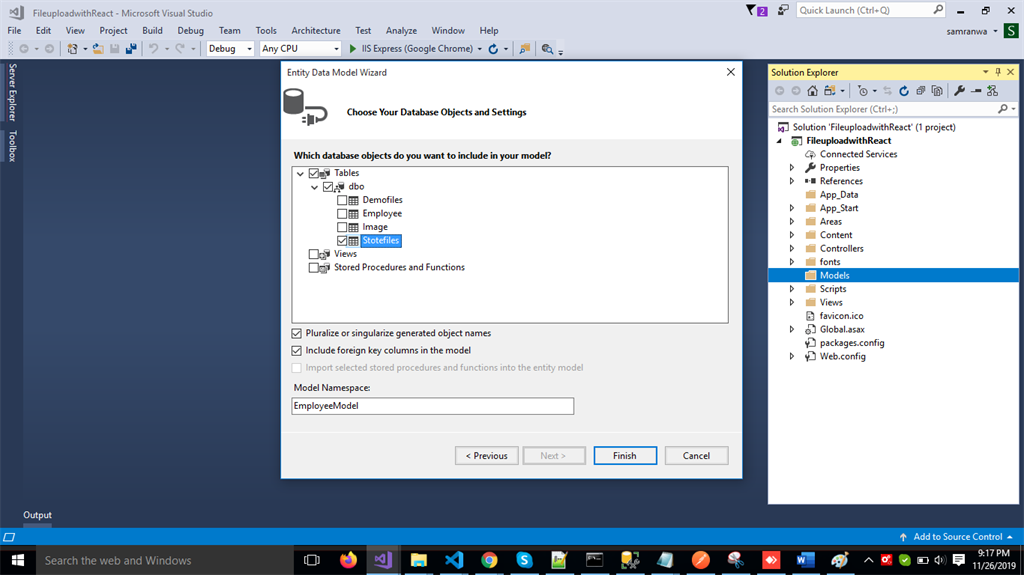 Our data model is successfully created now.
Our data model is successfully created now.
Right-click on the Models folder and add a class Response. Now, paste the following code in the class.
public class Response
{
public string Status { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
}
Right-click on the Controllers folder and add a new controller. Name it as “Uploadfiles controller” and add following namespace
using FileuploadwithReact.Models;
Create a method in this controller to uppload file and add the following code in this controller.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Http;
using FileuploadwithReact.Models;
namespace FileuploadwithReact.Controllers
{
public class UploadfilesController : ApiController
{
EmployeeEntities DB = new EmployeeEntities();
public async Task<object> Uploadfile()
{
try
{
var fileuploadPath = "C:\\Users\\sanwar\\Documents\\Visual Studio 2017\\Projects\\FileuploadwithReact\\FileuploadwithReact\\Files";
var provider = new MultipartFormDataStreamProvider(fileuploadPath);
var content = new StreamContent(HttpContext.Current.Request.GetBufferlessInputStream(true));
foreach (var header in Request.Content.Headers)
{
content.Headers.TryAddWithoutValidation(header.Key, header.Value);
}
await content.ReadAsMultipartAsync(provider);
string uploadingFileName = provider.FileData.Select(x => x.LocalFileName).FirstOrDefault();
string originalFileName = String.Concat(fileuploadPath, "\\" + (provider.Contents[0].Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName).Trim(new Char[] { '"' }));
var filename = provider.Contents[0].Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName;
if (File.Exists(originalFileName))
{
File.Delete(originalFileName);
}
File.Move(uploadingFileName, originalFileName);
Stotefile sf = new Stotefile();
sf.File = filename;
DB.Stotefiles.Add(sf);
DB.SaveChanges();
return new Response
{
Status = "Updated",
Message = "Updated Successfully"
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return new Response
{
Status = "Error",
Message = "Error"
};
}
}
}
}
Now, let’s enable Cors. Go to Tools, open NuGet Package Manager, search for Cors, and install the “Microsoft.ASP.NET.WebApi.Cors” package. Open Webapiconfig.cs and add the following lines.
EnableCorsAttribute cors = new EnableCorsAttribute("*", "*", "*");
config.EnableCors(cors);
Now go to Visual Studio code and run the React.js project by using ‘npm start’ command and upload a file.
In this article, we learned about upload files and images using React.js and ASP.NET web API.
#react #asp_net #javascript