1. Why is it called WiFi6?
I don’t seem to have heard of WiFi 5. Why did WiFi 6 pop up suddenly? In fact, WiFi6 is just a simplified name, the real scientific name is IEEE 802.11ax. It has five predecessors: IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac, but none of them have another name, so few people remember them.
The WiFi6 standard was released on September 16, 2019. It is indeed a very new standard. Its characteristics can be summarized as follows:
Faster
With a channel width of 160MHz, WiFi 6 has the fastest single-stream rate of 1201 Mbit/s and the theoretical maximum data throughput of 9.6Gbps. Compare with the previous five generations:
The first generation 802.11b (Wi-Fi 1), the fastest 11Mbit/s
The second generation 802.11a (Wi-Fi 2), the fastest 54Mbit/s
The third generation 802.11g (Wi-Fi 3), the fastest 54Mbit/s
The fourth generation 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4), the fastest single stream bandwidth is 150Mbit/s
The fifth generation 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5), the fastest single stream bandwidth is 867Mbit/s
Compared to WiFi 5 (802.11ac), it is increased to 1.4 times; compared to WiFi 4 (802.11n), it is increased to 8 times.
Low latency, no lag
Users who bought routers in 2019 have heard of MU-MIMO (Multi-User-Multiple Input Multiple Output). The advantage of supporting MU-MIMO is that multiple devices communicate at the same time.
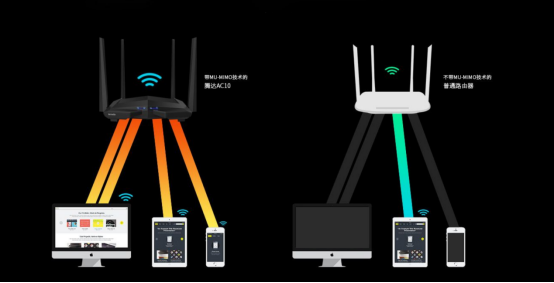
If you compare the router to a train station, sending data each time is like the originating train. Under the old SU-MIMO (single user-multiple input multiple output), each train can only reach the same place (device), and Under MU-MIMO, goods in different carriages can reach different locations, so the transmission efficiency is greatly improved. WiFi 6 can connect 4 sets of 2x2 or 8 sets of 1x1MU-MIMO at the same time, and does not limit the uplink and downlink, basically reducing the delay to the level of 5G-SA-imperceptible. In a multi-user Internet environment, the average transmission rate per user is greatly improved, the average network delay is reduced by 75%, and the network efficiency is significantly improved. Especially in multiplayer mobile game scenarios, the reduction in network latency has significantly improved the gaming experience.
More power saving
The power saving here is for the terminal connected to the WiFi 6 router. WiFi 6 (802.11ax) supports TWT technology. The router can uniformly schedule the sleep and data transmission time of wireless terminals. It can not only wake up and coordinate the timing of wireless terminals to send and receive data, reduce the situation of disorderly competition among multiple devices, but also connect wireless Terminals are grouped into different TWT cycles to increase sleep time and improve device battery life.
02
2. WiFi-6 and 5G, who is faster?
As mentioned earlier, the current theoretical speed of WiFi 6 can reach 9.6Gb/s, which is about the same as the speed of 5G, 10Gb/s. However, if WiFi 6 wants to achieve this rate, 8 antennas are needed in parallel, and our current smart phones generally only have 2 antennas (integrated in the phone), so the peak rate of WiFi 6 can only reach 2.4Gb/s. So in terms of speed alone, 5G has more advantages.

From the point of view of signal strength, 5G uses UHF spectrum from 24Ghz to 52Ghz. The higher the frequency, the weaker the wall penetration capability. Therefore, indoors, WiFi 6 is more reliable. Finally, we must consider tariffs. WiFi 6 uses broadband charges, and 5G uses traffic charges. The two are not at the same level. Therefore, 5G main external WiFi 6 main internal is definitely the future trend.
#wifi-6 #wifi
