How To Develop Mobile App using React Native
How To Develop Mobile App using React Native
How I Developed React Native Tutor (One stop destination to learn React Native)
Youtube Video link : React Native Tutor Web link : React Native Tutor Web App
Recommended Way to View React Native Tutor
If you have a Non-Tech Background or are unfamiliar with Node.js, interested in learning and knowing more about developing mobile apps using ReactNative, then I would highly suggest you first check out ReactNative Tutor Web App by clicking on the link below.
Web link : React Native Tutor Web App
If you are familiar with Node.js and want to contribute to this repository, or is interested in developing the first two screens of the ReactNative Tutor mobile app in a step by step manner, then please go on reading.
Introduction
We are living in the 21st-century. A place where people are so obsessed with technology that most of them cannot live without their smartphones. We live in a world of a variety of mobile devices majorly dominated by two platforms - iOS and Android. I am sure we all can agree on that. Building a mobile app is not an easy task though
For iOS, we have to write code in Objective-C and Swift, while for Android, We have to code in java and Kotlin. Apart from using these different programming languages, the dev tools required to develop applications that can run on any of these platforms differs too. It’s like two entirely different tech stack used by people to create applications for eighter of the mobile platforms.
Modern-day developers, on the other hand, use a specific set of technology (HTML, CSS, and JavaScript) that is not only used to build web apps but also native mobile apps. These frameworks fall under an entirely separate category, also known as Cross-Platform Hybrid Frameworks. These are the sets of classes and libraries used by developers to create dynamic apps for different mobile devices. One such framework that we will be going to discuss in this tutorial is ReactNative. It is a cross-platform development framework that allows developers to create native apps for Android and iOS.
Aim of the Tutorial
The tutorial aims to help JavaScript developers to build mobile apps (iOS and Android) using React Native. This tutorial is also for people who are aspiring developers and want to learn and develop mobile applications in less than a week. We will briefly discuss the following things in this tutorial:
- What is React Native? What are its pros and cons?
- Step by step tutorial to develop a React Native mobile app
- How to boost productivity as a ReactNative Developer?
- A closer look into ReactNative Tutor
About React Native
ReactNative is a cross-platform development framework allowing you to create native apps for Android and iOS. Unlike some other frameworks likes PhoneGap and Cordova, It does not have any web views. Instead, React Native uses native components that are provided by platforms like iOS and Android, giving developers a full-fledged native development experience while ensuring the safety of the users’ experience.
Why should you choose ReactNative for your Next Mobile Project?
-
In a nutshell, one should use ReactNative for developing mobile apps for the love of JavaScript. Yes, you read it right! If you know JavaScript, you can use your existing JavaScript skills to build Native Mobile Apps using ReactNative. You don’t need to hire two separate teams of developers to handle the two different mobile app code bases. Write apps using JavaScript, and share your product across Android and iOS. It is the sole reason why ReactNative exist in the first place (According to me).
-
It provides a feature called Hot Reloading that increases the developer’s productivity and also enhances the developer’s experience. It allows developers to see the reflected change made in the code of the application instantaneously. Any change made in the large codebase will show in the app in less than 1 second. It is one feature that even the native mobile app development framework does not provide.
-
One can use ReactNative in an existing Android or iOS app or can develop the new application from scratch with ease.
-
React Native follows the “Learn Once, Write Everywhere” philosophy. It allows developers to use the components that best follow the native concept of each platform. ReactJs is used to develop web apps, whereas ReactNative can be used to build mobile apps.
Developing React Native Tutor
In a simple language, ReactNative allows us to build mobile applications that look, feel, and perform much more like native apps. It uses the same fundamental UI building blocks as used by regular iOS and Android apps. We just put those building blocks together using JavaScript and React. The best thing is that we use similar concepts that we use while developing web applications.
The below tutorial has four parts, where, by the end of each, you will learn a new React Native concept. They are as follows-
- Setting up the Development Environment and Starting the new ReactNative App
- Building Blocks of ReactNative
- Implementing Third-party Libraries in ReactNative App
- Navigation in ReactNative App (Stack Navigator)
Pre-requisites:
To follow this tutorial, please make sure you are familiarized with JavaScript/ES6 and meet the following requirements in your local dev environment.
