Weather App with “flutter_bloc”
Hey everyone, today we’re going to build a minimal (but functional) weather app in Flutter which demonstrates how to manage multiple blocs to implement dynamic theming, pull-to-refresh, and much more.
Our weather app will pull real data from an API and demonstrate how to apply a layered architecture to separate presentational logic from business logic.
The finished product will look like this:
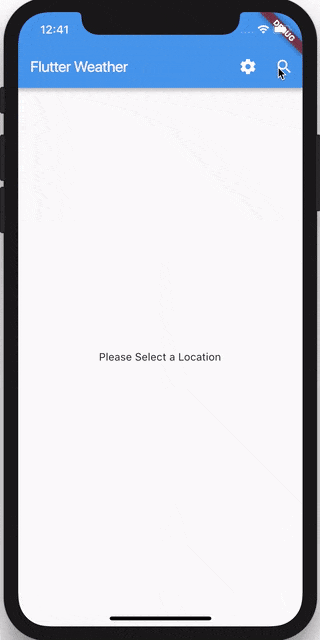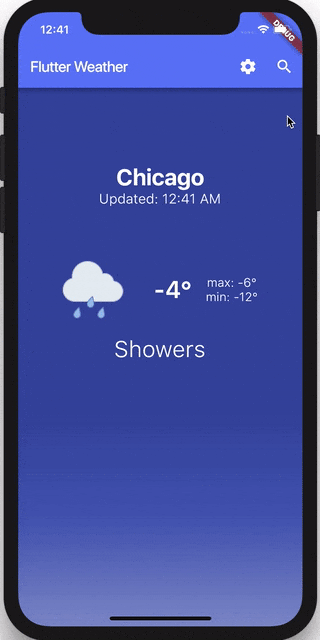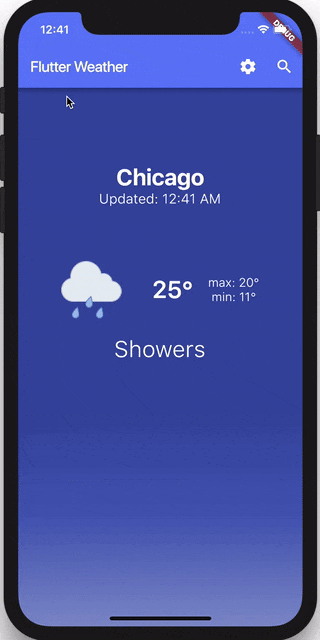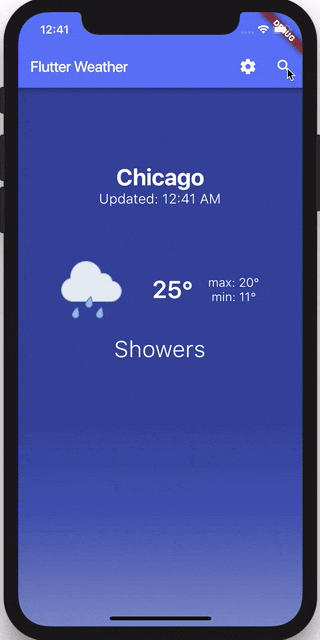
Let’s get started!
Setup
We’ll start off by creating a brand new Flutter project
flutter create flutter_weather
We can then go ahead and replace the contents of pubspec.yaml with:
name: flutter_weather
description: A new Flutter project.
version: 1.0.0+1
environment:
sdk: ">=2.0.0-dev.68.0 <3.0.0"
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_bloc: ^0.5.0
http: ^0.12.0
equatable: ^0.1.0
dev_dependencies:
flutter_test:
sdk: flutter
flutter:
uses-material-design: true
assets:
- assets/
Note: We are going to use custom assets in our project so we include the entire assets directory.
Now we can install all of our dependencies with flutter packages get.
REST API
For this application we’ll be hitting the metaweather API.
We’ll be focusing on two endpoints:
/api/location/search/?query=$cityto get a locationId for a given city name/api/location/$locationIdto get the weather for a given locationId
Open https://www.metaweather.com/api/location/search/?query=london in your browser and you’ll see the following response:
[
{
"title": "London",
"location_type": "City",
"woeid": 44418,
"latt_long": "51.506321,-0.12714"
}
]
We can then get the where-on-earth-id (woeid) and use it to hit the location API.
