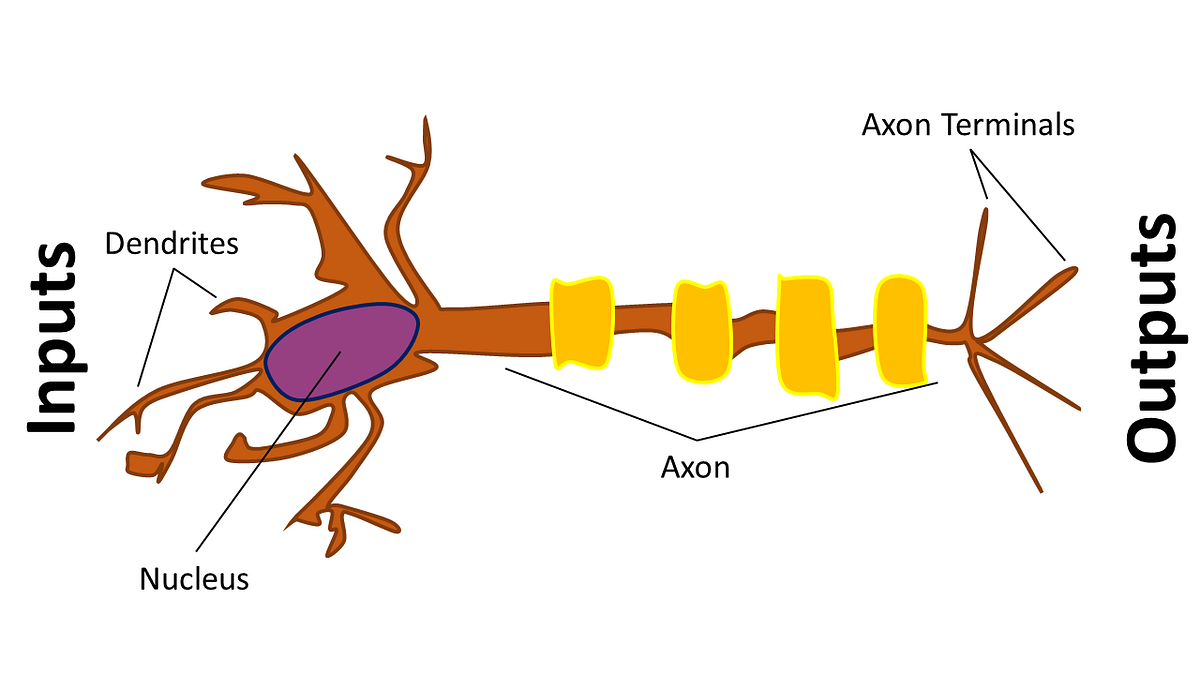
Many inventions have been taken from the natural world, such as artificial neural networks whose idea comes from the action of the human brain. Simple classical artificial neural networks consist of nodes that are called neurons. The figure shows the biological concept of the neuron. The nucleus of the cell is affected by information in the form of an electric charge through dendrites. If a sufficient number of dendrites is active in this short period of time, the neuron starts up and transfers the information through axon to the next [1].
An artificial neuron only in a few aspects resembles a biological neuron. Today, it provides a pragmatic solution to many problems of regression and classification.
The main differences include:
• the number of neurons,
• topology — in artificial networks, layers are calculated in a certain order, and biological neurons can act asynchronously,
• speed of information transfer,
• learning process.
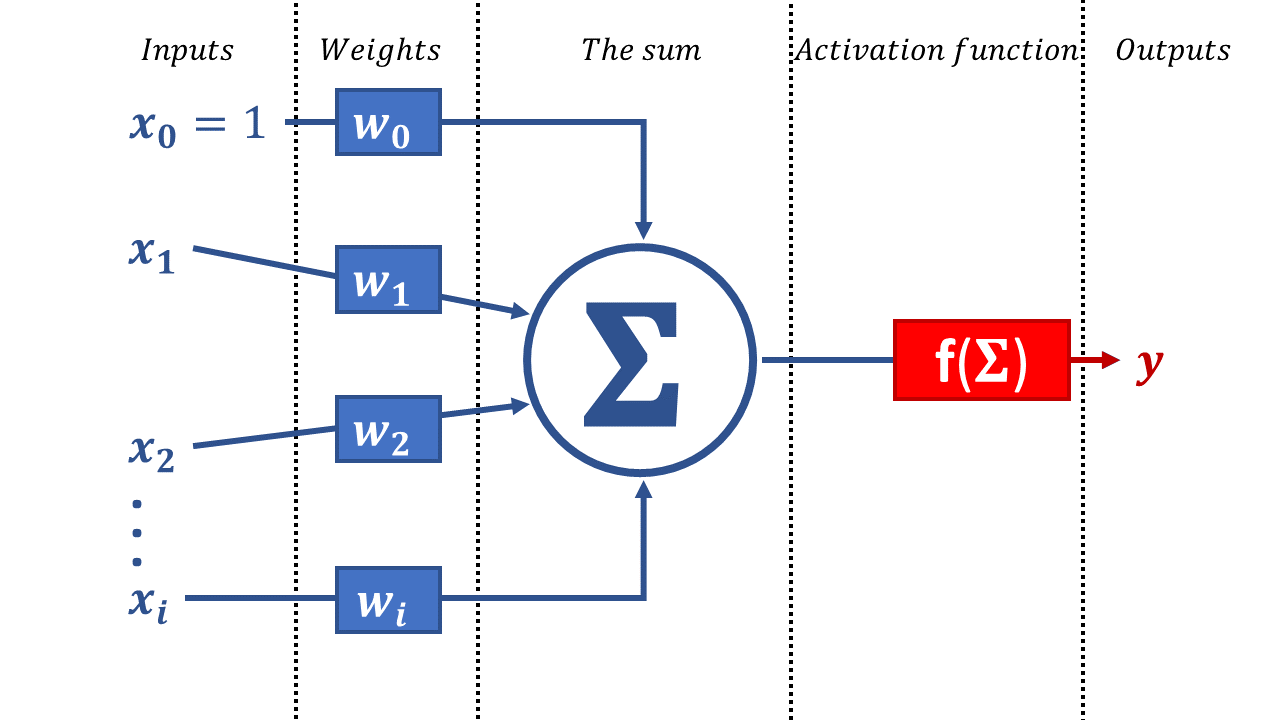
McCulloch-Pitts neuron model, Image by author
An artificial single neuron is represented by a mathematical function. It takes i inputs x, and each of them usually has its own weight w. The neuron calculates the sum and it is passed through the activation function to the network further (Figure next to the text).
According to this model, the mathematical formula for the output of this neuron is:
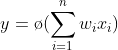
Output of Artificial Neuron, Image by author
where:
ø — activation function
This single neuron is called the McCulloch-Pitts neuron. It has multiple inputs and one output, which is analogous to the axon of the biological neuron. The output can be both the last in the network architecture and the input of the next neuron.
#neural-networks #logistics #relu #activation-functions #artificial-intelligence