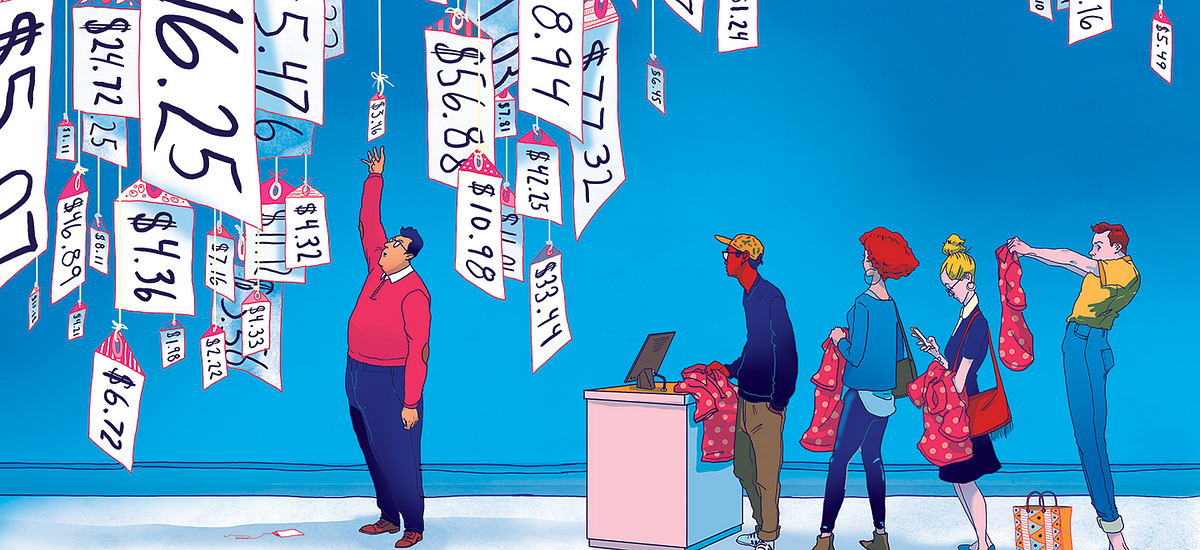
Have you ever wondered how product prices are determined? How do large corporations (i.e. Hotel.com, Amazon, or American Airlines) decide on the right price for their products? Whether that product is an airline ticket, an insurance policy, or a loan. Companies have to use price optimization, as a vital tool for your pricing process.

To best understand price optimization, we first need to understand a core concept of microeconomics: Price Elasticity.
What is price elasticity?
As the price increases, your demand for the orange juice decreases. If we plot this behavior the trend would appear as below:
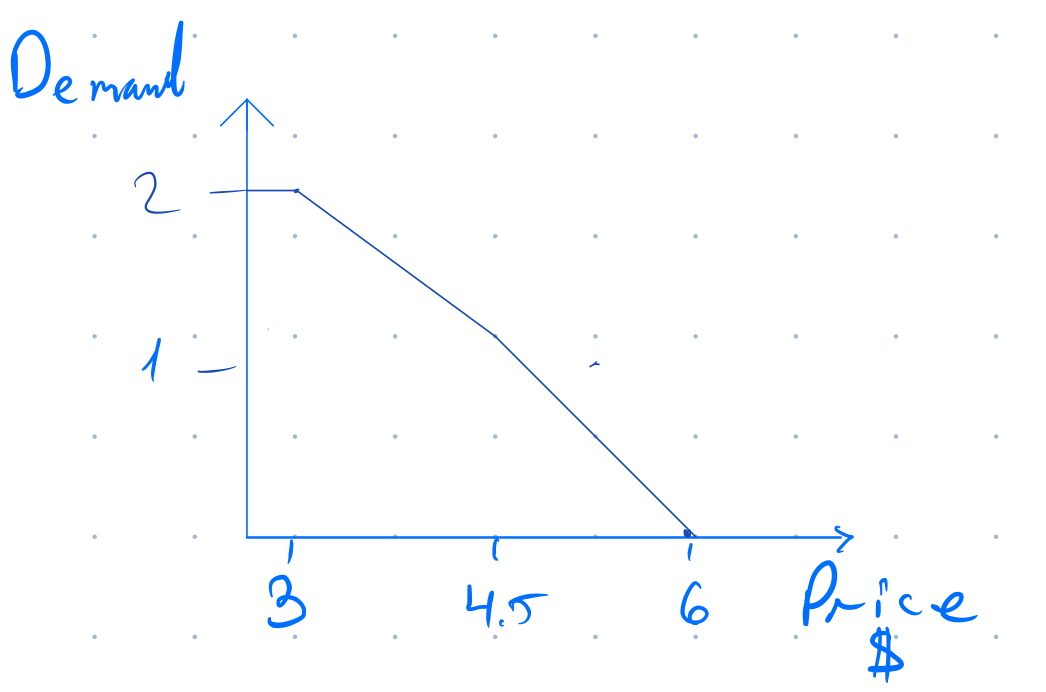
The price elasticity for purchasing the orange juice is different for every point in the graph.