Navigate to https://www.metaweather.com/api/location/44418 in your browser and you’ll see the response for weather in London. It should look something like this:
{
"consolidated_weather": [
{
"id": 5565095488782336,
"weather_state_name": "Showers",
"weather_state_abbr": "s",
"wind_direction_compass": "WNW",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:02.434940Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-10",
"min_temp": 3.75,
"max_temp": 6.883333333333333,
"the_temp": 6.885,
"wind_speed": 10.251177687940428,
"wind_direction": 288.4087075064449,
"air_pressure": 998.9649999999999,
"humidity": 79,
"visibility": 8.241867493835997,
"predictability": 73
},
{
"id": 5039805855432704,
"weather_state_name": "Light Cloud",
"weather_state_abbr": "lc",
"wind_direction_compass": "NW",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:02.537745Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-11",
"min_temp": 1.7699999999999998,
"max_temp": 8.986666666666666,
"the_temp": 8.105,
"wind_speed": 5.198548786091227,
"wind_direction": 319.24869874195554,
"air_pressure": 1027.4,
"humidity": 75,
"visibility": 11.027785234232084,
"predictability": 70
},
{
"id": 6214207016009728,
"weather_state_name": "Heavy Cloud",
"weather_state_abbr": "hc",
"wind_direction_compass": "SW",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:02.736577Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-12",
"min_temp": 3.2699999999999996,
"max_temp": 11.783333333333333,
"the_temp": 10.425,
"wind_speed": 6.291005350509027,
"wind_direction": 225.7496998927606,
"air_pressure": 1034.9099999999999,
"humidity": 77,
"visibility": 9.639331305177762,
"predictability": 71
},
{
"id": 6548160117735424,
"weather_state_name": "Heavy Cloud",
"weather_state_abbr": "hc",
"wind_direction_compass": "SSW",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:02.687267Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-13",
"min_temp": 3.526666666666667,
"max_temp": 11.476666666666667,
"the_temp": 10.695,
"wind_speed": 6.524550068392587,
"wind_direction": 203.1296143014564,
"air_pressure": 1035.775,
"humidity": 76,
"visibility": 12.940987135130836,
"predictability": 71
},
{
"id": 4957149578919936,
"weather_state_name": "Light Cloud",
"weather_state_abbr": "lc",
"wind_direction_compass": "SSE",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:03.487370Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-14",
"min_temp": 3.4500000000000006,
"max_temp": 12.540000000000001,
"the_temp": 12.16,
"wind_speed": 5.990352212916568,
"wind_direction": 154.1901674720193,
"air_pressure": 1035.53,
"humidity": 71,
"visibility": 13.873665294679075,
"predictability": 70
},
{
"id": 5277694765826048,
"weather_state_name": "Light Cloud",
"weather_state_abbr": "lc",
"wind_direction_compass": "S",
"created": "2019-02-10T19:55:04.800837Z",
"applicable_date": "2019-02-15",
"min_temp": 3.4,
"max_temp": 12.986666666666666,
"the_temp": 12.39,
"wind_speed": 5.359238182348418,
"wind_direction": 176.84978678797177,
"air_pressure": 1030.96,
"humidity": 77,
"visibility": 9.997862483098704,
"predictability": 70
}
],
"time": "2019-02-10T21:49:37.574260Z",
"sun_rise": "2019-02-10T07:24:19.235049Z",
"sun_set": "2019-02-10T17:05:51.151342Z",
"timezone_name": "LMT",
"parent": {
"title": "England",
"location_type": "Region / State / Province",
"woeid": 24554868,
"latt_long": "52.883560,-1.974060"
},
"sources": [
{
"title": "BBC",
"slug": "bbc",
"url": "http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/",
"crawl_rate": 180
},
{
"title": "Forecast.io",
"slug": "forecast-io",
"url": "http://forecast.io/",
"crawl_rate": 480
},
{
"title": "HAMweather",
"slug": "hamweather",
"url": "http://www.hamweather.com/",
"crawl_rate": 360
},
{
"title": "Met Office",
"slug": "met-office",
"url": "http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/",
"crawl_rate": 180
},
{
"title": "OpenWeatherMap",
"slug": "openweathermap",
"url": "http://openweathermap.org/",
"crawl_rate": 360
},
{
"title": "Weather Underground",
"slug": "wunderground",
"url": "https://www.wunderground.com/?apiref=fc30dc3cd224e19b",
"crawl_rate": 720
},
{
"title": "World Weather Online",
"slug": "world-weather-online",
"url": "http://www.worldweatheronline.com/",
"crawl_rate": 360
},
{
"title": "Yahoo",
"slug": "yahoo",
"url": "http://weather.yahoo.com/",
"crawl_rate": 180
}
],
"title": "London",
"location_type": "City",
"woeid": 44418,
"latt_long": "51.506321,-0.12714",
"timezone": "Europe/London"
}
Great, now that we know what our data is going to look like, let’s create the necessary data models.
Data Model
Even though the weather API returns weather for multiple days, for simplicity, we’re only going to worry about today’s weather.