- [x] NodeJs
- [x] Have access to one package manager such as npm or yarn
- [x] Expo-cli version installed or use npm
- [x] Visual Studio Code Editor
However, steps to set up the dev environment exist below.
Setting Up the Development Environment
To dive deeply into the React Natives ecosystem, we need to install a few things first to get started. Let us go through each of them one by one.
Node JS
ReactNative uses NodeJs, a JavaScript runtime, to build our Javascript code. If you don’t have Nodejs installed already, you can get it from its official website. Link: https://nodejs.org/
Node Package Manager
npm is the default package manager for the JavaScript runtime environment Node.js. It consists of a command-line client, also called npm, with which developers can download all npm software packages that contain in the npm software registry. When we download Node.js, we automatically get npm installed on our computer. I have added a tutorial to create the first node.js app using npm in the React Native Tutor Web App
CLI
There are two ways to develop our mobile app in ReactNative. We can do it with the help of either the Expo CLI or ReactNative CLI.
What is Expo CLI and ReactNative CLI?
The primary use of both the CLI is to scaffold a starter project containing everything we need to build and run a ReactNative App. We will install one of the CLI with the help of the Node Package Manager. The Package Manager will install this CLI tool as a global module.
-
The first way to develop a starter ReactNative App is with the help of Expo CLI. Expo is a set of tools built around React Native. If you are new to mobile development, I would highly recommend you to use it as it can get you started within minutes.
-
The second is through ReactNative CLI. It is best to install ReactNative CLI when we want to use native code in our app. It does not require the expo library. However, it makes things a little complex for code Newbies.
For simplicity, I will use Expo CLI here, as it is easy and as simple as writing the hello world program. One can download expo-cli using npm.
npm install -g expo-cli
Start ReactNative Tutor Project
To create a new app, we will use the expo init command that will set up a new ReactNative app called ReactNativeTutor. Create a directory where you would want to create your project, go into the directory, open the terminal, and type the below commands-
expo init ReactNativeTutor
Select the blank template, as clean as an empty canvas template as shown in the image below-
cd ReactNativeTutor
Open the folder in VS code editor.
Small Tiny Steps: One At a Time
Let’s look at the file structure and understand each file and folder one by one.
App.js
The first file in any react native app that is the entry point of the app development process. Whatever you write inside this file, it will get displayed on mobile devices.
import { StatusBar } from 'expo-status-bar';
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>Open up App.js to start working on your app!</Text>
<StatusBar style="auto" />
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
},
});
package.json
It is where every dependency installed gets listed.
{
"main": "node_modules/expo/AppEntry.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "expo start",
"android": "expo start --android",
"ios": "expo start --ios",
"web": "expo start --web",
"eject": "expo eject"
},
"dependencies": {
"expo": "~39.0.2",
"expo-status-bar": "~1.0.2",
"react": "16.13.1",
"react-dom": "16.13.1",
"react-native": "https://github.com/expo/react-native/archive/sdk-39.0.3.tar.gz",
"react-native-web": "~0.13.12"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "~7.9.0"
},
"private": true
}
gitignore
gitignore file is a file that can be any file or a folder that contains all the files that we want to ignore. The developers ignore files that are not necessary to execute the project.
node_modules/**/*
.expo/*
npm-debug.*
*.jks
*.p8
*.p12
*.key
*.mobileprovision
*.orig.*
web-build/
# macOS
.DS_Store
node_modules/
It is a folder that contains all the dependencies/ packages used to develop and run our mobile application.
ios/
It is for containing an Xcode project and the code required to bootstrap the app for ios devices. Since we are using expo-cli, we will not see the folder in our starter project.
android/
It is for containing the Android-related code to bootstrap the app for android devices. Since we are using expo-cli, we will not see the folder in our starter project.
App Registry
AppRegistory is the Js entry point to run a React Native Application. App Component or any other root component in the app should register by using AppRegistry.registerComponent such that the native system can load the bundle of the app and run the app by starting the AppRegistory.runApplication() method. Again, Expo handles this for us.
Run The App
Open the terminal in VS code editor and run the below command in it -
npm start
The command will start the development server at- link: exp://127.0.0.1:19000 Clicking on the link, Metro Bundler will open in the browser.
