What is Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
In a network, computers use the IP Address to communicate with other devices, however, in reality, the communication happens over the MAC Address. ARP is used to find out the MAC Address of a particular device whose IP address is known. For instance, a device wants to communicate with the other device on the network, then the sending device uses ARP to find the MAC Address of the device that it wants to communicate with. ARP involves two steps to find the MAC address:
- The sending device sends an ARP Request containing the IP Address of the device it wants to communicate with. This request is broadcasted meaning every device in the network will receive this but only the device with the intended IP address will respond.
- After receiving the broadcast message, the device with the IP address equal to the IP address in the message will send an ARP Response containing its MAC Adress to the sender.
If it is still not clear what ARP is and how it works then refer to the images below.
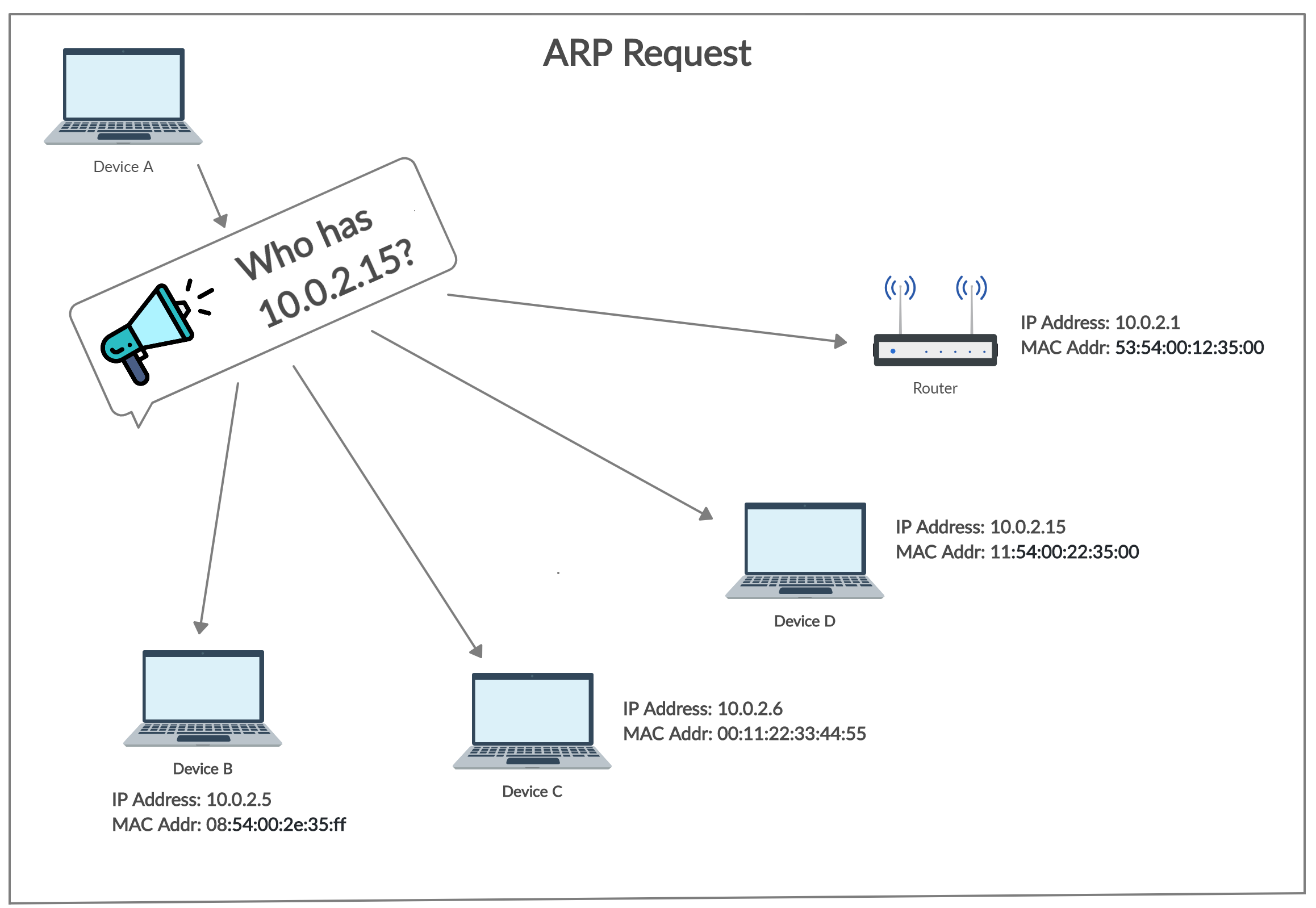
Fig 1. ARP Request
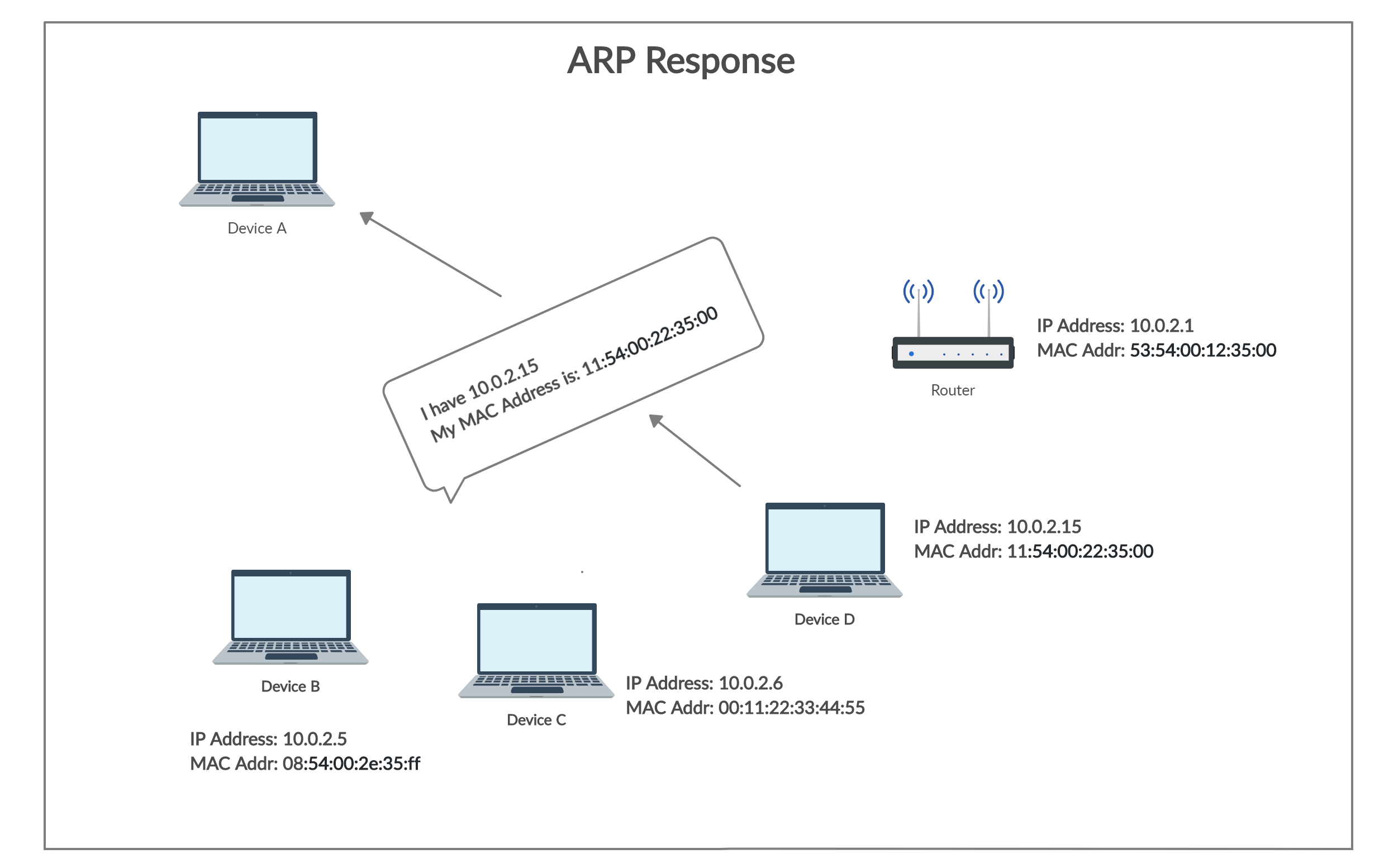
Fig 2. ARP Response
What is ARP Spoofing?
ARP spoofing is a Man In The Middle (MITM) attack in which the attacker (hacker) sends forged ARP Messages. This allows the attacker to pretend as a legitimate user as it links the attacker machine’s MAC Address to the legitimate IP Address. Once the MAC Address has been linked the attacker will now receive the messages intended for the legitimate IP Address. Furthermore, ARP Spoofing allows the attacker can intercept, modify, and drop the incoming messages.
ARP Spoofing is only possible on 32-bit IP Addresses (IPv4) and not on IPv6.However, it is widely used because most of the internet still works on IPv4.
Let’s understand ARP Spoofing more clearly with the help of diagrams 😃.
