The voice interface and conventional system are the practical implementations of AI technology in the industry. This article will explore the basic knowledge and techniques then extend to the challenges faced in different business use cases.
1. Conversational System
What is the conversational system or a virtual agent? One of the best-known fictional agents is Jarvis from Iron Man. It can think independently and help Tony do almost anything, including running chores, processing massive data sets, making intelligent suggestions, and providing emotional support. The most impressive feature of Jarvis is the chat capability, you can talk to him like an old friend, and he can understand you without ambiguity. The technology behind the scene is conversational AI.
The core of Conversational AI is a smartly designed voice user interface(VUI). Compared with the traditional GUI (Graphic User Interface), VUI free user’s hands by allowing them to perform nested queries via simple voice control (not ten clicks on the screen).
However, I have to admit that there’s still a big gap between the perfect virtual agent Jarvis and the existing conversational AI platforms’ capabilities.
Human and machine conversations have received tons of tractions from academia and industry over the past decade. In the research lab, we saw the following movement:
- Natural language understanding has moved from manual annotation_ and__ linguistic analysis_ to _deep learning __and _sequenced language modeling.
- The dialog management system has moved from rule-based****policies_ to supervised learning and reinforcement learning._
- The language generation engine has moved from the pre-defined template_ and__ syntax parsing_ to _end-to-end language transformer _and_ attention mechanisms._
In addition, we also saw conversational products spring up in the cross-market domain. All the big players have their signature virtual agent, for instance, Siri for Apple, Alexa for Amazon, Cortana for Microsoft and Dialogflow for Google. (Diagram below are out of date, please use it a reference only)

Report from Recast.AI
2. Key Components of a Conversational System
There are few main components in the conversational platform, 1) ASR: Automatic Speech Recognition, 2) NLU: Natural Language Understanding, 3) Dialog Management, 4)NLG: Natural Language Generation, 5) TTS: Text to Speech. (Additional components could include public API, integration gateway, action fulfillment logic, Language model training stack, versioning, and chat simulation, etc.)
For simplicity, let’s explore the basics now.
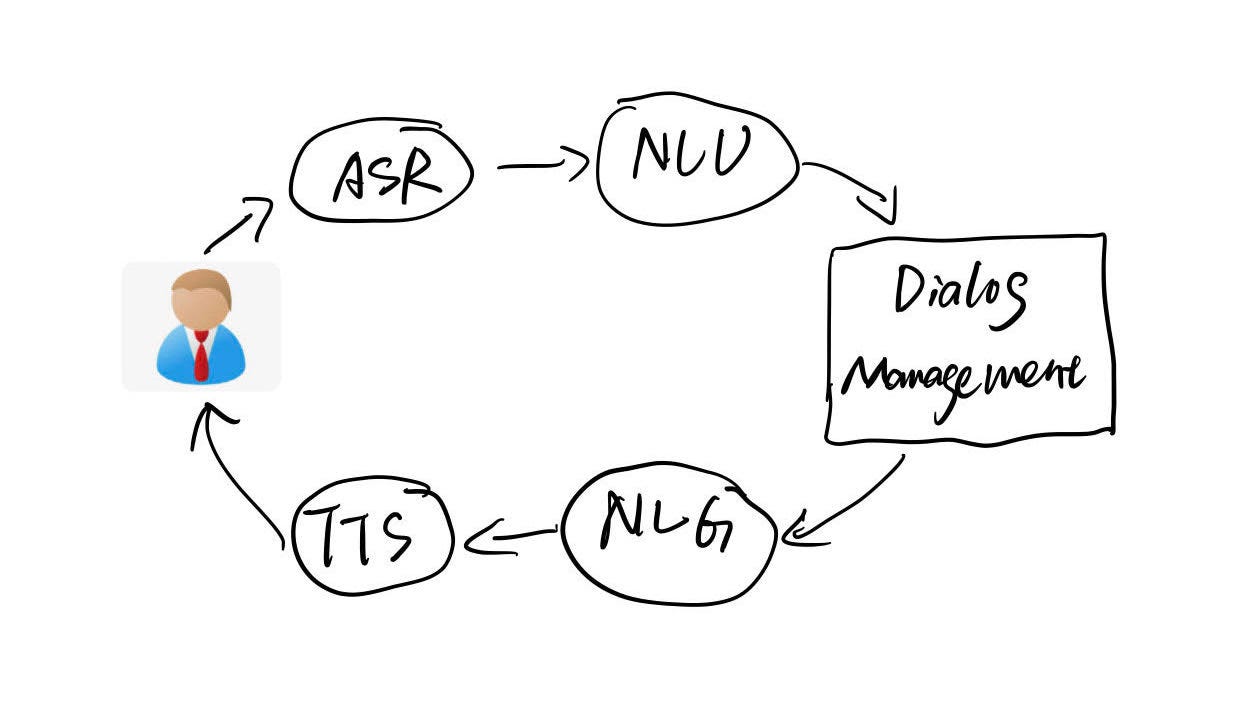
Simple Dialog System by Catherine Wang
**2.1. ASR: **Automatic speech recognition is a model trained on speaker voice record and transcript, then fine-tuned to recognize the unseen voice queries. Most of the conversational platforms offer this feature as an embedded element. Thus developers can leverage the state of the art ASR on their product(e.g., voice input, voice search, real-time translation, and smart home devices).
**2.2. NLU:**Indisputably, the most important part of a conversational system. ASR will only transcribe what you have said, but NLU will understand exactly what do you mean? Natural Language Understanding can be seen as a subset of Natural Language Processing. The relationship can be loosely described as below.
 By Sciforce
By Sciforce
Both NLP and NLU are board topics, so instead of going too deep into the topic, I will explain the high-level concept by using practical examples from the virtual agent use case.
#nlp #data-science #deep-learning #deep learning
