A well-known market phenomenon in the futures market is that the futures prices may deviate from the spot price of the underlying asset. As shown in an earlier article, the differential between futures and spot prices, called the basis, can be positive or negative, but are expected to converge to zero or near-zero at the expiration of the futures contract.
For each underlying asset, there are multiple futures with different maturities (ranging from 1 month to over a year). And for each futures contract, there is one basis process. Therefore, when we consider all different spot assets and their associated futures, there are a high number of basis processes.
Moreover, these stochastic processes are clearly dependent. First, the spot assets, such as silver and gold, can be (possibly highly) correlated. Second, the futures written on the same underlying asset are clearly driven by a common source of randomness, among other factors. For anyone trading futures (on the same underlying or different assets), it is crucial to understand the dependence among these processes.
Multidimensional Scaled Brownian Bridge
This motivates us to develop a novel model to capture the joint dynamics of stochastic basis from different underlyings and different futures contracts. Once this model is built, we apply it to dynamic futures trading, as studied in this paper.
The Multidimensional Scaled Brownian Bridge (MSBB) is a continuous-time stochastic model described by the following multidimensional stochastic differential equation (SDE):
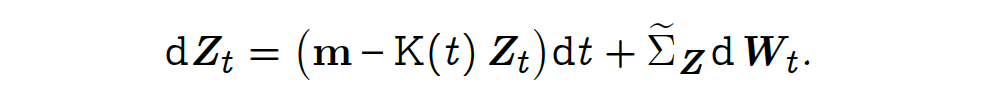
where
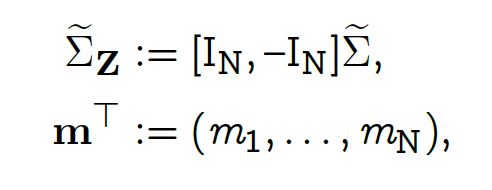
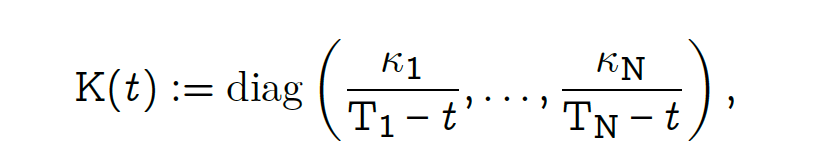
and W consists of Brownian motions.
#time-series-analysis #simulation #data-science #quantitative-finance #futures-trading #data science