We are going to extract a subset of the data from the API and create a Weather model which will look something like:
import 'package:equatable/equatable.dart';
enum WeatherCondition {
snow,
sleet,
hail,
thunderstorm,
heavyRain,
lightRain,
showers,
heavyCloud,
lightCloud,
clear,
unknown
}
class Weather extends Equatable {
final WeatherCondition condition;
final String formattedCondition;
final double minTemp;
final double temp;
final double maxTemp;
final int locationId;
final String created;
final DateTime lastUpdated;
final String location;
Weather({
this.condition,
this.formattedCondition,
this.minTemp,
this.temp,
this.maxTemp,
this.locationId,
this.created,
this.lastUpdated,
this.location,
}) : super([
condition,
formattedCondition,
minTemp,
temp,
maxTemp,
locationId,
created,
lastUpdated,
location,
]);
static Weather fromJson(dynamic json) {
final consolidatedWeather = json['consolidated_weather'][0];
return Weather(
condition: _mapStringToWeatherCondition(
consolidatedWeather['weather_state_abbr']),
formattedCondition: consolidatedWeather['weather_state_name'],
minTemp: consolidatedWeather['min_temp'] as double,
temp: consolidatedWeather['the_temp'] as double,
maxTemp: consolidatedWeather['max_temp'] as double,
locationId: json['woeid'] as int,
created: consolidatedWeather['created'],
lastUpdated: DateTime.now(),
location: json['title'],
);
}
static WeatherCondition _mapStringToWeatherCondition(String input) {
WeatherCondition state;
switch (input) {
case 'sn':
state = WeatherCondition.snow;
break;
case 'sl':
state = WeatherCondition.sleet;
break;
case 'h':
state = WeatherCondition.hail;
break;
case 't':
state = WeatherCondition.thunderstorm;
break;
case 'hr':
state = WeatherCondition.heavyRain;
break;
case 'lr':
state = WeatherCondition.lightRain;
break;
case 's':
state = WeatherCondition.showers;
break;
case 'hc':
state = WeatherCondition.heavyCloud;
break;
case 'lc':
state = WeatherCondition.lightCloud;
break;
case 'c':
state = WeatherCondition.clear;
break;
default:
state = WeatherCondition.unknown;
}
return state;
}
}
We extend [_Equatable_]([https://pub.dartlang.org/packages/equatable)](https://pub.dartlang.org/packages/equatable) "https://pub.dartlang.org/packages/equatable)") so that we can compare _Weather_ instances. By default, the equality operator returns true if and only if this and other are the same instance.
There’s not much happening here; we are just defining our Weather data model and implementing a fromJson method so that we can create a Weather instance from the API response body.
Next, we need to build our WeatherApiClient which will be responsible for making http requests to the weather API.
Data Provider
The WeatherApiClient is the lowest layer in our application architecture (the data provider). Its only responsibility is to fetch data directly from our API.
As we mentioned earlier, we are going to be hitting two endpoints so our WeatherApiClient needs to expose two public methods:
/api/location/search/?query=$cityto get a locationId for a given city name/api/location/$locationIdto get the weather for a given locationId
It should look something like this:
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart';
class WeatherApiClient {
static const baseUrl = 'https://www.metaweather.com';
final http.Client httpClient;
WeatherApiClient({@required this.httpClient}) : assert(httpClient != null);
Future<int> getLocationId(String city) async {
final locationUrl = '$baseUrl/api/location/search/?query=$city';
final locationResponse = await this.httpClient.get(locationUrl);
if (locationResponse.statusCode != 200) {
throw Exception('error getting locationId for city');
}
final locationJson = jsonDecode(locationResponse.body) as List;
return (locationJson.first)['woeid'];
}
Future<Weather> fetchWeather(int locationId) async {
final weatherUrl = '$baseUrl/api/location/$locationId';
final weatherResponse = await this.httpClient.get(weatherUrl);
if (weatherResponse.statusCode != 200) {
throw Exception('error getting weather for location');
}
final weatherJson = jsonDecode(weatherResponse.body);
return Weather.fromJson(weatherJson);
}
}
Note: Our _WeatherApiClient_ has an _httpClient_ injected via the constructor and it handles making the network request and serializing the response json into the respective data model.
We’ve got our DataProvider done so it’s time to move up to the next layer of our app’s architecture: the repository layer.
Repository
The WeatherRepository serves as an abstraction between the client code and the data provider so that as a developer working on features, you don’t have to know where the data is coming from.
Our WeatherRepository will have a dependency on our WeatherApiClient that we just created and it will expose a single public method called, you guessed it, getWeather(String city).
No one needs to know that under the hood we need to make two API calls (one for locationId and one for weather) because no one really cares. All we care about is getting the Weather for a given city.
Our WeatherRepository is quite simple and should look something like this:
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/weather_api_client.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart';
class WeatherRepository {
final WeatherApiClient weatherApiClient;
WeatherRepository({@required this.weatherApiClient})
: assert(weatherApiClient != null);
Future<Weather> getWeather(String city) async {
final int locationId = await weatherApiClient.getLocationId(city);
return weatherApiClient.fetchWeather(locationId);
}
}
Awesome! We are now ready to move up to the business logic layer and start building our WeatherBloc.
Business Logic (Bloc)
Our WeatherBloc is responsible for receiving WeatherEvents and converting them into WeatherStates. It will have a dependency on WeatherRepository so that it can retrieve the Weather when a user inputs a city of their choice.
Before jumping into the Bloc we need to define what events our WeatherBloc will be handling as well as how we are going to represent our WeatherState.
Weather Event
For simplicity, we’re going to start off by having a single event called FetchWeather.
We can define it like:
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:equatable/equatable.dart';
abstract class WeatherEvent extends Equatable {
WeatherEvent([List props = const []]) : super(props);
}
class FetchWeather extends WeatherEvent {
final String city;
FetchWeather({@required this.city})
: assert(city != null),
super([city]);
}
Whenever a user inputs a city, we will dispatch a FetchWeather event with the given city and our bloc will responsible for figuring out what the weather is there and returning a new WeatherState.