Install Expo and Test App
We will also need to install the Expo app on the ios and Android phone to test our mobile app. After installing from the App Store and Google Play Store by clicking on the link below.
Google PlayStore: Download Expo Client
Apple AppStore: Download Expo Client
connect it with the same wireless network.
Open the app and scan the QR code that appears in the Metro Bundler to test the app.
Change the text in the app.js file to HelloWorld to get the desired result.
Press ctrl+c in the terminal to stop the server.
Building Blocks Of ReactNative
Components are the visual elements that you see on the screen in a ReactNative App. There are several components made available for you to use by the ReactNative core. That’s what makes ReactNative great! To understand it better, we can categorize these components into different categories:
-
Core Components : These include - View, Text, Image, ScrollView, TextInput, StyleSheet.
-
List Components : These include - FlatList and Section List.
-
Form Control Components: These include Button, Slider, Picker, Switch.
-
Platform Dependent Specific Components: iOS : AlertIOS, PushNotificationIOS, ActionSheetIOS, etc. Android: ToastAndroid, PermissionsAndroid, DatePickerAndroid, etc.
-
Miscellaneous Components : There are tons of other components that ReactNative provide for us to make developers job easy. Some of these include Alert, Animated, CameraRoll, Dimensions, Keyboard, WebView, etc.
Apart from these built-in components, we can create our custom components, or we can incorporate custom components created by someone else into our projects. For instance,Here, we will use Card Component provided by the react-native-elements library created by a community of ReactNative developers.
Let us look at how to use these components one by one in detail-
Simply make the respective changes in the app.js file to learn the building blocks of React Native and get the desired result.
View, StyleSheet and Text
View
We start by declaring a View component, which is the basic building block in a ReactNative file. It maps the fundamental native iOS (UIView) and Android’s (View) Components. You can think of this component as a div element from HTML. Hence, the View component can contain nested components.
StyleSheet
We provide styles to the View component via the Stylesheet. Stylesheet in ReactNative provides a way to create styles inside the component file. It takes a JavaScript object as it does from above and returns a new StyleSheet object from it. There is no id or class in ReactNative, like in Web development. To create a new style object, we can use Stylesheet.create() method.
Text
The text component, in many ways, is just like the View component, except that it is specifically available to display text. Also, like a View component, it supports styling.
Example
Code
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.viewstyle}>
<Text style={styles.textstyle}>Text Component Inside a View</Text>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
viewstyle:{
flex:1,
margin:10
},
textstyle: {
fontSize:18,
backgroundColor: '#f50057',
marginBottom: 10,
color:'#ffffff',
padding:10,
textAlign: 'center',
borderRadius:20
},
});
Explanation
The above code snippet is a typical pattern style that you will see quite often in React Native. Let us understand the code line by line.
import React from 'react'
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'
The first line import the modules required to run the app using React Library. The second line imports the specific module from the React Native core Library. In the above code, we are importing Stylesheet, Text, and View Component.
export default function func_name(){
return ( // View )}
As we know from above that the ReactNative App consists of components. These are the visual blocks that we see on the screen. The above code is a standard way of creating a function-based that can be used anywhere within the app.
ScrollView and FlatList
ScrollView
As the name suggests, it provides a solution to scrolling content across any screen height. It supports both vertical and horizontal scrolling along with an optional option to pinch to zoom feature.
Flat List
It is a component that allows developers to present a list of similarly structured data items in a scrollable way. It is generally preferred over the scroll view when the number of data items in the list changes over time.
Example
Code
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View,ScrollView } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12];
return (
<ScrollView>
{
arr.map((num)=>
<View>
<Text style={styles.textstyle}>Scrollable Content Text {num}</Text>
</View>
)}
</ScrollView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
textstyle: {
fontSize:18,
backgroundColor: '#00B0FF',
marginBottom: 5,
color:'#000000',
padding:20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
});
Explanation
The above code snippet is pretty much self-explanatory. First, we import the module ScrollView from the react-native library. Next, we create a function-based component where we add Views to the ScrollView Component. In the above code, we add list items to the ScrollView Component with an array with the help of JSX. We pass style as a prop to the text component that takes an object created using the StyleSheet component.
Image and Dimensions
Replace the assets folder with the one found in the Link: Download Assets
Image
It is a component that provides a way to display images on the screen. It supports images from any format. One can get the picture from either the local storage or the network.
