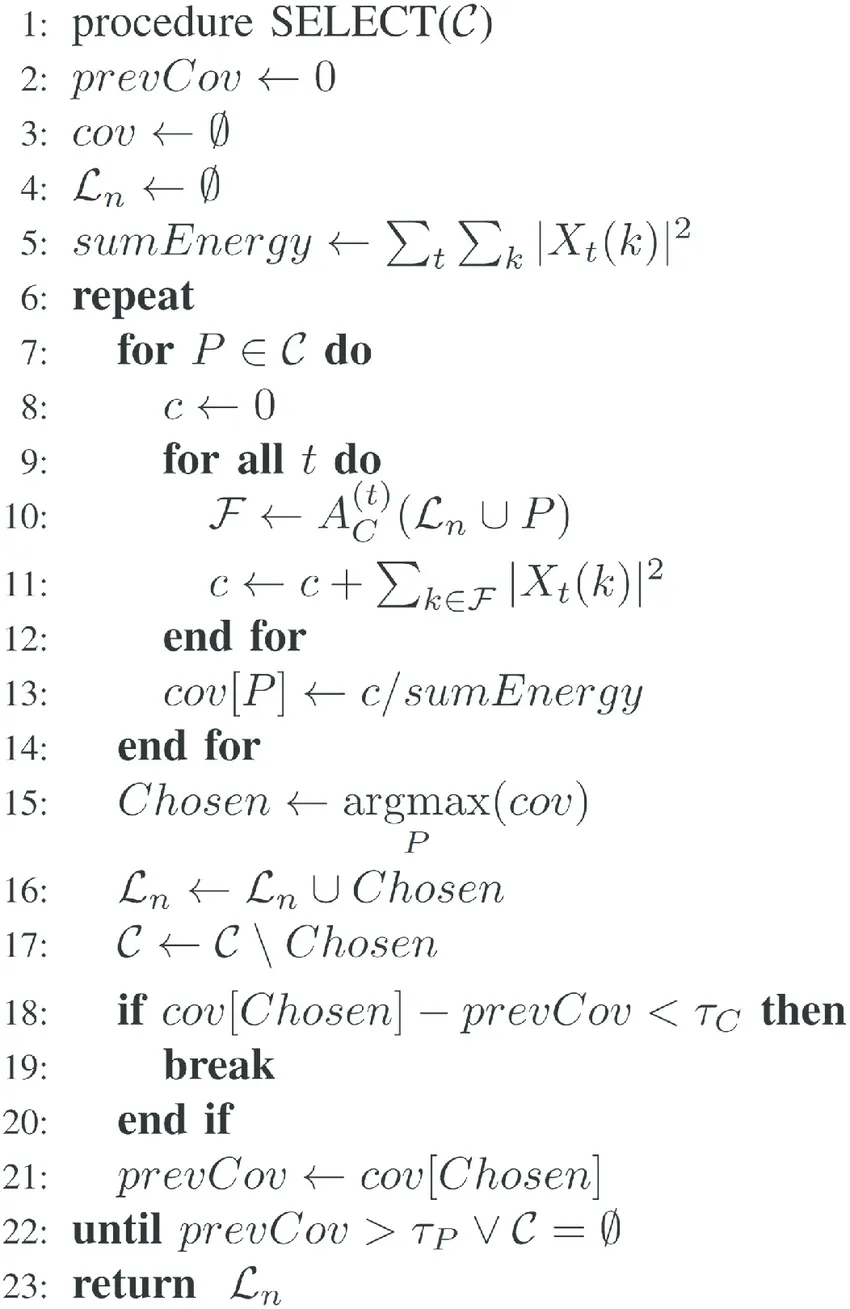Given three integers N, M and K and an array a[] consisting of N integers, where M and K denotes the total number of possible moves and the number of possible moves(shift by an index) on the left of the current element in an array respectively, the task is to maximize the sum possible by traversing the array utilizing all the available moves.
Examples:
_Input: _N = 5, M = 4, K = 0, a[] = {1, 5, 4, 3, 2}
Output:_ 15_
Explanation:
Since no moves towards left is possible, therefore, the only possible path is a[0] -> a[1] -> a[2] -> a[3] -> a[4].
Therefore, the sum calculated is 15.
_Input: _N = 5, M = 4, K = 1, a[]= {1, 5, 4, 3, 2}
Output:_ 19_
Explanation:
The maximum sum can be obtained in the path a[0] -> a[1] -> a[2] -> a[1] -> a[2]
Therefore, the maximum possible sum = 19
**Approach: **The above problem can be solved using Dynamic Programming. Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize a dp[][] matrix such that dp[i][j] stores the maximum sum possible up to ith index by using j left moves.
- It can be observed that left move is possible only if** i ≥ 1** and** k > 0** and a right move is possible if i < n – 1.
- Check the conditions and update the maximum of the sums possible from the above two moves and store in dp[i][j].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
- Java
filter_none
edit
play_arrow
brightness_4
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
**import** java.io.*;
**import** java.util.*;
**public** **class** GFG {
// Function to find the maximum sum possible
// by given moves from the array
**public** **static** **int** maxValue(``**int** a[], **int** n, **int** pos,
**int** moves, **int** left,
**int** dp[][])
{
// Checking for boundary
**if** (moves == 0 || (pos > n - 1 || pos < 0``))
**return** 0``;
// If previously computed subproblem occurs
**if** (dp[pos][left] != -``1``)
**return** dp[pos][left];
**int** value = 0``;
// If element can be moved left
**if** (left > 0 && pos >= 1``)
// Calculate maximum possible sum
// by moving left from current index
value = Math.max(
value, a[pos] + maxValue(a, n, pos - 1``,
moves - 1``, left - 1``, dp));
// If element can be moved right
**if** (pos <= n - 1``)
// Calculate maximum possible sum
// by moving right from current index
// and update the maximum sum
value = Math.max(
value, a[pos]
+ maxValue(a, n, pos + 1``,
moves - 1``, left, dp));
// Store the maximum sum
**return** dp[pos][left] = value;
}
// Driver Code
**public** **static** **void** main(String args[])
{
**int** n = 5``;
**int** a[] = { 1``, 5``, 4``, 3``, 2 };
**int** k = 1``;
**int** m = 4``;
**int** dp[][] = **new** **int**``[n + 1``][k + 1``];
**for** (``**int** i[] : dp)
Arrays.fill(i, -``1``);
System.out.println(
(a[``0``] + maxValue(a, n, 1``, m, k, dp)));
}
}
Output:
19
_Time Complexity: _O(N * K)
_Auxiliary Space: _O(N * K)
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready.
#arrays #dynamic programming #mathematical #recursion #array-traversal-question