Weather State
For the current application, we will have 4 possible states:
/api/location/search/?query=$cityto get a locationId for a given city name/api/location/$locationIdto get the weather for a given locationId
We can represent these states like so:
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:equatable/equatable.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart';
abstract class WeatherState extends Equatable {
WeatherState([List props = const []]) : super(props);
}
class WeatherEmpty extends WeatherState {}
class WeatherLoading extends WeatherState {}
class WeatherLoaded extends WeatherState {
final Weather weather;
WeatherLoaded({@required this.weather})
: assert(weather != null),
super([weather]);
}
class WeatherError extends WeatherState {}
Now that we have our Events and our States defined and implemented we are ready to make our WeatherBloc.
Weather Bloc
Our WeatherBloc is very straightforward. To recap, it converts WeatherEvents into WeatherStates and has a dependency on the WeatherRepository.
Tip: Check out the Bloc VSCode Extension in order to take advantage of the bloc snippets and even further improve your efficiency and development speed.
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:bloc/bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/repositories.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart';
class WeatherBloc extends Bloc<WeatherEvent, WeatherState> {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
WeatherBloc({@required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null);
@override
WeatherState get initialState => WeatherEmpty();
@override
Stream<WeatherState> mapEventToState(
WeatherState currentState,
WeatherEvent event,
) async* {
if (event is FetchWeather) {
yield WeatherLoading();
try {
final Weather weather = await weatherRepository.getWeather(event.city);
yield WeatherLoaded(weather: weather);
} catch (_) {
yield WeatherError();
}
}
}
}
We set our initialState to WeatherEmpty since initially, the user has not selected a city. Then, all that’s left is to implement mapEventToState.
Since we are only handling the FetchWeather event all we need to do is yield our WeatherLoading state when we get a FetchWeather event and then try to get the weather from the WeatherRepository.
If we are able to successfully retrieve the weather we then yield a WeatherLoaded state and if we are unable to retrieve the weather, we yield a WeatherError state.
That’s all there is to it! Now we’re ready to move on to the final layer: the presentation layer.
Presentation
Setup
As you’ve probably already seen in other tutorials, we’re going to create a SimpleBlocDelegate so that we can see all state transitions in our application.
import 'package:bloc/bloc.dart';
class SimpleBlocDelegate extends BlocDelegate {
@override
onTransition(Transition transition) {
print(transition);
}
}
Next, we’re going to set our delegate in our main function like so:
void main() {
BlocSupervisor().delegate = SimpleBlocDelegate();
}
Lastly, we need to create our WeatherRepository and inject it into our App widget.
void main() {
BlocSupervisor().delegate = SimpleBlocDelegate();
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository = WeatherRepository(
weatherApiClient: WeatherApiClient(
httpClient: http.Client(),
),
);
runApp(App(weatherRepository: weatherRepository));
}
App
Our App widget is going to start off as a StatelessWidget which has the WeatherRepository injected and builds the MaterialApp with our Weather widget.
class App extends StatelessWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
App({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Weather',
home: Weather(
weatherRepository: weatherRepository,
),
);
}
}
Weather
Our Weather Widget will be a StatefulWidget responsible for creating and disposing a WeatherBloc.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/repositories.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Weather extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
Weather({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<Weather> createState() => _WeatherState();
}
class _WeatherState extends State<Weather> {
WeatherBloc _weatherBloc;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_weatherBloc = WeatherBloc(weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Weather'),
actions: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () async {
final city = await Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => CitySelection(),
),
);
if (city != null) {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(FetchWeather(city: city));
}
},
)
],
),
body: Center(
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _weatherBloc,
builder: (_, WeatherState state) {
if (state is WeatherEmpty) {
return Center(child: Text('Please Select a Location'));
}
if (state is WeatherLoading) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
if (state is WeatherLoaded) {
final weather = state.weather;
return ListView(
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 100.0),
child: Center(
child: Location(location: weather.location),
),
),
Center(
child: LastUpdated(dateTime: weather.lastUpdated),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 50.0),
child: Center(
child: CombinedWeatherTemperature(
weather: weather,
),
),
),
],
);
}
if (state is WeatherError) {
return Text(
'Something went wrong!',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red),
);
}
},
),
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_weatherBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
All that’s happening in this widget is we’re using BlocBuilder with our WeatherBloc in order to rebuild our UI based on state changes in our WeatherBloc.
You’ll notice that we are referencing a Location, LastUpdated, and CombinedWeatherTemperature widget which we will create in the following sections.