Dimensions
The dimension component of ReactNative allows the developers to get the dimensions of the application’s window / mobile screen. It may change according to device rotation and type.
Example
Code
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet,View, Image, Dimensions } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
return (
<View>
<Image
source={require('..assets/raw_images/undraw_react.png')}
style = {styles.im}
/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
im:{
width:Dimensions.get('window').width,
height:Dimensions.get('window').height/2
}
});
Explanation
In the above code snippet, we load an image stored in the assets folder of our project directory. The image component of the React Native takes source as a prop using which we can add our pictures to the screen. We set the image width and height using the Dimensions component provided by the React Native library that contains methods to capture the dimensions of the application window.
Button, TextInput, ToastAndroid, and Alert
Button
As the name suggests, the button component is the easiest way to allow the developers to provide a way for their users, handle touch gestures on the mobile screen.
Text Input
It is a core component that lets users input text on the screen.
Pressable
It is a core component of ReactNative that provides a more flexible way to respond to touch gestures on the mobile screen. With its help, we can make the child components feel and appear much more native.
ToastAndroid
ToastAndroid component of ReactNative exposes the Android platform’s ToastAndroid module as a JS module. It will only appear on mobile phones with Android as an Operating System.
Alert
Alert Component of React Native provides an Alert box with title and message. It can be merely compared to a dialogue box, as seen on Android or iOS devices. It has an option to provide optional buttons for users to interact.
Example
Code
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet,View,Button, Alert, Platform, ToastAndroid, TextInput } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const showalert = ()=>{ Alert.alert('Alert Component','You Pressed Alert Button!')}
const showtoast = ()=>{ if(Platform.OS=="android")ToastAndroid.show('You Pressed ToastMessage',ToastAndroid.SHORT)}
return (
<View>
<Button
style = {styles.button}
onPress={showalert}
title="Button For Alert" />
<Button
style = {styles.button}
onPress={showtoast}
title="Button For Toast" />
<TextInput
style={styles.tinput}
placeholder="This is a Text Input Component!" />
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
button:{padding:10,marginBottom:10,backgroundColor:"#F9A826",color:"#ffffff" },
tinput:{ padding:10, marginBottom:5,fontSize:15 }
});
Explanation
The above code snippet is pretty much self-explanatory. The Button component of ReactNative takes style, title, and onPress props. In the above code, we pass methods as props that display an alert message and toast message (Android) on the button click. We check the information on the platform by using the Platform component of React Native.
Props, State and Hooks
Props, State and Hooks are utilized to customize the components and make them interactive. In general, while developing, we will use these components (built-in and user-defined), props state, and hooks together to create a stunning mobile app. We will briefly discuss and implement the code for each of the above, one by one.
Props
Props, short form for Properties are the parameters for components. They are the easiest way to customize it at the time of creation.
For instance: In Text(core component), style is a prop provided by React Native.
The only thing to remember is that we can pass data or functions as props. With props and core components combined, we can create a wide variety of stunning visuals for our app by reutilizing one component with different props as parameters whenever required. Let us look at a simple example:
Example
Code
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
function Mycomponent(props){
return(
<Text style={styles.textstyle}>
Hello {props.addtext}
</Text>
);
}
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.cv}>
<Mycomponent addtext="From 1st Prop" />
<Mycomponent addtext="From 2nd Prop" />
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({ viewstyle:{ flex:1, margin:10 },
textstyle: {fontSize:18,backgroundColor: '#f50057',marginBottom: 10,color:'#ffffff',padding:10,textAlign: 'center',borderRadius:20},
cv:{ marginBottom:15 }
});
Explanation
In the above code snippet, we have customized core ReactNative component MyComponent that takes prop ‘addtext’ as a parameter. It is a fundamental principle concept provided by React that ensures code reusability. MyComponent is a customized component that can be used anywhere within the app using the import statement.
State
We use a state for the data that is going to change over time. Consider state as mutable while props immutable in a React Native App.
Hooks
Hooks in React are functions that allow developers to use React state and a component’s lifecycle methods in a functional Component. React provides a few built-in Hooks like useState and use effect. Developers can also create their Hooks to re-use the stateful behavior between different components. It provides an API to ReactNative concepts such as props, state, context, refs, and lifecycle.