It can be calculated using the following formula:
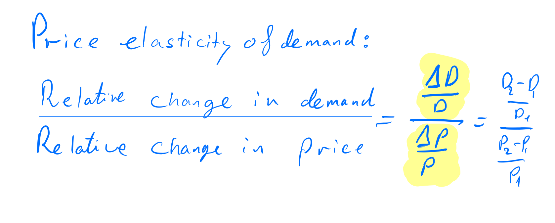
We can see that the price elasticity at a price of $3 is -1. Then, for every 1% of price increase, the demand will drop by 1%. And at a price of $4.5 is -3. Then, for every 1% of price increase, the demand will drop by 3%.
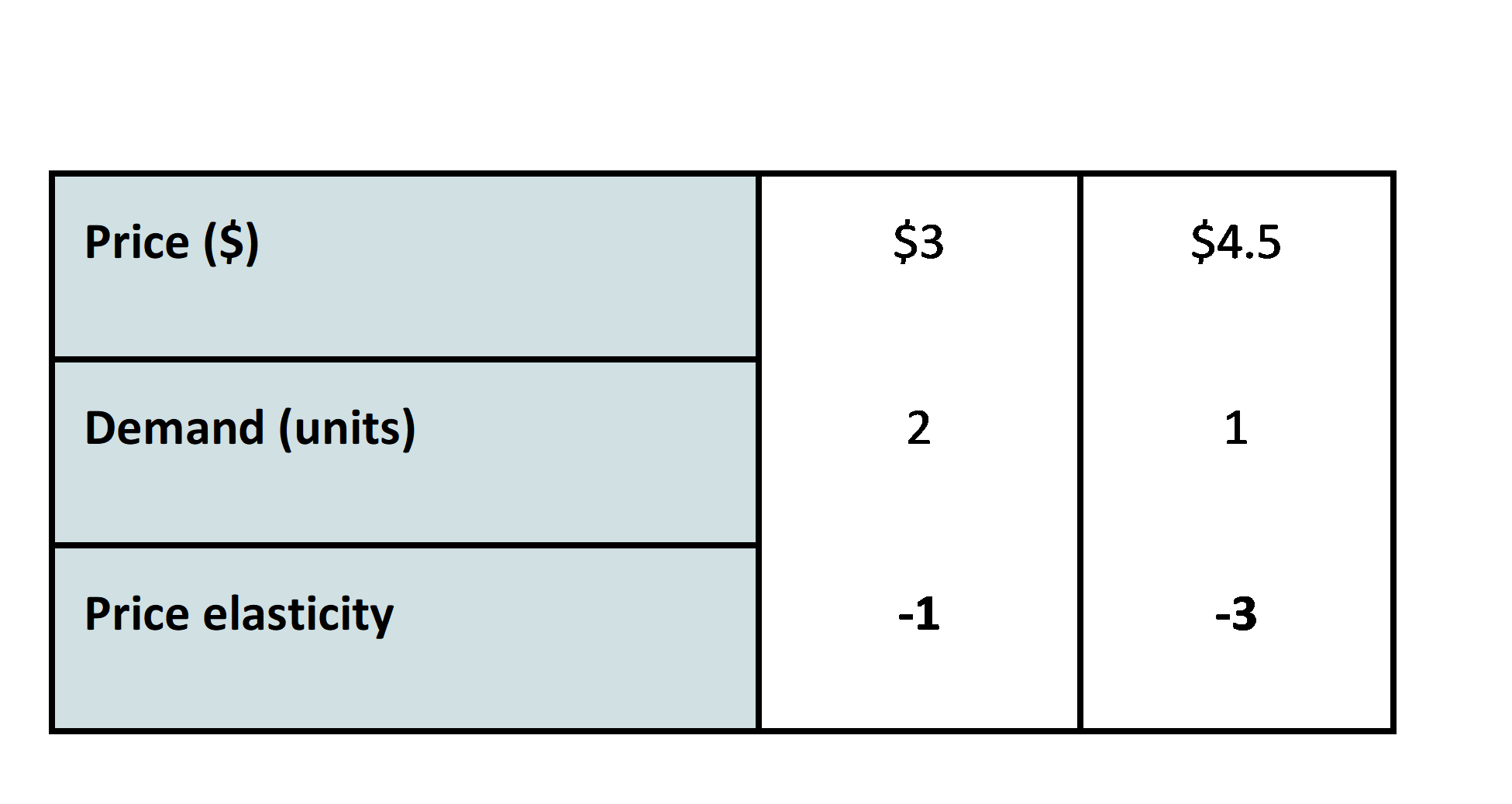
What can we understand from the Price elasticity of demand?
When the customer has a high price elasticity, they are very sensitive to the change in price. Therefore, if we can set the price, we would aim towards the area where the price elasticity is lower in absolute terms. In our example: around $3. Based on the price elasticity and other factors, we can build a demand model that estimates the probability of buying the product. Now that we have a grasp of what price elasticity is, we have a solid foundation to dive into price optimization…
What is price optimization?
Price optimization will help us to understand how much to charge in order to maximize the profits of a given product.
Price optimization is based on two factors:
1. The behavior factor, also known as the demand model based on “Price Elasticity” — the customer’s sensitivity to change in price.
2. The profitability factor: how much potential profit the company can earn from selling this product at a given price.
Let us look at the following example: Rebecca is 30 years old, and she wants to take a $10,000 loan to replace her car. She went to shop around for a loan from different banks and settled on her local branch.
#banking-technology #data-science #financial-planning #price-analysis #fintech #data analysis
