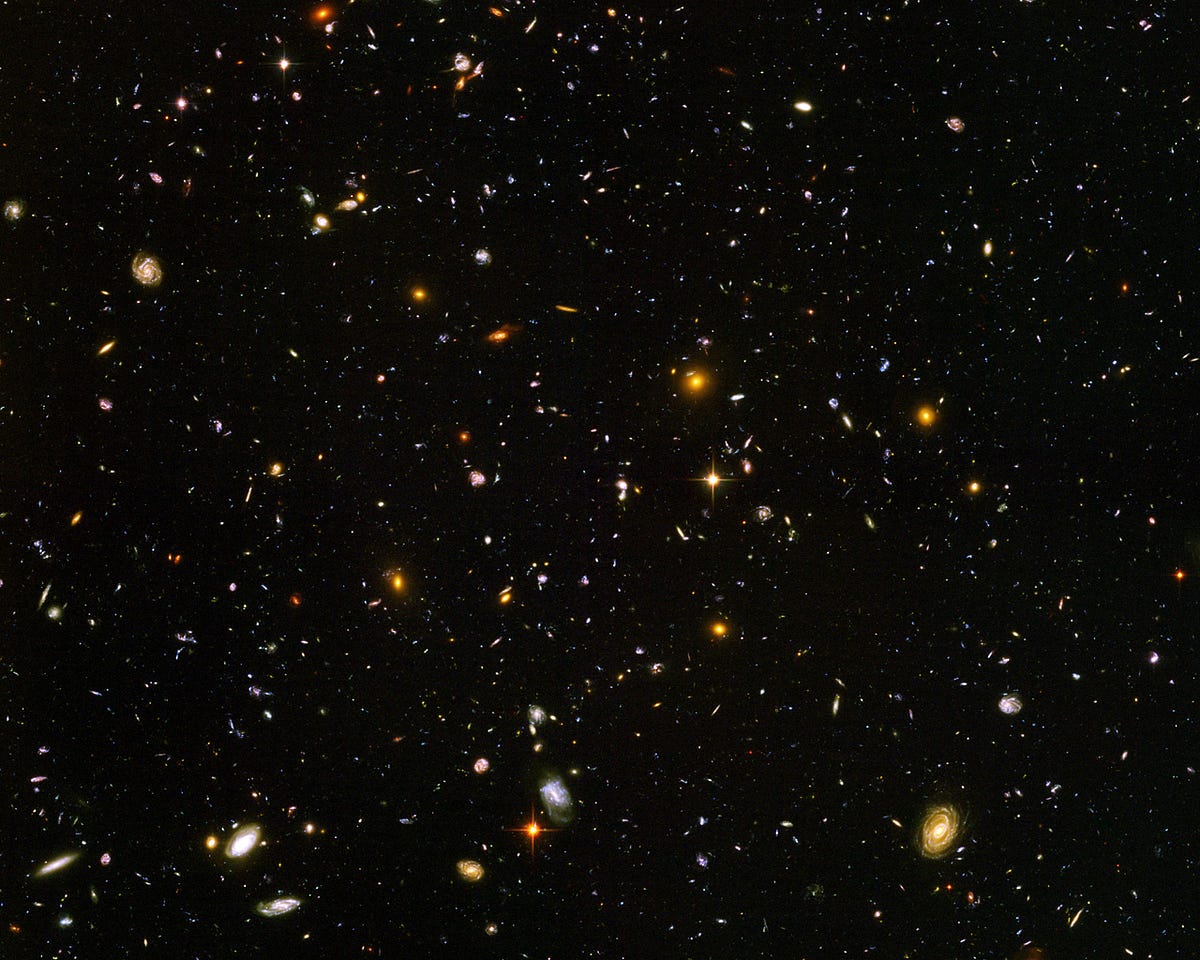
osmos is an intriguing space to observe and analyse, it is the stronghold for any science we discovered to this point. Galaxies are the mines with immense data clusters just lying there to be explored in this infinite space. the above picture is the result of a 1 Million-second-long exposure of Hubble space telescope revealing the earliest galaxies named as Hubble Ultra Deep Field. Each star-like object in the photograph is actually an entire galaxy.
The first galaxy was observed by a Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman over a 1,000 years ago, and it was first believed to be an unknown extended structure. which is now known as the Messier-31 or the infamous**Andromeda Galaxy**. From that point, these unknown structures are more frequently observed and recorded but it took over 9 centuries for the astronomers to manifest on an agreement that they were not simply any astronomical objects but are entire galaxies. As the discoveries of these galaxies increased astronomers observed the divergent morphologies. Then they started grouping the previously reported and the newly discovered galaxies according to the morphological characteristics which later formed a significant classification Scheme.
Modern Advancements
Astronomy in this contemporary age has massively evolved parallelly with computational advancement during the years. Sophisticated computational techniques like Machine Learning models are much more efficient now because of the substantially increased computers performance efficiency and the enormous data that we have now. Centuries ago, Classification tasks like these were done by hand with a massive group of people, evaluating the results by cross-validation and collective post-agreement.