Difference between Props and State and When to use what?
Props, in general, are immutable and are fixed throughout the lifetime of the component. State, on the other hand, is mutable and can be changed at any time in the future.
Example
Code
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, TextInput,Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState('');
return (
<View style = {styles.viewstyle}>
<TextInput
style={{height: 40, padding:20,margin:15}}
placeholder="Type Anything! "
onChangeText={name => setName(name)}
/>
<Text style={styles.textstyle}>{name}</Text>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
viewstyle:{flex:1,margin:10 },
textstyle: {
fontSize:18,
backgroundColor: '#f50057',
marginBottom: 10,
color:'#ffffff',
padding:10,
textAlign: 'center',
borderRadius:20},
});
Explanation
In the above code snippet, We import a hook, UseState provided by the React library to manage the state. We have declared a state called name whose initial value is assigned to be null and attached a method called setName that updates its state value every time the input text is changed. The above is a typical coding style to implement a hook in React Native.
Building the UI of ReactNative Tutor
Up till now, we have briefly discussed the concepts and code paradigms required to create ReactNativeTutor. In this part, we will build the real and same UI as that of the app shown above by developing the first two screens of the app.
We need to install a few packages before moving forward. They are as follows -
- React Native Elements
- React Native WebView
About React Native Elements
It is a cross-platform UI toolkit for React Native. It has more than 19.6k stars on GitHub and provides a useful set of reusable components for React Native applications. Link: https://github.com/react-native-elements/react-native-elements
About React Native WebView
React Native WebView is a modern, well-supported, and cross-platform WebView for React Native. It is a replacement for the built-in WebView that React Native provides. Link: https://github.com/react-native-webview/react-native-webview
Developers all around the world use open-source libraries/packages in their software and applications. It not only helps developers to complete their day-to-day work on time but, to the most extent, improves their developing experience. So, always remember, there is no shame in downloading extra packages.
We can add both the libraries into our project using npm by typing the following commands in the terminal.
npm install react-native-elements
npm install react-native-webview
You are also required to download the raw_images folder from this repository and add it in the assets directory.
Link To Download: Download raw_images
Follow the next steps to set up the initial file structure of our app.
-
Create two new folders(screens and components) in the root directory of the project.
-
Add a new JavaScript file (home.js) in the screen directory.
-
The home.js is the starting screen of the app. Screens is nothing but component. Let’s look at the screen structure in detail.
image add… -
Kindly copy the code below and add it to home.js.
import * as React from 'react';
import { Text, ScrollView } from 'react-native';
import { Card, Button } from 'react-native-elements';
export default function Home() {
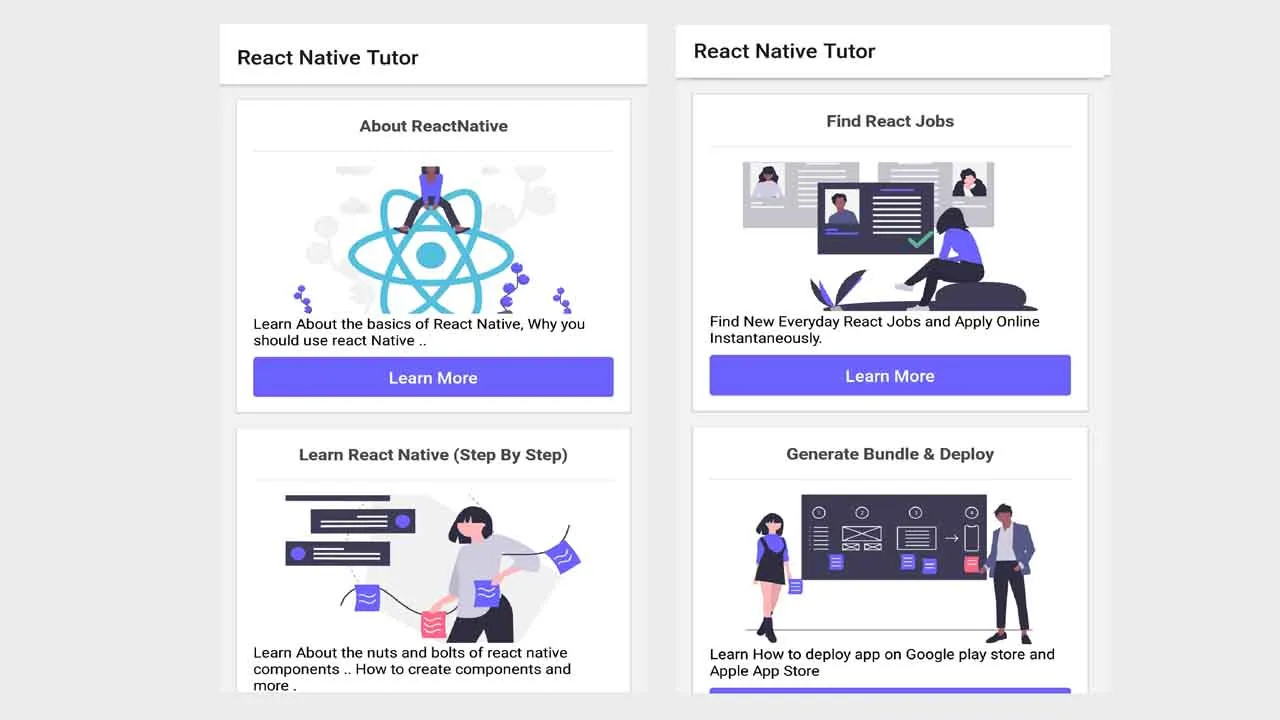
const data = [