Location
Our Location widget is simple; it displays the current location.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
class Location extends StatelessWidget {
final String location;
Location({Key key, @required this.location})
: assert(location != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(
location,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
);
}
}
Last Updated
Our LastUpdated widget is also super simple; it displays the last updated time so that users know how fresh the weather data is.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
class LastUpdated extends StatelessWidget {
final DateTime dateTime;
LastUpdated({Key key, @required this.dateTime})
: assert(dateTime != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Text(
'Updated: ${TimeOfDay.fromDateTime(dateTime).format(context)}',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w200,
color: Colors.white,
),
);
}
}
Note: We are using [_TimeOfDay_]([https://docs.flutter.io/flutter/material/TimeOfDay-class.html)](https://docs.flutter.io/flutter/material/TimeOfDay-class.html) "https://docs.flutter.io/flutter/material/TimeOfDay-class.html)") to format the _DateTime_ into a more human-readable format.
Combined Weather Temperature
The CombinedWeatherTemperature widget is a compositional widget which displays the current weather along with the temperature. We are still going to modularize the Temperature and WeatherConditions widgets so that they can all be reused.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart' as model;
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
class CombinedWeatherTemperature extends StatelessWidget {
final model.Weather weather;
CombinedWeatherTemperature({
Key key,
@required this.weather,
}) : assert(weather != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: WeatherConditions(condition: weather.condition),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: Temperature(
temperature: weather.temp,
high: weather.maxTemp,
low: weather.minTemp,
),
),
],
),
Center(
child: Text(
weather.formattedCondition,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w200,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
],
);
}
}
Note: We are using two unimplemented widgets: _WeatherConditions_ and _Temperature_ which we will create next.
Weather Conditions
Our WeatherConditions widget will be responsible for displaying the current weather conditions (clear, showers, thunderstorms, etc…) with an icon.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart';
class WeatherConditions extends StatelessWidget {
final WeatherCondition condition;
WeatherConditions({Key key, @required this.condition})
: assert(condition != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) => _mapConditionToImage(condition);
Image _mapConditionToImage(WeatherCondition condition) {
Image image;
switch (condition) {
case WeatherCondition.clear:
case WeatherCondition.lightCloud:
image = Image.asset('assets/clear.png');
break;
case WeatherCondition.hail:
case WeatherCondition.snow:
case WeatherCondition.sleet:
image = Image.asset('assets/snow.png');
break;
case WeatherCondition.heavyCloud:
image = Image.asset('assets/cloudy.png');
break;
case WeatherCondition.heavyRain:
case WeatherCondition.lightRain:
case WeatherCondition.showers:
image = Image.asset('assets/rainy.png');
break;
case WeatherCondition.thunderstorm:
image = Image.asset('assets/thunderstorm.png');
break;
case WeatherCondition.unknown:
image = Image.asset('assets/clear.png');
break;
}
return image;
}
}
Tip: Check out icons8 for the assets used in this tutorial.
Temperature
Our Temperature widget will be responsible for displaying the average, min, and max temperatures.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class Temperature extends StatelessWidget {
final double temperature;
final double low;
final double high;
Temperature({
Key key,
this.temperature,
this.low,
this.high,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Row(
children: [
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(right: 20.0),
child: Text(
'${_formattedTemperature(temperature)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 32,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w600,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
Column(
children: [
Text(
'max: ${_formattedTemperature(high)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w100,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
Text(
'min: ${_formattedTemperature(low)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w100,
color: Colors.white,
),
)
],
)
],
);
}
int _formattedTemperature(double t) => t.round();
}
The last thing we need to implement to have a functional app is our CitySelection widget which allows users to type in the name of a city.
City Selection
The CitySelection widget will allow users to input a city name and pass the selected city back to the App widget.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class CitySelection extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<CitySelection> createState() => _CitySelectionState();
}
class _CitySelectionState extends State<CitySelection> {
final TextEditingController _textController = TextEditingController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('City'),
),
body: Form(
child: Row(
children: [
Expanded(
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(left: 10.0),
child: TextFormField(
controller: _textController,
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'City',
hintText: 'Chicago',
),
),
),
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.pop(context, _textController.text);
},
)
],
),
),
);
}
}
CitySelection needs to be a StatefulWidget because it has to maintain a TextController.
Note: When we press the search button we use _Navigator.pop_ and pass the current text from our _TextController_ back to the previous view.
At this point we have a fully functioning weather app but upon running it you’ll notice it has a few problems:
/api/location/search/?query=$cityto get a locationId for a given city name/api/location/$locationIdto get the weather for a given locationId
Let’s address these problems and take our Weather App to the next level!
Pull-To-Refresh
In order to support pull-to-refresh we will need to update our WeatherBloc to handle a second event: RefreshWeather.
class RefreshWeather extends WeatherEvent {
final String city;
RefreshWeather({@required this.city})
: assert(city != null),
super([city]);
}
Next, we need to update our mapEventToState to handle a RefreshWeather event.
