UserDefaults within apps are used to store data related to user configurations. It’s an easily accessible data store for saving states, statistics, and other app-related data.
Launch arguments are passed to the application on launch and can be used to alter the application for debugging purposes. It’s often used by Apple to allow developers to enable specific debugging modes, like in Core Data. We can do the same ourselves to enable certain debug modes in our apps.
An Example Case: UserDefaults to Trigger an App Introduction
A common use case for using launch arguments is to force enable an introduction screen during development. Without this, we’d need to reinstall the app every time so the introduction screen shows up.
An example code implementation could look as follows:
var shouldShowIntroduction: Bool {
/// Use a launch argument to always skip the app introduction.
if ProcessInfo.processInfo.arguments.contains("-skipAppIntroduction") {
return false
}
/// Use a launch argument to always show the app introduction.
if ProcessInfo.processInfo.arguments.contains("-requireAppIntroduction") {
return true
}
/// No launch arguments found, read from the user defaults.
return UserDefaults.standard.bool(forKey: "hasSeenAppIntroduction") == false
}
In this case, we have three options:
- Force skip the introduction using the
-skipAppIntroductionlaunch argument - Force enable the introduction using the
-requireAppIntroductionlaunch argument - Read the value from the user defaults
Although this works, it’ll easily fill up your launch arguments, and it requires extra code with potential bugs. It’d be much easier to simply override the user defaults directly. If so, we could have a simple code implementation like:
import SwiftUI
@main
struct UserDefaultsLaunchArgumentsApp: App {
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
if UserDefaults.standard.bool(forKey: "hasSeenAppIntroduction") == false {
IntroductionView()
} else {
ContentView()
}
}
}
}
Using Launch Arguments to Override User Defaults
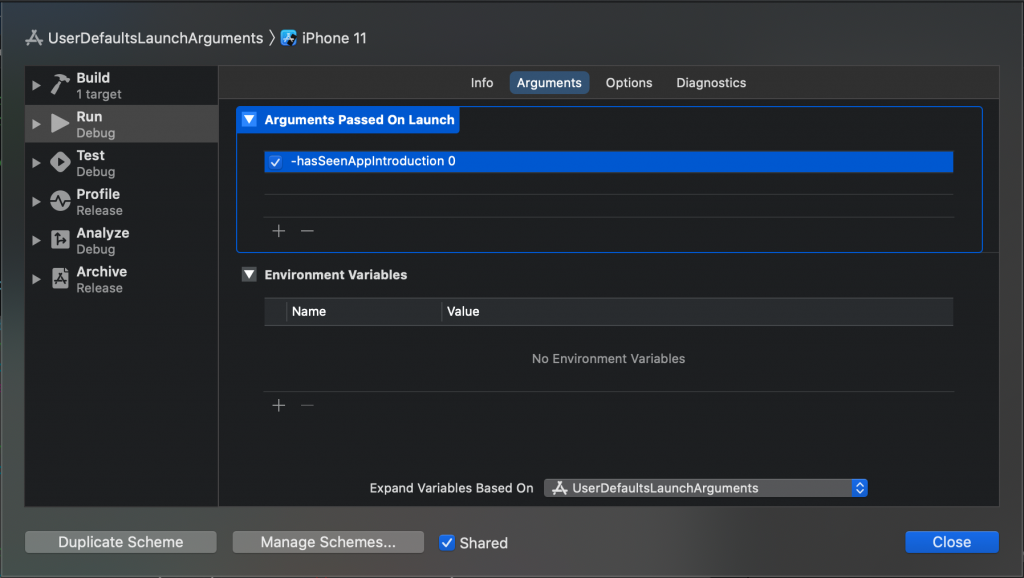
Overriding user defaults using launch arguments can be done in the scheme editor. In this case, we’d like to force enable the introduction screen by overriding the hasSeenAppIntroduction user defaults value.
You can do this by following these steps:
- Select your scheme, and click
Edit Scheme..., or useProduct ➞ Scheme ➞ Edit Scheme... - Go to
Run, and open theArgumentstab - Add a new value to
Arguments Passed On Launch - In this example, add:
-hasSeenAppIntroduction 0
#xcode #programming #swift #mobile #ios