{title: "About ReactNative",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_react.png"),info:"Learn About the basics of React Native, Why you should use react Native .. ", id:1},
{title: "Learn React Native (Step By Step)",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_ideas_flow.png"),info:"Learn About the nuts and bolts of react native components .. How to create components and more .", id:2},
{title: "Find React Jobs",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_hire.png"),info:"Find New Everyday React Jobs and Apply Online Instantaneously.", id:3},
{title:"Code Snippets",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_source_code.png"),info:"Powered by Wit.ai, find code snippets for your next ReactNative project.",id:4},
{title: "Generate Bundle & Deploy",source:require("../assets/raw_images/dply.png"),info:"Learn How to deploy app on Google play store and Apple App Store", id:5}
]
const CARD_COMPONENT = (props)=> {
return(
<Card>
<Card.Title>{props.title}</Card.Title>
<Card.Divider/>
<Card.Image source={props.source} />
<Text style={{marginBottom: 8}}>
{props.info}
</Text>
<Button
buttonStyle={{borderRadius: 0, marginLeft: 0, marginRight: 0, marginBottom: 0,backgroundColor:"#6C63FF"}}
title='Learn More' id ={props.id} />
</Card>);
}
return (
<ScrollView>
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[0].title} source={data[0].source} info={data[0].info} id={data[0].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[1].title} source={data[1].source} info={data[1].info} id={data[1].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[2].title} source={data[2].source} info={data[2].info} id={data[2].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[3].title} source={data[3].source} info={data[3].info} id={data[3].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[4].title} source={data[4].source} info={data[4].info} id={data[4].id} />
</ScrollView>
);
}
- Replace the code of App.js with the code found below-
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
import Home from './screens/home';
export default function App() {
return (
<View>
<Home />
</View>
);
}
- Run the app. The output should appear similar to the gif below.
Similarly,We will create the second screen of our app.
- To create the second screen of our app, let us create another file (component.js) in the screens folder.
- Add the code shown below in component.js
import * as React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, View, Text, ScrollView, Image } from 'react-native';
import { Card, Button,Icon } from 'react-native-elements'
export default function Component() {
const data = [{title:"Getting Started",id:1}, {title:"Core Components",id:2}, {title:"State Hooks and Props",id:3},{title:"Storage In React Native",id:4},{title:"Permissions In React Native",id:5},{title:"React Native Navigation",id:6},{title:"Animations In React Native",id:7},{title:"ES6 Essentials",id:8},{title:"Open Source Libraries",id:9}];
return (
<ScrollView>
<Card>
<Card.Title >Step By Step Tutorials</Card.Title>
<Card.Divider/>
<Card.Image resizeMode='cover' source={require('../assets/raw_images/undraw_teacher.png')} />
</Card>
{
data.map( (title)=>
<Card key={title.id}>
<Button
buttonStyle={{borderRadius: 0, marginLeft: 0, marginRight: 0, marginBottom: 0,backgroundColor:"#6C63FF"}}
title={title.title} id={title.id} />
</Card>
)
}
</ScrollView>
);
}
- Change the app.js code with the one found below.
