JavaScript Tutorial: DOM in JavaScript
What is DOM in JavaScript?
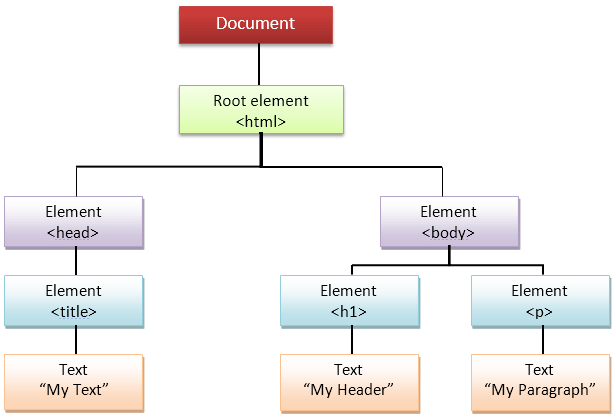
JavaScript can access all the elements in a webpage making use of Document Object Model (DOM). In fact, the web browser creates a DOM of the webpage when the page is loaded. The DOM model is created as a tree of objects like this:
How to use DOM and Events
Using DOM, JavaScript can perform multiple tasks. It can create new elements and attributes, change the existing elements and attributes and even remove existing elements and attributes. JavaScript can also react to existing events and create new events in the page.
getElementById, innerHTML Example
- getElementById: To access elements and attributes whose id is set.
- innerHTML: To access the content of an element.
Try this Example yourself:
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM!!!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="one">Welcome</h1>
<p>This is the welcome message.</p>
<h2>Technology</h2>
<p>This is the technology section.</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
var text = document.getElementById("one").innerHTML;
alert("The first heading is " + text);
</script>
</body>
</html>
getElementsByTagName Example
getElementsByTagName: To access elements and attributes using tag name. This method will return an array of all the items with the same tag name.
Try this Example yourself:
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM!!!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome</h1>
<p>This is the welcome message.</p>
<h2>Technology</h2>
<p id="second">This is the technology section.</p>
<script type="text/javascript">
var paragraphs = document.getElementsByTagName("p");
alert("Content in the second paragraph is " + paragraphs[1].innerHTML);
document.getElementById("second").innerHTML = "The orginal message is changed.";
</script>
</body>
</html>
Event handler Example
- createElement: To create new element
- removeChild: Remove an element
- You can add an event handler to a particular element like this:
document.getElementById(id).onclick=function()
{
lines of code to be executed
}
OR
document.getElementById(id).addEventListener("click", functionname)
Try this Example yourself:
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM!!!</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" id="btnClick" value="Click Me!!" />
<script type="text/javascript">
document.getElementById("btnClick").addEventListener("click", clicked);
function clicked()
{
alert("You clicked me!!!");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
This code is editable. Thank you for reading!
#javascript #developer
