A resizable and draggable HTML div element can add more possibilities into your website by allowing you to make more flexible components, such as a draggable back-to-top button, a resizable calendar, a movable video window and etc.
In this post, we will go through the process of making a resizable and draggable component step by step with less than 100 lines of code. The structure of this article is shown below:
- Create a resizable component
- Make the component draggable
- Add boundary restrictions into moving & resizing actions
View details in my github repo: angular-resizable-draggable.
1. Create a resizable component
1.1 Component Initialization
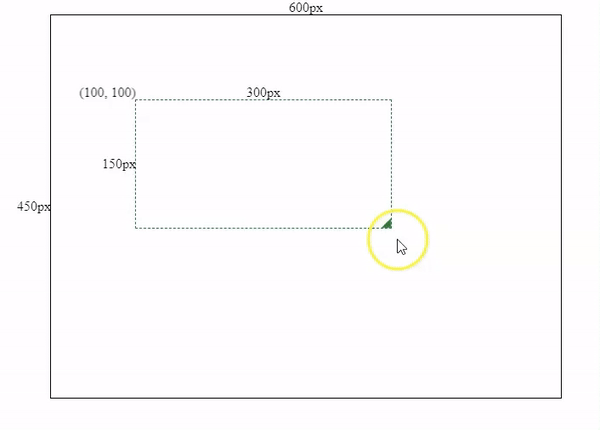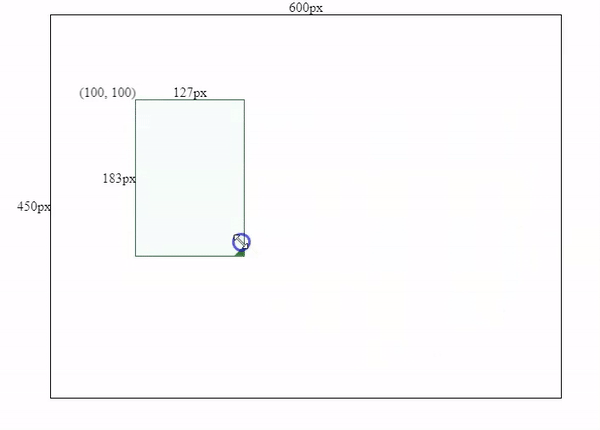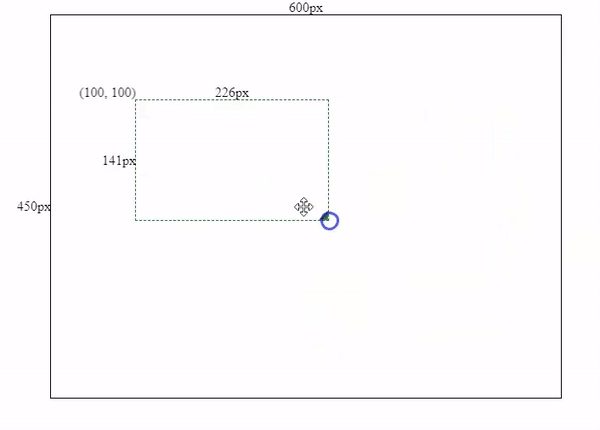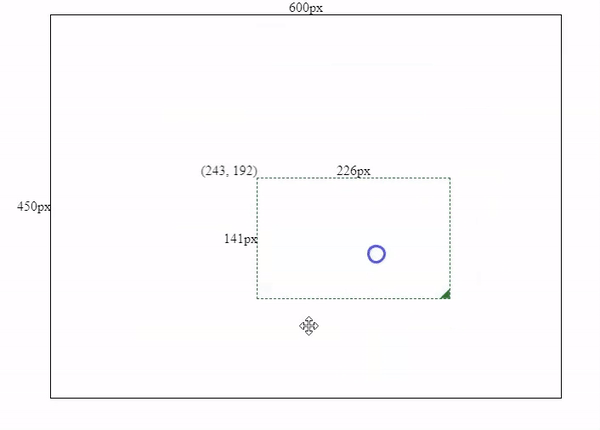
As part of the initial settings, I have initialized an Angular project with a 600x450px container for the component we are going to make.
After that, we need to initialize a resizable-draggable component and pass some initial @Input values into the component, and bind them with the component’s style.

Initialize Component
app.component.html
<app-resizable-draggable
[width]="300"
[height]="150"
[left]="100"
[top]="100">
</app-resizable-draggable>
resizable-draggable.component.ts
@Input('width') public width: number;
@Input('height') public height: number;
@Input('left') public left: number;
@Input('top') public top: number;
resizable-draggable.component.html
<div class="resizable-draggable"
[style.width.px]="width"
[style.height.px]="height"
[style.transform]="'translate3d(' + left + 'px,' + top + 'px,' + '0px)'">
<div class="resize-action"></div>
</div>
1.2 Add resize logics into the component
After component initialization, we need to add some resize logics. The core of resizing is to recalculate the box’s width and height by subtracting the box’s initial x & y coordinates (left and top values) from our mouse’s current X & Y coordinates.
pseudocode: newWidth = mouseX - boxLeft;
pseudocode: newHeight = mouseY - boxTop;
To get the box’s initial X & Y coordinates, we can use Web API getBoundingClientRect().
The
_Element.getBoundingClientRect()_method returns the size of an element and its position relative to the viewport.
const {left, top} = this.box.nativeElement.getBoundingClientRect();
this.boxSpec = {left, top};
To get our mouse’s current viewport X & Y coordinates, we will need to add a mousemove listener, and use the clientX and clientY values.
@HostListener('window:mousemove', ['$event'])
onMouseMove(event: MouseEvent){
this.mouse = {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
}
}
#javascript #angular #web-development #software-development #web-design