What model suits best for a given dataset? — From Naïve to ARIMA.

Modeling a Time-series: from the ground-up!!
Let’s just say, you already have a time series data and you have done all basic exploratory data analysis on it. You have also decomposed the time series to understand various inherent components within the data. You have a fairly good idea of what you need to forecast, to address the business problem at hand.
At this point, You are wondering which model to implement!!
Don’t worry!! you have come to the right place!!
This article would guide you through the elaborate process of achieving your goal — “Accurate forecasting” while providing a comprehensive explanation for the model-building steps.
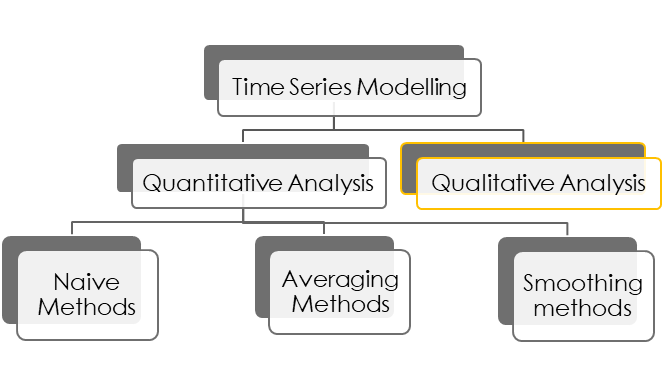
There are 3 fundamental ways to Quantitatively analyze any time series data.
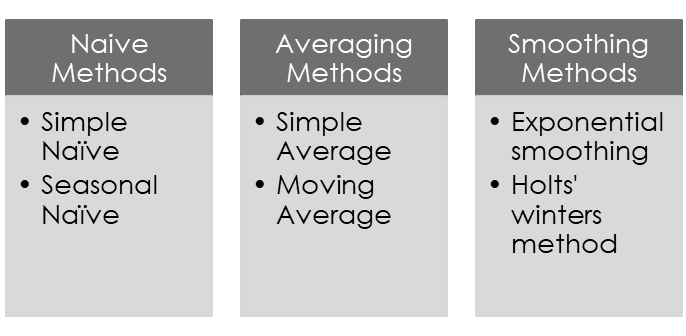
- Naïve methods
- Averaging methods
- Smoothing methods
Lets first try and understand what each model does in terms of forecasting.
1. Naïve methods:
These are modeling techniques in which the previous period’s values are used as the current period’s forecast.
These methods can be further split into simple and seasonal Naïve methods.
Simple Naïve method — Where the forecast value is equated to the value of the previous period.
Let’s take the in-built R dataset “gas” (belongs to the library — ‘forecast’) for all the examples that we are going to discuss here
#arima #time-series-analysis #data-science #r #data analysis
