Note from Towards Data Science’s editors:_ While we allow independent authors to publish articles in accordance with our rules and guidelines, we do not endorse each author’s contribution. You should not rely on an author’s works without seeking professional advice. See our Reader Terms for details._
1. Introduction
1.1. Time-series & forecasting models
Traditionally most machine learning (ML) models use as input features some observations (samples / examples) but there is no time dimension in the data.
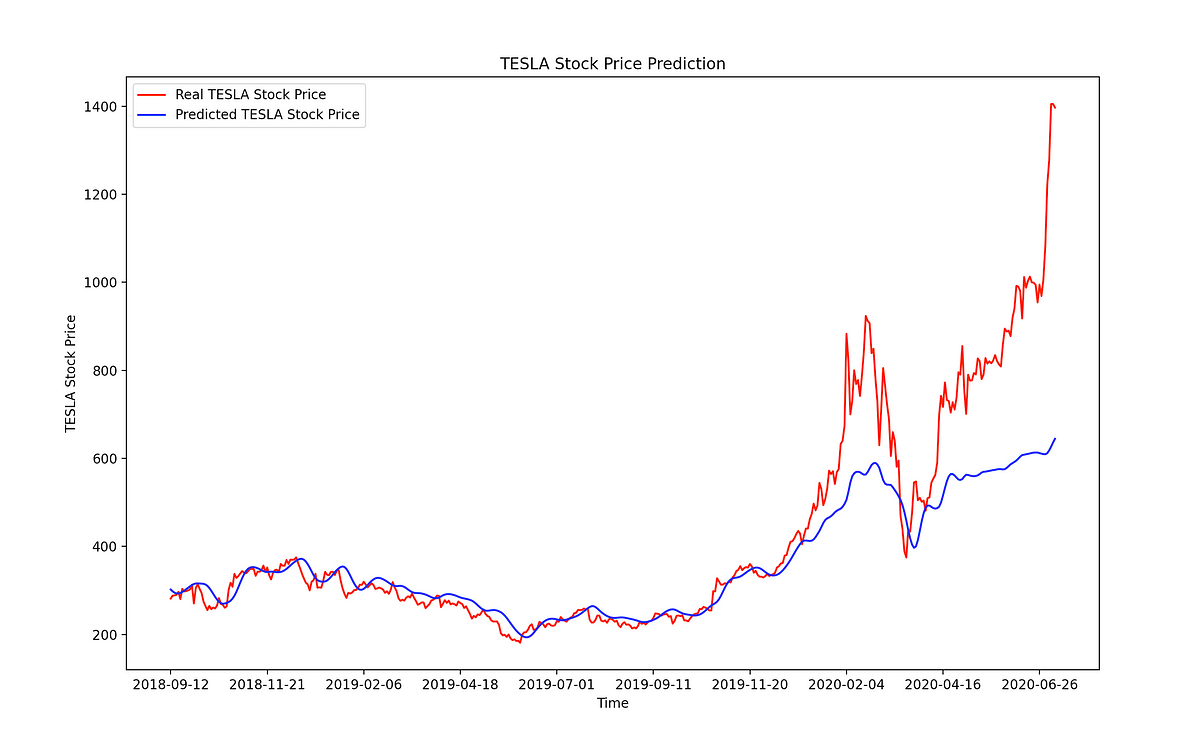
Time-series forecasting models are the models that are capable to predict future values based on previously observed values. Time-series forecasting is widely used for non-stationary data. **Non-stationary data **are called the data whose statistical properties e.g. the mean and standard deviation are not constant over time but instead, these metrics vary over time.
These non-stationary input data (used as input to these models) are usually called **time-series. **Some examples of time-series include the temperature values over time, stock price over time, price of a house over time etc. So, the input is a signal (time-series) that is defined by observations taken sequentially in time.
#machine-learning #data-science #forecasting #timeseries #stocks