There are all sorts of “backups” that help get you out of various situations. Think of the spare tire in your trunk or the extra pieces of webbing in a climbing anchor. If you’ve ever been rock climbing, you know that it’s essential to build redundancies into your anchors. That way, if one part fails, you’ve got another part as a backup.
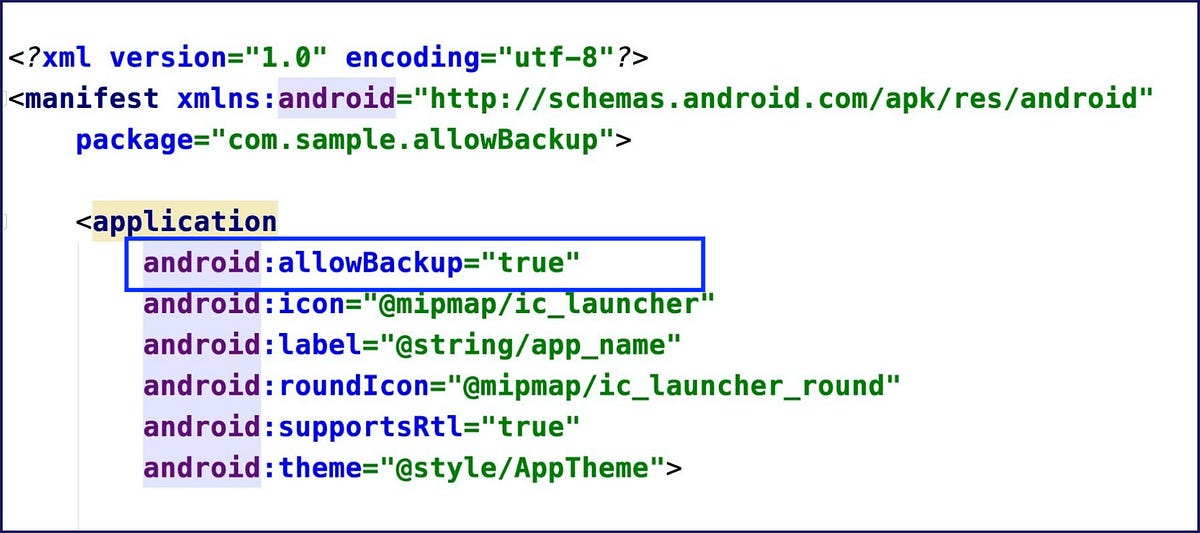
Likewise, Android provides you with an impressive setting by the name of allowBackup which helps us automatically backing up application data.
What Does Android allowBackup Do?
As the documentation says, “Auto Backup for Apps automatically backs up a user’s data from apps that target and run on Android 6.0 (API level 23) or later.”
We can leverage auto backup in our Android app so that our users can more quickly recover their data if they ever switch phones or reinstall our app after having uninstalled it.
If the user deletes the app in any way, including via a factory reset of their device, the data for the app will still be available when the user re-downloads the app and the .apk is installed. Auto Backup also works across devices, meaning that when your user gets a new phone, they won’t lose key information from your app.
Where Is the Backup Data Stored?
Android preserves app data by uploading it to the user’s Google Drive (by default) where it’s protected by the user’s Google Account credentials.
Data is stored in a private folder in the user’s Google Drive account. The saved data does not count towards the user’s personal Google Drive quota. Only the most recent backup is stored. When a backup is made, the previous backup (if one exists) is deleted. The backup data can’t be read by the user or other apps on the device.
Users can see a list of apps that have been backed up in the Google Drive Android app. On an Android-powered device, users can find this list in the Drive app’s navigation drawer under Settings > Backup and reset > App data.
#mobile-development #android #programming #mobile #androiddev