What is SVM?
A Support Vector Machine is a powerful and versatile Machine Learning model, capable of performing linear or non-linear classification, regression, and even outlier detection. SVMs are well suited for the classification of complex or medium size datasets. SVM is a binary classifier, to classify more than 2 class we have to use the one-vs-all or one-vs-one approach
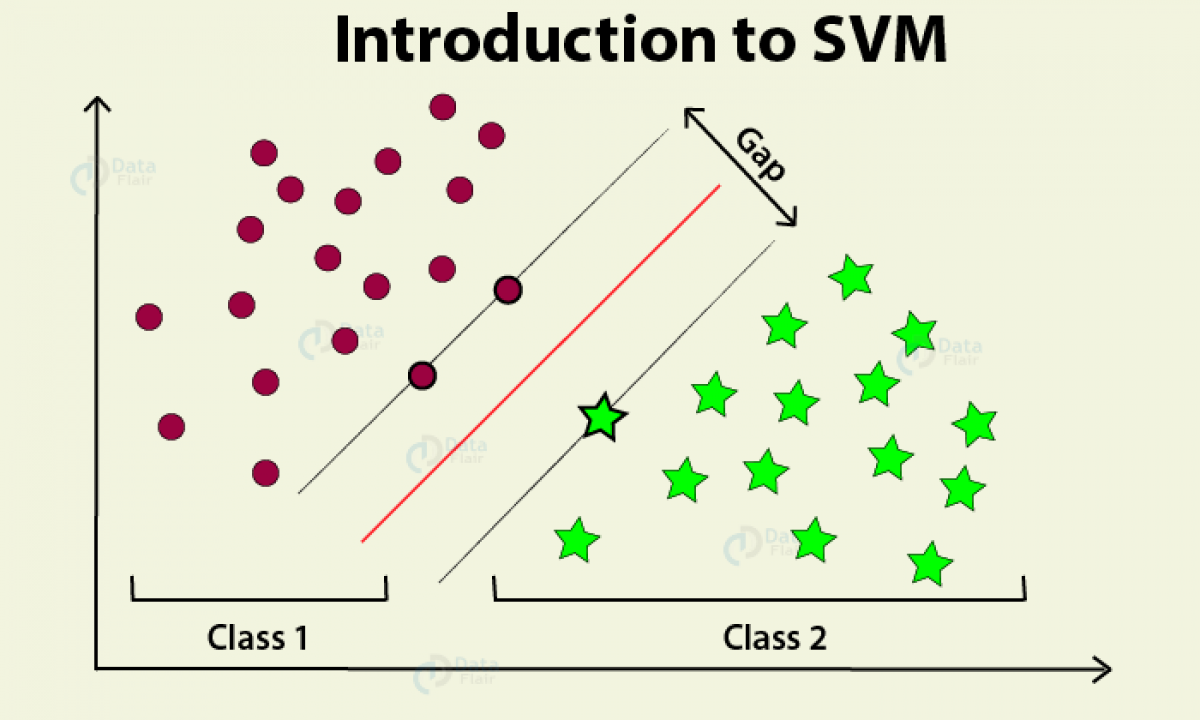
You can think of the SVM classifier as fitting the widest possible street between the classes. This is called large margin classification. Adding training instances off the street won’t affect the decision boundary at all.
In the above image we see some words, let us understand them one by one.
Starting with the Support vector, it plays a crucial role in determining the boundary and classification. These are the points which are nearest to other classes.
The distance between the two support vectors is called Maximised margin and their center is called the Optimal Hyperplane. In the above image, if our new point lies on the right side of the optimal hyperplane or even on the maximized margin on the right, it will be classified as green, and if it lies on the left side, even on the maximized margin on the left, it will be classified as blue.
There are 2 classification methods we can use in SVM:
- If we strictly impose that all instances must be off the street and on the right side, this is called hard margin classification.
- If some of the points are allowed on-street or within the opposite boundary of their class it is called soft margin classification
#support-vector-machine #machine-learning #svm #data-science