JavaScript prototype is one of the most important concepts that every JavaScript developer must understand. This tutorial explains the prototype concept in detail and clears all confusion that you may have regarding the prototype.
To follow this tutorial, you must understand JavaScript objects. If you aren’t familiar with objects in JavaScript, you should follow the JavaScript objects tutorial before going forward with this tutorial.
Introduction to JavaScript prototype
By default, the JavaScript engine provides the Object() function and an anonymous object that can be referenced via the Object.prototype.
console.log(Object);
console.log(Object.prototype);

The Object.prototype object has many built-in methods and properties such as toString(), valueOf(), etc.
And it has a property named constructor that references the Object() function:
console.log(Object.prototype.constructor === Object); // true
Assuming that the circle represents a function and the square represents an object.
The following figure illustrates the relationships between the Object() function and the Object.prototype object:

First, define a function named Foo as follows:
function Foo(name) {
this.name = name;
}
In this code, the Foo() function accepts an argument, adds the name property to the object, and sets the value of the name property to the name argument.
Behind the scenes, the JavaScript engine creates a new function Foo() and an anonymous object.
The Foo() function has a property named prototype that references the anonymous object. And the anonymous object has the constructor property which references the Foo() function.
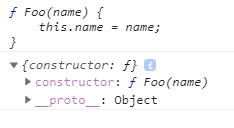
The following shows the function Foo() and the anonymous object:
console.log(Foo);
console.log(Foo.prototype);
In addition, the Foo.prototype object is linked to the Object.prototype object via [[Prototype]], which is known as a prototype linkage.
The prototype linkage is denoted by [[Prototype]] in the following figure:

Second, add a new method named whoAmI() to the Foo.prototype object:
Foo.prototype.whoAmI = function() {
return "I am " + this.name;
}

Third, create a new instance of the Foo object:
let a = new Foo('a');
Internally, the JavaScript engine creates a new object named a and links the a object to the Foo.prototype object via the prototype linkage.

The link of a, Foo.prototype, and Object.protoype is called the prototype chain.
#javascript #programming #developer #web-development
