To work with GraphQL in flutter, we are going to use graphql_flutter package, which has over 1000 stars on GitHub and I frequently contribute to.
So, without further ado, let’s get started.
Our GraphQL Schema
To upload files, we are going to use a very simple schema. Our mutation will accept a file and then return a download URL for the file. We won’t look at the implementation at the server end.
scalar Upload
type Mutation {
upload(file: Upload!): String!
}
NB: If you are interested, you can find the GraphQL Server for this articles’ demo here.
Demo and Source Code
Here is how our app will work:
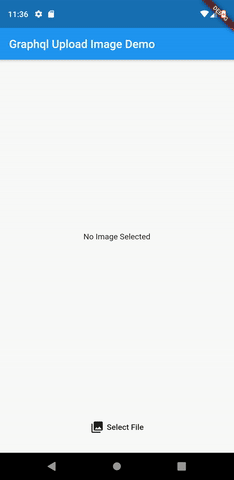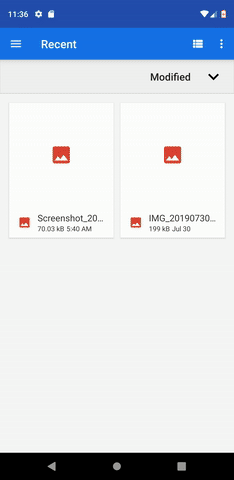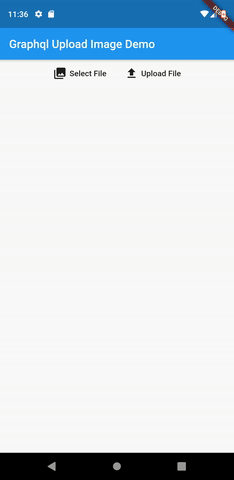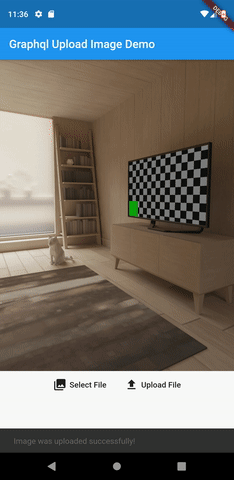
Flutter Upload Image Demo
You can find the accompanying repo for this article on here on GitHub.
Dependencies and Imports
For this articles’ demo, we are going to need the following dependencies for our flutter project – graphql_flutter and image_picker.
Let’s add them to our projects pubspec file.
graphql_flutter: ^2.0.0
image_picker: ^0.6.0
And we are going to import the following packages:
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:graphql_flutter/graphql_flutter.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart';
import 'package:http_parser/http_parser.dart';
import 'package:image_picker/image_picker.dart';
Feel free to add any extra dependencies and imports to make your UI look better.
About our Demo Application
For this article’ demo, we are going to use the image_picker package to pick an image. Then, the picked image can then be uploaded to our server. We are going to build a very simplistic UI for our demo application, where we will have a simple button to pick an image. And when an image is picked, it shall be displayed inside an Image widget, and an upload button revealed. The user can then click the upload button to upload the image.
First, let’s define our GraphQL Mutation – uploadImage – which will accept variable called $file of type Upload. The $file variable will be the image selected using the image_picker and will be passed to the upload mutation.
const uploadImage = r"""
mutation($file: Upload!) {
upload(file: $file)
}
""";
Then, inside our StatefulWidget, let’s add a selectImage method and a private File property called _image. When the select image method is called, it is going to call the ImagePicker.pickImage method, showing a file picker dialog, where a user picks an image. After a user selects an image, we are going to set the _image property to the resulting file (image).
Future selectImage() async {
var image = await ImagePicker.pickImage(source: ImageSource.gallery);
setState(() {
_image = image;
});
}
Next, let’s create our UI using:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
child: Column(
// mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
children: <Widget>[
if (_image != null)
Flexible(
flex: 9,
child: Image.file(_image),
)
else
Flexible(
flex: 9,
child: Center(
child: Text("No Image Selected"),
),
),
Flexible(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
children: <Widget>[
FlatButton(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
Icon(Icons.photo_library),
SizedBox(
width: 5,
),
Text("Select File"),
],
),
onPressed: () => selectImage(),
),
// Mutation Widget Here
],
),
)
],
),
);
}
Now, we are just missing is the GraphQL Upload Implementation. There are two approaches for this, and we will look at each below:
Using the Mutation Widget
graphql_flutter package provides some easy to use widgets that you can drop inside your flutter app. One of these widgets is the Mutation widget which you can use to run mutation. But before using the Mutation widget, we are going to need a GraphQLClient. The GraphQLClient needs to be provided somewhere up our widget tree, preferably at the very beginning.
