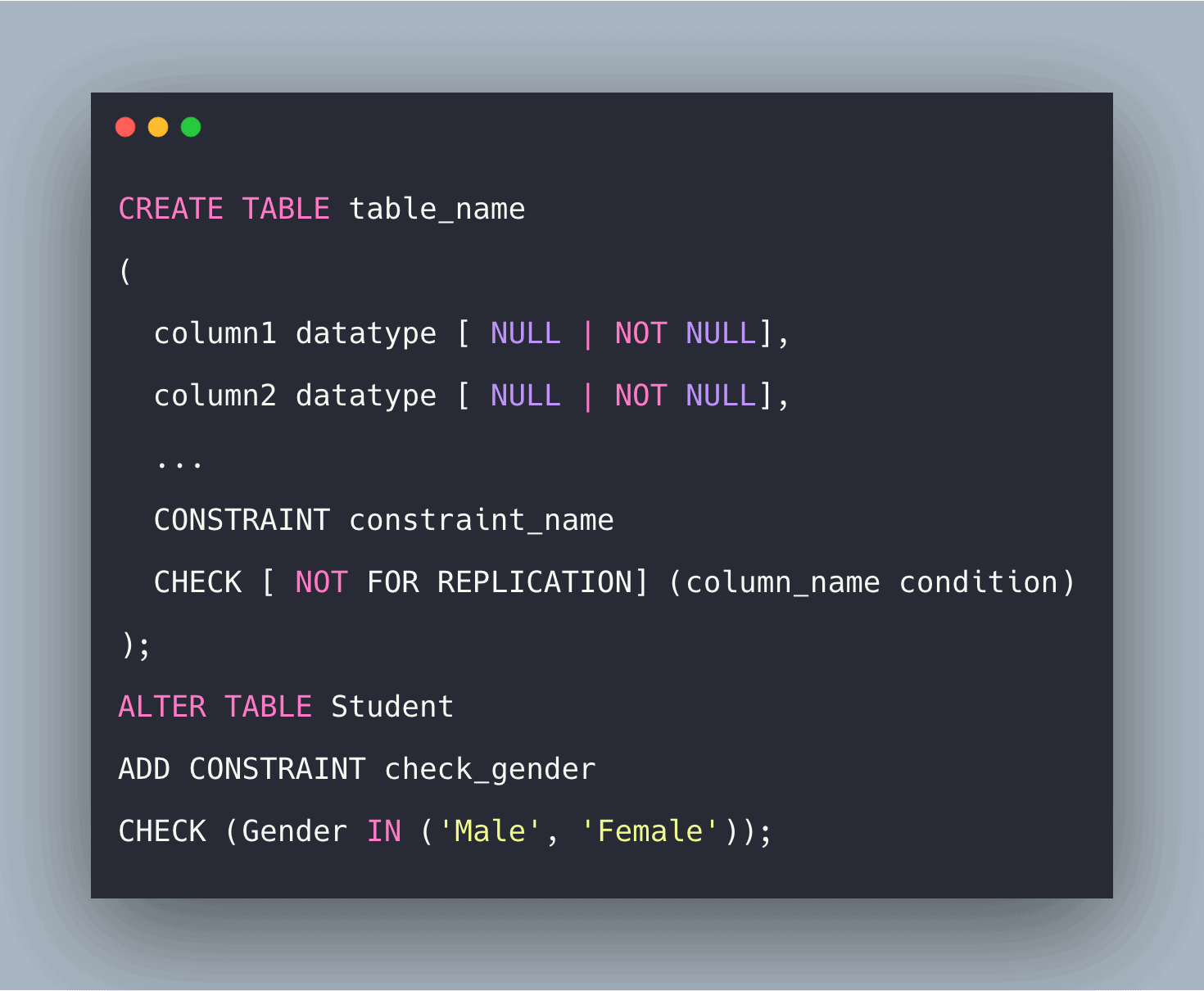
SQL check constraint is used for specifying the predicate that every tuple must satisfy in a relation. For example, it is used for limiting the values that a column can hold in a relation. It is used for giving a condition to check the value to be entered into a record. If the condition results in false then that value will not be added to the record.
SQL Check Constraint
The CHECK constraint is used to limit the value range that can be placed in a column.
If you define a CHECK constraint on a single column it allows only certain values for this column.
If you define a CHECK constraint on a table it can limit the values in certain columns based on values in other columns in the row.
Some key points of SQL Check Constraint are the following.
- Check constraints cannot be defined inside the SQL views.
- Check constraints only refers to the column of that table in which it is created not in the other table.
- A subquery is not allowed in check constraint.
- Check constraint is not only defined inside the CREATE TABLE statement but also in an ALTER TABLE statement.
#sql #sql check constraint