Why I chose to work on this Data
I recently started working on theoretical Deep Learning concepts and wanted my first practical approach of Technically applying those concepts to a task, which is driven by passion, yet is still prominent and relatable to my core attempt of learning Neural Networks.
Data Collection
The Galaxy Zoo project hosted diverse Sky-survey data Catalogues online for astronomers around the world who are allowed to access, study and analyse the data. For this Classification task, I grabbed the data with the features very well defining the classes. For feature description [METADATA].
The Classification Schema
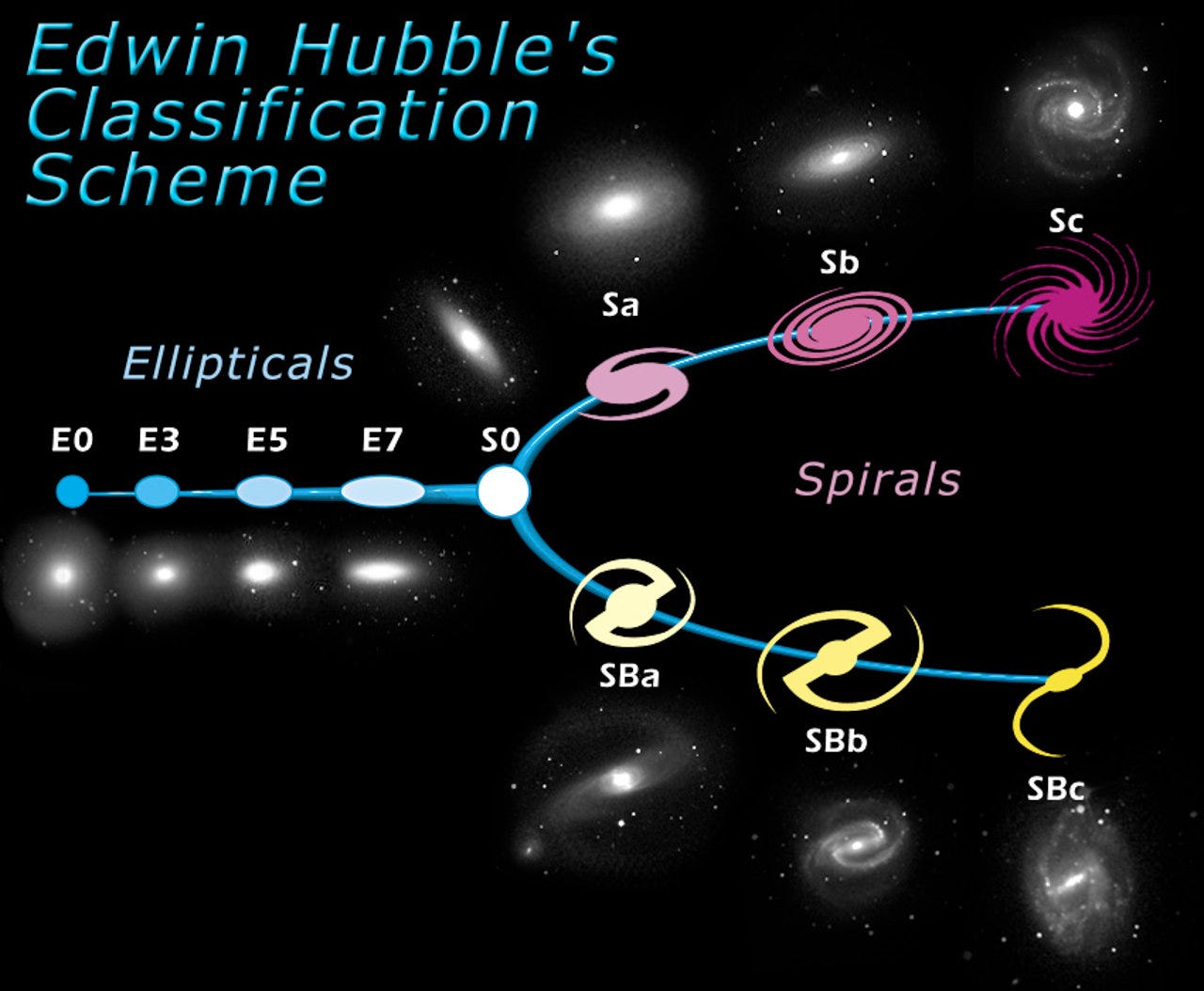
The Hubble’s Tuning fork is the most famous Classification Scheme, Edwin Hubble divided Galaxies into three main types to be simplified they are Elliptical, Spiral and Merger classes.
Elliptical galaxies have a smooth, spheroidal appearance with little internal structure. They are dominated by a spheroidal bulge and have no prominent thin disk. Spiral galaxies all show spiral arms. And the third class, Merger galaxies are Irregular looking often described as chaotic appearances, are most likely the remnants of a collision between two Galaxies as described in The Realm of Nebulae.
#astronomy #machine-learning #data-science #neural-networks
