The use of serverless computing has become a must nowadays, and some of you may already know a thing or two about Amazon Web Services like Lambda Functions, Step Functions, and other services AWS provides. However, if this is the first time you hear about them – fantastic!
In this article, we’ll discuss AWS Step Functions, what they are used for, how to use them, and the advantages or disadvantages that they bring.
AWS Step Functions 101
Before we can jump into Step Functions, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic structure behind them. Step Functions are an AWS-managed service that uses Finite-State Machine (FSM) model.
Why is that important?
By coordinating multiple AWS services into different serverless workflows, you can quickly build and update the apps. Additionally, with Step Functions, you’ll be able to both design and run workflows that’ll bring together various services, including Amazon ECS and AWS Lambda, into feature-rich applications.
FSM Model Explained
The two keywords you need to remember are States and Transitions.
Now, why are these words so important?
FSM model does a simple job – it uses given states and transitions to complete the tasks at hand. Finite-State Machines are also known as a behavioral model. It’s an abstract machine (system) that can be in 1 (one) state at a time, but it can also switch between a finite number of states.
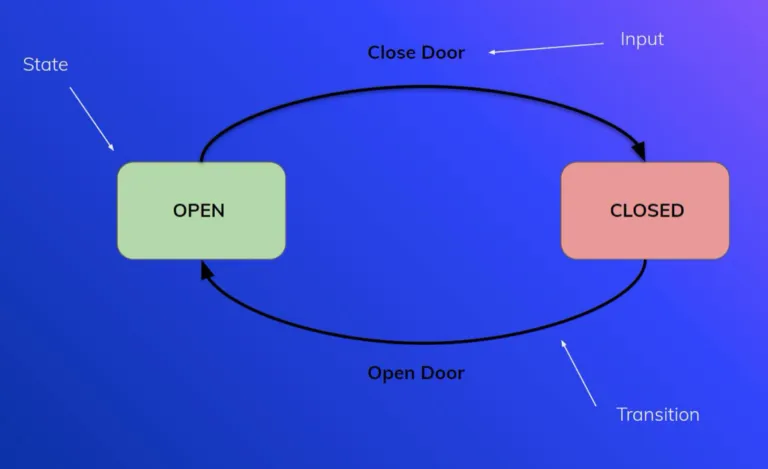
This machine is defined solely by its states and the relationship these states have between themselves. A good and very straightforward example is the “closed-door example.” The door can either be open or closed, and these are the only two possible states. Now, the transition part is the switch between two states, but you need to provide some input first to get there. When you close the door, you’re placing an input. Additionally, the sequence of opening the closed door is known as the switch between two states (transition).
Step Functions state input and transition
You can also apply the same thing to other examples, like your daily life routines. Let’s take “Work, home, bed” as states. From work (state), you take a bus (input) to get home (state), and when you arrive home, you go to bed (another input leading to another state). Tomorrow morning when you wake up and get out of your bed, you’re transitioning from the last state you were in into a previous one, and yet again, taking the bus from home to work is one more transition.
There are other, more complex examples with many more states, inputs, and transitions between them, and the more states you add, the more complex the FSM model becomes.
The conclusion is simple — FSMs are a method of modeling your system by defining the states and transitions between those states.
#devops #microservices #aws #cloud computing #serveless #step functions #fsm