class WeatherBloc extends Bloc<WeatherEvent, WeatherState> {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
WeatherBloc({@required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null);
@override
WeatherState get initialState => WeatherEmpty();
@override
Stream<WeatherState> mapEventToState(
WeatherState currentState,
WeatherEvent event,
) async* {
if (event is FetchWeather) {
yield WeatherLoading();
try {
final Weather weather = await weatherRepository.getWeather(event.city);
yield WeatherLoaded(weather: weather);
} catch (_) {
yield WeatherError();
}
}
if (event is RefreshWeather) {
try {
final Weather weather = await weatherRepository.getWeather(event.city);
yield WeatherLoaded(weather: weather);
} catch (_) {
yield currentState;
}
}
}
}
Lastly, we need to update our presentation layer to use a RefreshIndicator widget.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/repositories.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Weather extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
Weather({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<Weather> createState() => _WeatherState();
}
class _WeatherState extends State<Weather> {
WeatherBloc _weatherBloc;
Completer<void> _refreshCompleter;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_refreshCompleter = Completer<void>();
_weatherBloc = WeatherBloc(weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Weather'),
actions: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () async {
final city = await Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => CitySelection(),
),
);
if (city != null) {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(FetchWeather(city: city));
}
},
)
],
),
body: Center(
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _weatherBloc,
builder: (_, WeatherState state) {
if (state is WeatherEmpty) {
return Center(child: Text('Please Select a Location'));
}
if (state is WeatherLoading) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
if (state is WeatherLoaded) {
final weather = state.weather;
_refreshCompleter?.complete();
_refreshCompleter = Completer();
return RefreshIndicator(
onRefresh: () {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(
RefreshWeather(city: state.weather.location),
);
return _refreshCompleter.future;
},
child: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 100.0),
child: Center(
child: Location(location: weather.location),
),
),
Center(
child: LastUpdated(dateTime: weather.lastUpdated),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 50.0),
child: Center(
child: CombinedWeatherTemperature(
weather: weather,
),
),
),
],
),
);
}
if (state is WeatherError) {
return Text(
'Something went wrong!',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red),
);
}
},
),
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_weatherBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
In order to use the RefreshIndicator we had to create a [Completer]([https://api.dartlang.org/stable/2.1.0/dart-async/Completer-class.html)](https://api.dartlang.org/stable/2.1.0/dart-async/Completer-class.html) "https://api.dartlang.org/stable/2.1.0/dart-async/Completer-class.html)") which allows us to produce a Future which we can complete at a later time.
That’s it! We now have solved problem #1 and users can refresh the weather by pulling down.
Next, let’s tackle the plain looking UI by creating a ThemeBloc.
Dynamic Theme
Our ThemeBloc is going to be responsible for converting ThemeEvents into ThemeStates.
Our ThemeEvents are going to consist of a single event called WeatherChanged which will be dispatched whenever the weather conditions we are displaying have changed.
abstract class ThemeEvent extends Equatable {
ThemeEvent([List props = const []]) : super(props);
}
class WeatherChanged extends ThemeEvent {
final WeatherCondition condition;
WeatherChanged({@required this.condition})
: assert(condition != null),
super([condition]);
}
Our ThemeState will consist of a ThemeData and a MaterialColor which we will use to enhance our UI.
class ThemeState extends Equatable {
final ThemeData theme;
final MaterialColor color;
ThemeState({@required this.theme, @required this.color})
: assert(theme != null),
assert(color != null),
super([theme, color]);
}
Now, we can implement our ThemeBloc which should look like:
class ThemeBloc extends Bloc<ThemeEvent, ThemeState> {
@override
ThemeState get initialState => ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData.light(),
color: Colors.lightBlue,
);
@override
Stream<ThemeState> mapEventToState(
ThemeState currentState,
ThemeEvent event,
) async* {
if (event is WeatherChanged) {
yield _mapWeatherConditionToThemeData(event.condition);
}
}
ThemeState _mapWeatherConditionToThemeData(WeatherCondition condition) {
ThemeState theme;
switch (condition) {
case WeatherCondition.clear:
case WeatherCondition.lightCloud:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData(
primaryColor: Colors.orangeAccent,
),
color: Colors.yellow,
);
break;
case WeatherCondition.hail:
case WeatherCondition.snow:
case WeatherCondition.sleet:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData(
primaryColor: Colors.lightBlueAccent,
),
color: Colors.lightBlue,
);
break;
case WeatherCondition.heavyCloud:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData(
primaryColor: Colors.blueGrey,
),
color: Colors.grey,
);
break;
case WeatherCondition.heavyRain:
case WeatherCondition.lightRain:
case WeatherCondition.showers:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData(
primaryColor: Colors.indigoAccent,
),
color: Colors.indigo,
);
break;
case WeatherCondition.thunderstorm:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData(
primaryColor: Colors.deepPurpleAccent,
),
color: Colors.deepPurple,
);
break;
case WeatherCondition.unknown:
theme = ThemeState(
theme: ThemeData.light(),
color: Colors.lightBlue,
);
break;
}
return theme;
}
}
Even though it’s a lot of code, the only thing in here is logic to convert a WeatherCondition to a new ThemeState.
We can now update our App widget to create a ThemeBloc and use BlocBuilder to react to changes in ThemeState.
Since our **App** widget will now be responsible for creating and disposing of a **ThemeBloc** we need to refactor it into a **StatefulWidget**.
class App extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
App({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<App> createState() => _AppState();
}
class _AppState extends State<App> {
ThemeBloc _themeBloc = ThemeBloc();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BlocProvider(
bloc: _themeBloc,
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _themeBloc,
builder: (_, ThemeState themeState) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Weather',
theme: themeState.theme,
home: Weather(
weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository,
),
);
},
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_themeBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
Note: We are using _BlocProvider_ to make our _ThemeBloc_ globally available using _BlocProvider.of<ThemeBloc>(context)_.
