Marketing authorization of a drug is granted on the basis that, in the proposed indication(s) and at the time of authorization, its therapeutic effect outweigh the safety risk(s) for the target population (a.k.a “positive benefit-risk balance”). All drugs differ from each other in terms of their safety risk profile, even within the same therapeutic class, but no drug is without safety risk.
What’s a safety risk?…It’s any untoward occurrence associated with the use of a drug. Safety risks are named “identified” when there is adequate evidence of a causal relationship with the concerned drug, or “potential”, when there is some basis for suspicion of an association with the drug, but this has not been confirmed. An adverse drug reaction (ADR), contraindication or even the incorrect use of the drug might be considered as safety risks. When safety risks are important, these could have an impact in the benefit-risk balance of the drug and/or have implications for public health.
Every year, more drugs are launched and their utilization raise consequently. Moreover, polypharmacy (i.e., concurrent use of 5 or more drugs) increases ADR occurrence risk due to a multitude of factors, including drug-drug and drug-disease interactions. ADRs are an important cause of morbidity and mortality, even though many ADRs are potentially avoidable if drugs are used by the right patient at the right dose [1]. This reflects the importance to ensure the drug safety vigilance throughout the entire life cycle.
Photo by Laurynas Mereckas on Unsplash
Polypharmacy is common in the older population and the risk of ADRs and injury increases with increasing numbers of drugs
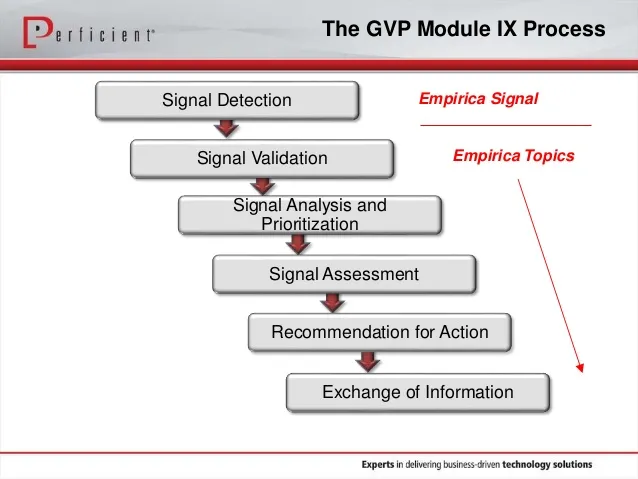
Pharmacovigilance (PV) is a multidisciplinary science aimed to the collection, assessment, monitoring and prevention of ADRs and other safety-related data, e.g., off-label use, pregnancy exposure, overdose. As a science, the knowledge on drug safety is built through the analysis of data received from various type of reporters (e.g., patients, health professionals) and by means of active (e.g., studies) and passive (e.g., spontaneous notification) surveillance strategies. All of us are part of a global PV network and contribute to the safe use of drugs when reporting suspected ADRs to the national health authority, drug manufacturer or PV/Poison center, given that underreporting of ADRs may result in the late identification of new safety risks.
#data-mining #pharmacovigilance #signal #data-science