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View, ScrollView } from 'react-native';
import Home from './screens/home';
import Component from './screens/component';
export default function App() {
return (
<ScrollView>
<Home />
<Component />
</ScrollView>
);
}
- After making the changes, Press ctrl+save. We will get an output similar to the one shown in the gif below.
Navigation In React Native
In this part, we will briefly discuss React Navigation, a third-party open-source library for routing and navigating in the ReactNative Apps. It has more than 18k stars on Github, and almost everyone I know in the ReactNative community has heard and used it at some point in their project.
Navigating through screens is a necessary part of any mobile application. It is vital for every mobile application. We all can agree with that, I am sure. However, for mobile applications, React Native does not provide a standard way or approach to solving the problem of navigating through different screens. Therefore, there are various options out there on the web to get the job done.
Different Navigation Solutions
When we talk about navigation, there are many libraries out there on the web because there is no standard way in the ReactNative documentation for navigating screens. Because of ReactNative popularity, a large number of open-source developers came together and developed a solution to the problem. We can categorize each of these navigating solutions into two separate categories-
-
JavaScript Navigators: These are navigators written and executed in the JavaScript language.
-
Native Navigators: These are navigators written in the platform (iOS and Android) native language (typically Objective-C or Java) and are exposed to React Native via a JavaScript API.
Why ReactNavigation?
Honestly, I don’t know. I searched online, and ReactNavigation came up at the top of the web page search result. I looked at the documentation, tried out one of its samples application, and voila! I found the solution to the navigating problem in my ReactNative App. ReactNavigation has more than 18k stars on Github and has an active community of developers working on the project consistently. ReactNavigation is built and funded by expo and Software Mansion, with contributions from many individual sponsors.
It is a powerful library that provides different types of navigation options like :
- Stack Navigator
- Drawer Navigator
- Bottom Tab Navigator
- Material Top Tab Navigator and many more.
About Stack Navigator
In Stack Navigator, we place a new screen on top of a stack. ReactNative Tutor uses a StackNavigator as a navigator solution to navigate through different screens. So now, we will add it to the app to navigate from the home screen to the component screen.
Installing ReactNavigation
We need to install a few libraries before moving forward. These libraries are required to run ReactNavigation smoothly in our app. Run the following commands in the terminal-
npm install @react-navigation/native
npm install react-native-reanimated react-native-gesture-handler react-native-screens
npm install react-native-safe-area-context @react-native-community/masked-view
Now let us add navigation into our app.
-
Create a new folder ‘routes’ in the root directory of the app and add the home.js file into it.
-
Copy the below code and add it to the home.js file of the routes folder.
import * as React from 'react';
import { createStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/stack';
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import Home from '../screens/home';
import Component from '../screens/component';
const HomeStack = createStackNavigator();
export default function MyStack(){
return(
<NavigationContainer>
<HomeStack.Navigator>
<HomeStack.Screen title="React Native Tutor" name="Home" component={Home} options={{headerTitle:"React Native Tutor"}} />
<HomeStack.Screen name="Component" component={Component} options={{headerTitle:"Learn React Native"}}/>
</HomeStack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
- In App.js, replace the code with the code found below-
import * as React from 'react';
import MyStack from './routes/home';
export default function App() {
return (
<MyStack />
);
}
Now every screen and component will get a navigation prop that will help you to move between the screens through various built-in functions like push() and pop(), but will also be used to pass data around between the screens.