The last thing we need to do is create a cool GradientContainer widget which will color our background with respect to the current weather conditions.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
class GradientContainer extends StatelessWidget {
final Widget child;
final MaterialColor color;
const GradientContainer({
Key key,
@required this.color,
@required this.child,
}) : assert(color != null, child != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topCenter,
end: Alignment.bottomCenter,
stops: [0.6, 0.8, 1.0],
colors: [
color[700],
color[500],
color[300],
],
),
),
child: child,
);
}
}
Now we can use our GradientContainer in our Weather widget like so:
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/repositories.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Weather extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
Weather({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<Weather> createState() => _WeatherState();
}
class _WeatherState extends State<Weather> {
WeatherBloc _weatherBloc;
Completer<void> _refreshCompleter;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_refreshCompleter = Completer<void>();
_weatherBloc = WeatherBloc(weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Weather'),
actions: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.settings),
onPressed: () async {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => Settings(),
),
);
},
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () async {
final city = await Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => CitySelection(),
),
);
if (city != null) {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(FetchWeather(city: city));
}
},
)
],
),
body: Center(
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _weatherBloc,
builder: (_, WeatherState state) {
if (state is WeatherEmpty) {
return Center(child: Text('Please Select a Location'));
}
if (state is WeatherLoading) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
if (state is WeatherLoaded) {
final weather = state.weather;
final themeBloc = BlocProvider.of<ThemeBloc>(context);
themeBloc.dispatch(WeatherChanged(condition: weather.condition));
_refreshCompleter?.complete();
_refreshCompleter = Completer();
return BlocBuilder(
bloc: themeBloc,
builder: (_, ThemeState themeState) {
return GradientContainer(
color: themeState.color,
child: RefreshIndicator(
onRefresh: () {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(
RefreshWeather(city: state.weather.location),
);
return _refreshCompleter.future;
},
child: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 100.0),
child: Center(
child: Location(location: weather.location),
),
),
Center(
child: LastUpdated(dateTime: weather.lastUpdated),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 50.0),
child: Center(
child: CombinedWeatherTemperature(
weather: weather,
),
),
),
],
),
),
);
},
);
}
if (state is WeatherError) {
return Text(
'Something went wrong!',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red),
);
}
},
),
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_weatherBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
We are accessing our ThemeBloc via BlocProvider.of<ThemeBloc>(context) and are then dispatching a WeatherChanged event on each WeatherLoad.
We also wrapped our GradientContainer widget with a BlocBuilder of ThemeBloc so that we can rebuild the GradientContainer and it’s children in response to ThemeState changes.
Awesome! We now have an app that looks way nicer (in my opinion 😛) and have tackled problem #2.
All that’s left is to handle unit conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit. To do that we’ll create a Settings widget and a SettingsBloc.
Unit Conversion
We’ll start off by creating our SettingsBloc which will convert SettingsEvents into SettingsStates.
Our SettingsEvents will consist of a single event: TemperatureUnitsToggled.
abstract class SettingsEvent extends Equatable {}
class TemperatureUnitsToggled extends SettingsEvent {}
Our SettingsState will simply consist of the current TemperatureUnits.
enum TemperatureUnits { fahrenheit, celsius }
class SettingsState extends Equatable {
final TemperatureUnits temperatureUnits;
SettingsState({@required this.temperatureUnits})
: assert(temperatureUnits != null),
super([temperatureUnits]);
}
Lastly, we need to create our SettingsBloc:
class SettingsBloc extends Bloc<SettingsEvent, SettingsState> {
@override
SettingsState get initialState =>
SettingsState(temperatureUnits: TemperatureUnits.celsius);
@override
Stream<SettingsState> mapEventToState(
SettingsState currentState,
SettingsEvent event,
) async* {
if (event is TemperatureUnitsToggled) {
yield SettingsState(
temperatureUnits:
currentState.temperatureUnits == TemperatureUnits.celsius
? TemperatureUnits.fahrenheit
: TemperatureUnits.celsius,
);
}
}
}
All we’re doing is using Fahrenheit if TemperatureUnitsToggled is dispatched and the current units are Celsius and vice versa.
Now we need to add our SettingsBloc to our App widget.
class App extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
App({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<App> createState() => _AppState();
}
class _AppState extends State<App> {
ThemeBloc _themeBloc = ThemeBloc();
SettingsBloc _settingsBloc = SettingsBloc();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BlocProvider(
bloc: _themeBloc,
child: BlocProvider(
bloc: _settingsBloc,
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _themeBloc,
builder: (_, ThemeState themeState) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: themeState.theme,
home: Weather(
weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository,
),
);
},
),
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_themeBloc.dispose();
_settingsBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
Again, we’re making SettingsBloc globally accessible using BlocProvider and we are also disposing it in the dispose override.
