Binary Tree: A Tree Data Structure with Two Children per Node
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each parent node can have at most two children. Each node of a binary tree consists of three items:
data item
address of left child
address of right child

Binary Tree
Types of Binary Tree
1. Full Binary Tree
A full Binary tree is a special type of binary tree in which every parent node/internal node has either two or no children.

Full Binary Tree
2. Perfect Binary Tree
A perfect binary tree is a type of binary tree in which every internal node has exactly two child nodes and all the leaf nodes are at the same level.

Perfect Binary Tree
3. Complete Binary Tree
A complete binary tree is just like a full binary tree, but with two major differences
- Every level must be completely filled
- All the leaf elements must lean towards the left.
- The last leaf element might not have a right sibling i.e. a complete binary tree doesn't have to be a full binary tree.
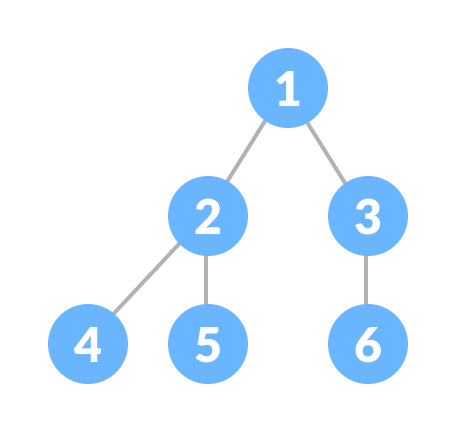
Complete Binary Tree
4. Degenerate or Pathological Tree
A degenerate or pathological tree is the tree having a single child either left or right.

Degenerate Binary Tree
5. Skewed Binary Tree
A skewed binary tree is a pathological/degenerate tree in which the tree is either dominated by the left nodes or the right nodes. Thus, there are two types of skewed binary tree: left-skewed binary tree and right-skewed binary tree.

Skewed Binary Tree
6. Balanced Binary Tree
It is a type of binary tree in which the difference between the height of the left and the right subtree for each node is either 0 or 1.

Balanced Binary Tree
Binary Tree Representation
A node of a binary tree is represented by a structure containing a data part and two pointers to other structures of the same type.
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};

Binary Tree Representation
Python, Java and C/C++ Examples
Python
Java
C
C++
# Binary Tree in Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.val = key
# Traverse preorder
def traversePreOrder(self):
print(self.val, end=' ')
if self.left:
self.left.traversePreOrder()
if self.right:
self.right.traversePreOrder()
# Traverse inorder
def traverseInOrder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.traverseInOrder()
print(self.val, end=' ')
if self.right:
self.right.traverseInOrder()
# Traverse postorder
def traversePostOrder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.traversePostOrder()
if self.right:
self.right.traversePostOrder()
print(self.val, end=' ')
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
print("Pre order Traversal: ", end="")
root.traversePreOrder()
print("\nIn order Traversal: ", end="")
root.traverseInOrder()
print("\nPost order Traversal: ", end="")
root.traversePostOrder()Binary Tree Applications
- For easy and quick access to data
- In router algorithms
- To implement heap data structure
- Syntax tree
- This blog post was originally published at:https://www.programiz.com/