- In home.js of the screens folder, copy the code below
import * as React from 'react';
import { Text, ScrollView } from 'react-native';
import { Card, Button } from 'react-native-elements';
export default function Home({ navigation }) {
const data = [
{title: "About ReactNative",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_react.png"),info:"Learn About the basics of React Native, Why you should use react Native .. ", id:1},
{title: "Learn React Native (Step By Step)",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_ideas_flow.png"),info:"Learn About the nuts and bolts of react native components .. How to create components and more .", id:2},
{title: "Find React Jobs",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_hire.png"),info:"Find New Everyday React Jobs and Apply Online Instantaneously.", id:3},
{title:"Code Snippets",source:require("../assets/raw_images/undraw_source_code.png"),info:"Powered by Wit.ai, find code snippets for your next ReactNative project.",id:4},
{title: "Generate Bundle & Deploy",source:require("../assets/raw_images/dply.png"),info:"Learn How to deploy app on Google play store and Apple App Store", id:5}
]
const presshandler = (id)=>{
navigation.push('Component');
}
const CARD_COMPONENT = (props)=> {
return(
<Card>
<Card.Title>{props.title}</Card.Title>
<Card.Divider/>
<Card.Image source={props.source} />
<Text style={{marginBottom: 8}}>
{props.info}
</Text>
<Button
buttonStyle={{borderRadius: 0, marginLeft: 0, marginRight: 0, marginBottom: 0,backgroundColor:"#6C63FF"}}
title='Learn More' id ={props.id} onPress={()=> presshandler(props.id)}/>
</Card>);
}
return (
<ScrollView>
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[0].title} source={data[0].source} info={data[0].info} id={data[0].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[1].title} source={data[1].source} info={data[1].info} id={data[1].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[2].title} source={data[2].source} info={data[2].info} id={data[2].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[3].title} source={data[3].source} info={data[3].info} id={data[3].id} />
<CARD_COMPONENT title={data[4].title} source={data[4].source} info={data[4].info} id={data[4].id} />
</ScrollView>
);
}
- The output should appear the same as the below gif -
Congrats and Next Steps
👍 👍 Congrats!! Now you have developed the first two screens of ReactNativeTutor.
However, it is not the end. It is just the beginning of developing the ReactNativeTutor. React Native Tutor is a big project, and it is impossible to cover everything in this tutorial. But, I am sure of the fact that by now, you have learned the skills and concepts required to understand this repository.
So as a DIY, I asked you to download or fork this repository and learn the rest by reading the source code of this project.
Before downloading, Let us know a little more about ReactNative Tutor
A closer look into ReactNative Tutor
If you like the above tutorial, then you would love React Native Tutor. A full-fledged mobile app for aspiring developers who want to learn React Native. Features of the app include -
-
More than 10+ step by step written tutorials (beginner to advanced) along with examples and code (embedded private Github Gists) that help people become React Native Ninja.
-
Exclusive tutorial on topics like Async Storage and Permissions and Deploying React Native app on Google Play Store and Apple App Store
-
Exclusive tutorial on topics like ES6 Essentials, Animations and Wit.ai
-
Find New React Jobs (worldwide) every day and Apply online instantaneously.
-
Find Quick Coding Snippets for your React Native Project. A feature powered by Wit.ai.
-
Beautiful UI
How to Start the app
ReactNative Tutor uses Wit.ai for fetching Code Snippets. Therefore, it requires a web token that one needs to generate from the Wit.ai official website. I have added a tutorial on creating the NLP based Wit.ai API Endpoint on the React Native Tutor Web App. Once you have made the API, follow the steps below to start the app-
-
Download or Fork the Repository.
-
Download the node modules and packages required to run the app by typing the below command
npm install.
-
Create a .env file in the root directory of the project.
-
Add the key in place of xxxxx
SECRET_KEY = xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
- Run the app by typing the following command in the terminal-
npm start
That’s it! That’s how you develop and run a ReactNative Project. I hope you had fun.
Inspiration and Credits
I started this repository as a tutorial, which later converted into a full-fledged React Native app. All of this was possible because of unDraw, Wit.ai and the open-source libraries that have been developed by the React Native community and React Native official documentation. Do check them out -
Expo
React Native Elements
Link: https://reactnativeelements.com/
React Navigation
Link:https://reactnavigation.org/
Async Storage
Link: https://react-native-async-storage.github.io/async-storage/
WebView
Link: https://github.com/react-native-webview/react-native-webview
unDraw
Wit.ai
Github Gists
Link: https://gist.github.com/
Github Jobs Api
Link: https://jobs.github.com/api
React Native Documentation
Link: https://reactnative.dev/
Download Details:
Author: karanjagota
Demo: https://www.reactnativetutor.tech/
Source Code: https://github.com/karanjagota/ReactNative-Tutor
#react #react-native #mobile-apps