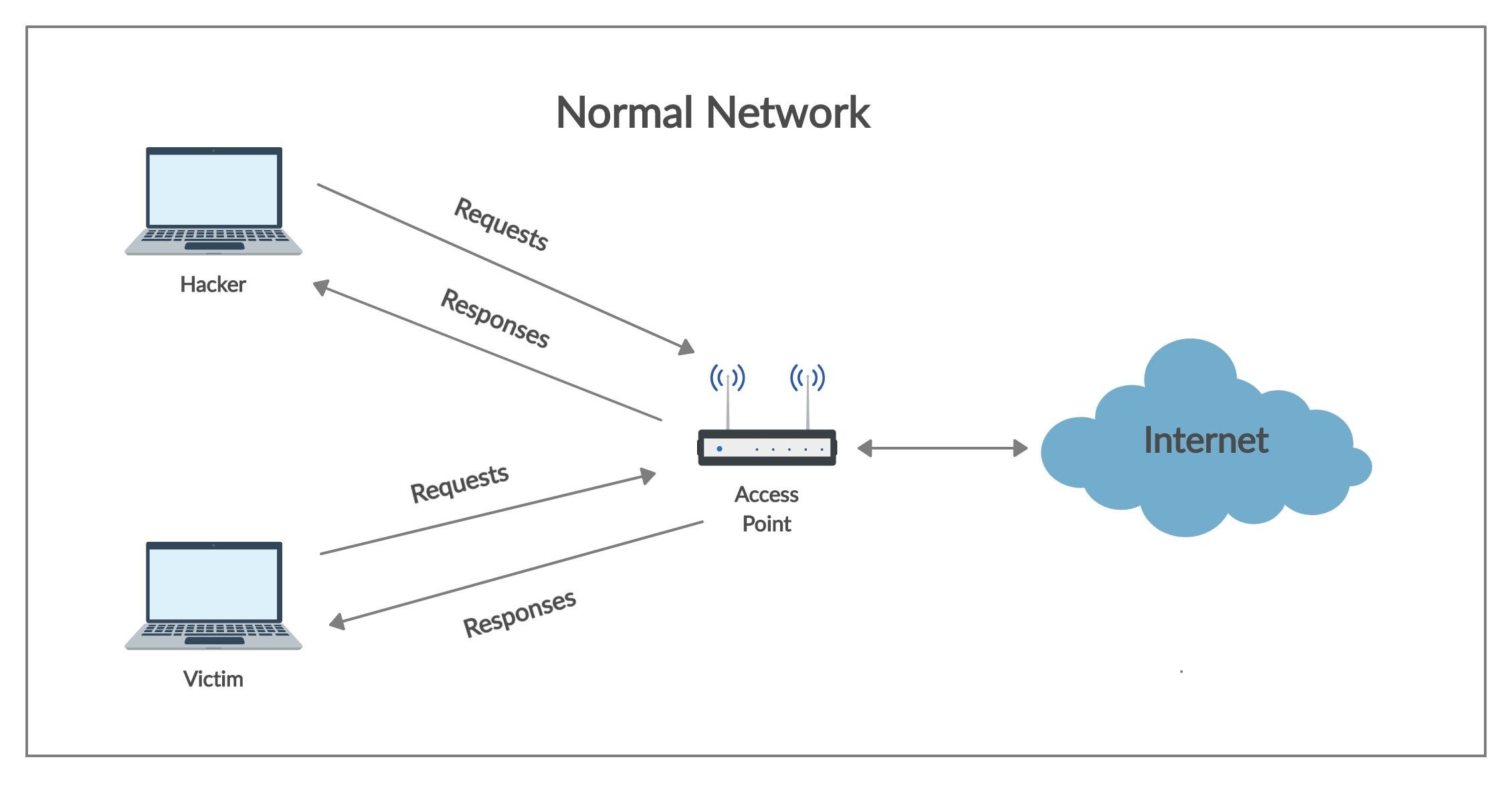
Fig 3. Normal Network
Fig 3. demonstrates the working of a normal network (no malicious activity) and how a device (hacker or victim) access the Internet with the help of an access point. All the messages pass through the access point. For instance, a device (hacker or victim) sends requests to access the resources on the Internet and in turn, receives responses. These **requests **and **responses **always pass through the access point and therefore the access point is called the Gateway to the Internet.
Note: In this article, the words **“Gateway”_, _“Access Point”, “Router”_ and _“Default Gateway” _are used interchangeably. Also the words _“attacker”_ and _“hacker” _are used similarly. The words _“target”_ and _“victim”**_ means the same._

#python #arp-spoofing #cybersecurity #man-in-the-middle-attack #security