Now we need to create our Settings widget from which users can toggle the units.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Settings extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final settingsBloc = BlocProvider.of<SettingsBloc>(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Settings')),
body: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
BlocBuilder(
bloc: settingsBloc,
builder: (_, SettingsState state) {
return ListTile(
title: Text(
'Temperature Units',
),
isThreeLine: true,
subtitle:
Text('Use metric measurements for temperature units.'),
trailing: Switch(
value: state.temperatureUnits == TemperatureUnits.celsius,
onChanged: (_) =>
settingsBloc.dispatch(TemperatureUnitsToggled()),
),
);
}),
],
),
);
}
}
We’re using BlocProvider to access the SettingsBloc via the BuildContext and then using BlocBuilder to rebuild our UI based on SettingsState changed.
Our UI consists of a ListView with a single ListTile which contains a Switch that users can toggle to select Celsius vs. Fahrenheit.
Note: In the switch’s _onChanged_ method we dispatch a _TemperatureUnitsToggled_ event to notify the _SettingsBloc_ that the temperature units have changed.
Next, we need to allow users to get to the Settings widget from our Weather widget.
We can do that by adding a new IconButton in our AppBar.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/repositories/repositories.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Weather extends StatefulWidget {
final WeatherRepository weatherRepository;
Weather({Key key, @required this.weatherRepository})
: assert(weatherRepository != null),
super(key: key);
@override
State<Weather> createState() => _WeatherState();
}
class _WeatherState extends State<Weather> {
WeatherBloc _weatherBloc;
Completer<void> _refreshCompleter;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_refreshCompleter = Completer<void>();
_weatherBloc = WeatherBloc(weatherRepository: widget.weatherRepository);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Weather'),
actions: <Widget>[
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.settings),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => Settings(),
),
);
},
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () async {
final city = await Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => CitySelection(),
),
);
if (city != null) {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(FetchWeather(city: city));
}
},
)
],
),
body: Center(
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: _weatherBloc,
builder: (_, WeatherState state) {
if (state is WeatherEmpty) {
return Center(child: Text('Please Select a Location'));
}
if (state is WeatherLoading) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
if (state is WeatherLoaded) {
final weather = state.weather;
final themeBloc = BlocProvider.of<ThemeBloc>(context);
themeBloc.dispatch(WeatherChanged(condition: weather.condition));
_refreshCompleter?.complete();
_refreshCompleter = Completer();
return BlocBuilder(
bloc: themeBloc,
builder: (_, ThemeState themeState) {
return GradientContainer(
color: themeState.color,
child: RefreshIndicator(
onRefresh: () {
_weatherBloc.dispatch(
RefreshWeather(city: state.weather.location),
);
return _refreshCompleter.future;
},
child: ListView(
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 100.0),
child: Center(
child: Location(location: weather.location),
),
),
Center(
child: LastUpdated(dateTime: weather.lastUpdated),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 50.0),
child: Center(
child: CombinedWeatherTemperature(
weather: weather,
),
),
),
],
),
),
);
},
);
}
if (state is WeatherError) {
return Text(
'Something went wrong!',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red),
);
}
},
),
),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_weatherBloc.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
We’re almost done! We just need to update our Temperature widget to respond to the current units.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
class Temperature extends StatelessWidget {
final double temperature;
final double low;
final double high;
final TemperatureUnits units;
Temperature({
Key key,
this.temperature,
this.low,
this.high,
this.units,
}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Row(
children: [
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(right: 20.0),
child: Text(
'${_formattedTemperature(temperature)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 32,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w600,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
Column(
children: [
Text(
'max: ${_formattedTemperature(high)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w100,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
Text(
'min: ${_formattedTemperature(low)}°',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w100,
color: Colors.white,
),
)
],
)
],
);
}
int _toFahrenheit(double celsius) => ((celsius * 9 / 5) + 32).round();
int _formattedTemperature(double t) =>
units == TemperatureUnits.fahrenheit ? _toFahrenheit(t) : t.round();
}
And lastly, we need to inject the TemperatureUnits into the Temperature widget.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
import 'package:flutter_bloc/flutter_bloc.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/blocs/blocs.dart';
import 'package:flutter_weather/models/models.dart' as model;
import 'package:flutter_weather/widgets/widgets.dart';
class CombinedWeatherTemperature extends StatelessWidget {
final model.Weather weather;
CombinedWeatherTemperature({
Key key,
@required this.weather,
}) : assert(weather != null),
super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: WeatherConditions(condition: weather.condition),
),
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
child: BlocBuilder(
bloc: BlocProvider.of<SettingsBloc>(context),
builder: (_, SettingsState state) {
return Temperature(
temperature: weather.temp,
high: weather.maxTemp,
low: weather.minTemp,
units: state.temperatureUnits,
);
},
),
),
],
),
Center(
child: Text(
weather.formattedCondition,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30,
fontWeight: FontWeight.w200,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
],
);
}
}
🎉 The full source for this example can be found here. 🎉
If you enjoyed this exercise as much as I did you can support me by ⭐️the repository, or 👏 for this story.
#mobile-apps #flutter #ios #android