One of the central concepts in Bayesian statistics is that of a posterior distribution. Simply put, this distribution is a combination of past data (prior distribution) and the probability of observing a particular set of data in the future (the likelihood function).
Here is what a posterior distribution looks like:
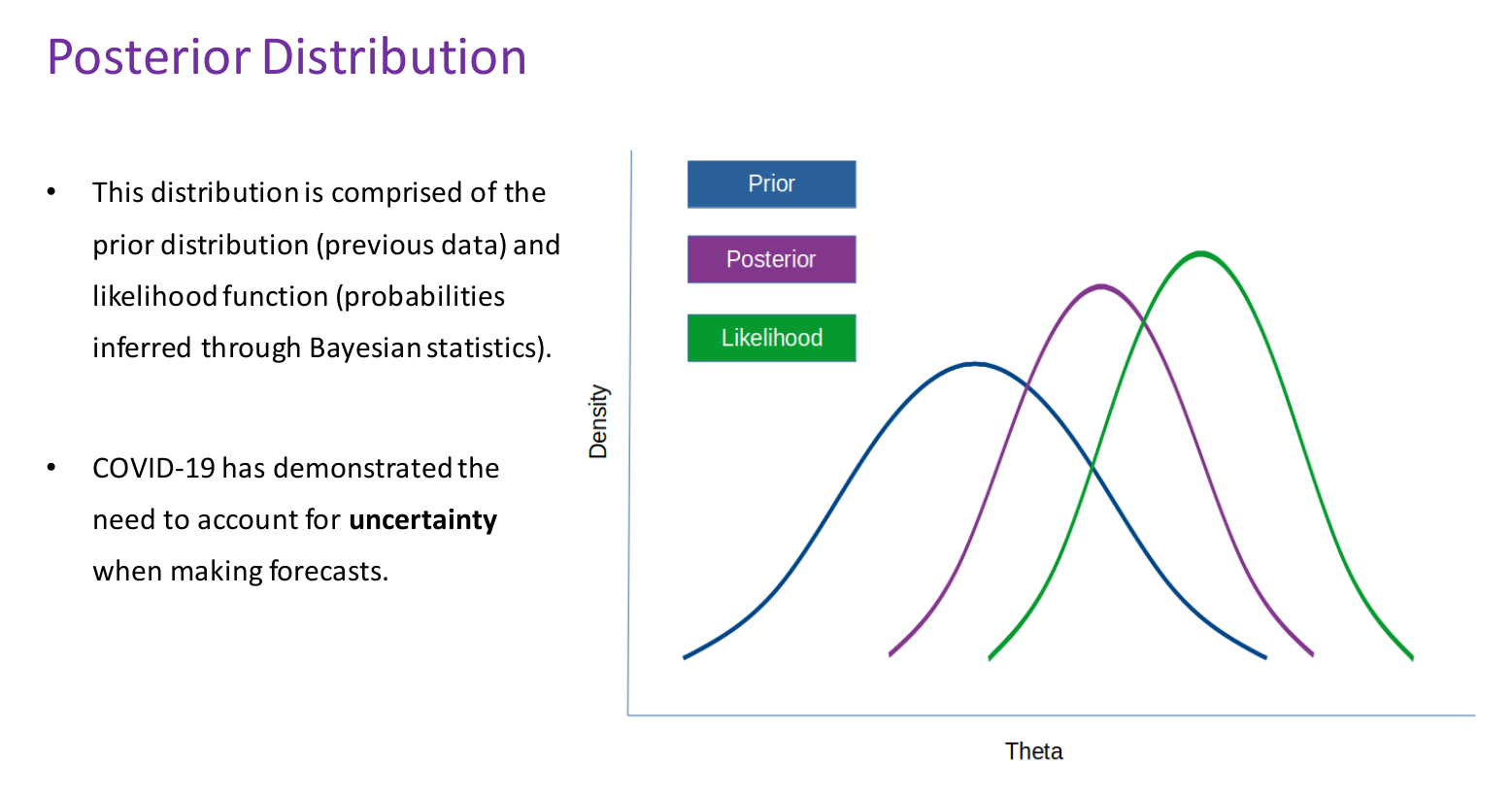
The traditional normal distribution (one where the mean = median = mode) relies completely on past data.
As a result, a sudden shift in the distribution of the data would mean that prior forecasts are no longer of relevance.
Let’s take an example.
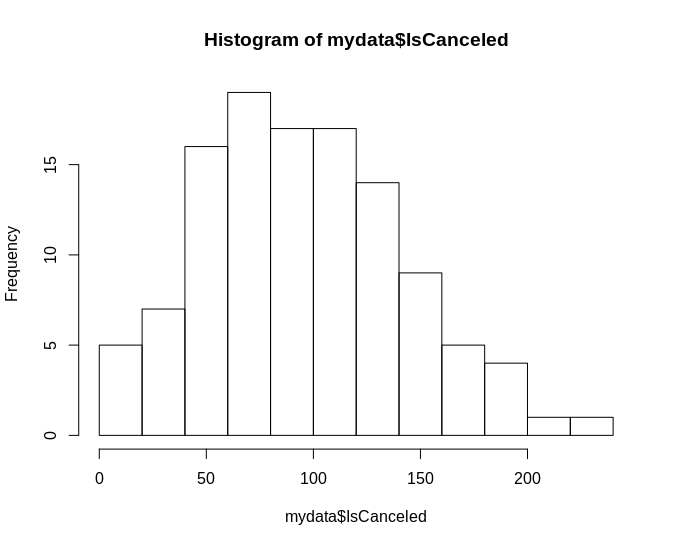
Here is a distribution of the **number of weekly cancellations **for a Portuguese hotel (pre-COVID). We can see that the number of cancellation incidences vary weekly, and roughly approximate a normal distribution.
However, the number of cancellations per week for this hotel would have been far higher due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and the distribution above would now be irrelevant in making any forecasts for the hotel.
#bayesian-machine-learning #bayesian-statistics #machine-learning #data-science #statistics #deep learning
