Java Data Types - Explained with Examples
Master Java data types with practical examples. Elevate your programming skills, optimizing variable handling and efficient data manipulation seamlessly.
Java Data Types
A variable in Java must be a specified data type:
Example
int myNum = 5; // Integer (whole number)
float myFloatNum = 5.99f; // Floating point number
char myLetter = 'D'; // Character
boolean myBool = true; // Boolean
String myText = "Hello"; // String
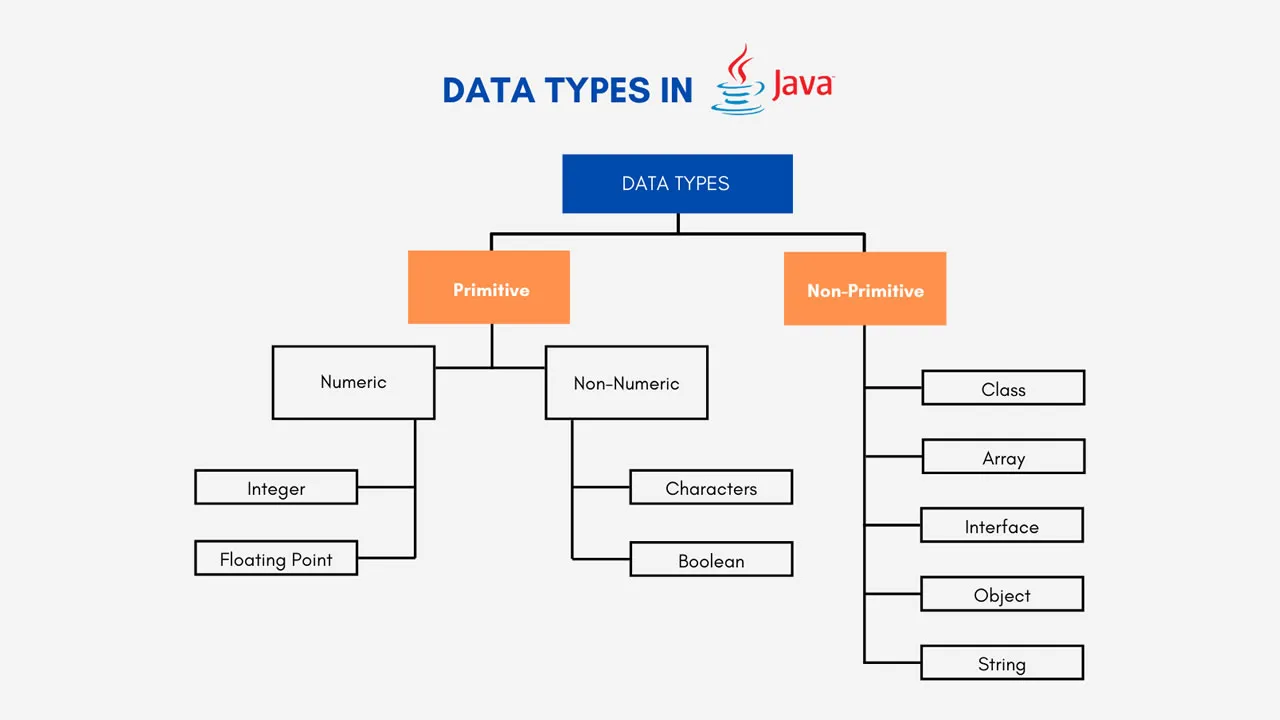
Data types are divided into two groups:
- Primitive data types - includes
byte,short,int,long,float,double,booleanandchar - Non-primitive data types - such as
String, Arrays and Classes (you will learn more about these in a later chapter)
Primitive Data Types
A primitive data type specifies the size and type of variable values, and it has no additional methods.
There are eight primitive data types in Java:
| Data Type | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|
byte | 1 byte | Stores whole numbers from -128 to 127 |
short | 2 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -32,768 to 32,767 |
int | 4 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
long | 8 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
float | 4 bytes | Stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 6 to 7 decimal digits |
double | 8 bytes | Stores fractional numbers. Sufficient for storing 15 decimal digits |
boolean | 1 bit | Stores true or false values |
char | 2 bytes | Stores a single character/letter or ASCII values |
#java
5.15 GEEK