You can achieve this by creating a GraphQLClient and then pass it down the widget tree using the GraphQLProvider widget. First, lets create a GraphQLClient wrapped with ValueNotifier:
final httpLink = HttpLink(
uri: 'http://$host:8080/query',
);
var client = ValueNotifier(
GraphQLClient(
cache: InMemoryCache(),
link: httpLink,
),
);
NB: The host points to localhost, which is different between IOS and Android emulator:
String get host => Platform.isAndroid ? '10.0.2.2' : 'localhost';
Next, we need to pass down the above client down the widget tree using the GraphQLProvider widget. In our case, we are going to wrap the Scaffold widget with it, you can also wrap the MaterialApp with if you so wish.
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: GraphQLProvider(
client: client,
child: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text("Graphql Upload Image Demo"),
),
body: MyHomePage(),
),
),
);
Now we are ready to use the Mutation widget. To use the Mutation widget, you just need to pass MutationOptions, a Widget Builder method and an onCompleted and/or update callbacks. The last two callbacks are called when a mutation is completed. With onCompleted callback passing the resulting data from the mutation results. While the update passing the QueryResults object which you can use to check for errors.
To use the Mutation widget, we are going to add it next to the select image button. We are going to also check whether the _image property is set before displaying the widget.
if (_image != null)
Mutation(
options: MutationOptions(
document: uploadImage,
),
builder: (RunMutation runMutation, QueryResult result) {
return FlatButton(
child: _isLoadingInProgress(),
onPressed: () {},
);
},
onCompleted: (d) {},
update: (cache, results) {},
),
The Mutation widget is going to return an upload button, which a user can press to upload the image. Let’s implement the onPressed method of the button so that it will upload the image when pressed. First, we are going to prepare the image for uploading by converting it into a MultipartFile. Then, we can pass the resulting MultipartFile variable as the variable for our Mutation, when calling the runMutation method passed from the builder.
var byteData = _image.readAsBytesSync();
var multipartFile = MultipartFile.fromBytes(
'photo',
byteData,
filename: '${DateTime.now().second}.jpg',
contentType: MediaType("image", "jpg"),
);
runMutation(<String, dynamic>{
"file": multipartFile,
});
Then we can use the update call-back to check if the upload has been completed successfully and show a response.
update: (cache, results) {
var message = results.hasErrors
? '${results.errors.join(", ")}'
: "Image was uploaded successfully!";
final snackBar = SnackBar(content: Text(message));
Scaffold.of(context).showSnackBar(snackBar);
},
And that’s it when a GraphQL operation completes successfully, a success message is going to be displayed, else the resulting error message will be displayed using a snackbar.
Without using the Mutation Widgets
There a lot of people who don’t like using the Mutation widget for various reasons. You can also do that with the graphql_flutter. We are going to replace the Mutation widget above, with a simple button, which will call a method – _uploadImage – when pressed. We are going to place the _uploadImage method inside our StatefulWidget.
if (_image != null)
FlatButton(
child: _isLoadingInProgress(),
onPressed: () => _uploadImage(context),
),
Then inside our _uploadImage method, we are going to first convert the image to a MultipartFile just like we did before.
var byteData = _image.readAsBytesSync();
var multipartFile = MultipartFile.fromBytes(
'photo',
byteData,
filename: '${DateTime.now().second}.jpg',
contentType: MediaType("image", "jpg"),
);
And then create MutationOptions variable for our mutation, passing the document and the multipart file above.
var opts = MutationOptions(
document: uploadImage,
variables: {
"file": multipartFile,
},
);
Then, create our GraphQLClient:
final httpLink = HttpLink(
uri: 'http://$host:8080/query',
);
var client = GraphQLClient(
cache: InMemoryCache(),
link: httpLink,
);
And finally, run the mutation by calling client.Mutation function which returns a Future of QueryResults, which you can use to show the final response:
var results = await client.mutate(opts);
var message = results.hasErrors
? '${results.errors.join(", ")}'
: "Image was uploaded successfully!";
final snackBar = SnackBar(content: Text(message));
Scaffold.of(context).showSnackBar(snackBar);
With this you can use it with scope models, BLoCs or any state management solution you comfortable with.
TIP
If you are not interested in using the flutter_graphql widgets, you can instead directly use the graphql package, which is the core of the flutter_graphql and are both maintained by the same team.
Originally published by Maina Wycliffe at codinglatte.com
#flutter #graphql