Mobile Testing with Emulator: A step-wise guide
An Emulator is an application that emulates real mobile device software, hardware, and operating systems, allowing us to check and debug our application. It is generally provided by the device manufacturer. Mobile emulators are free and provided as a neighborhood of SDK with each new OS release. As a developer or a tester, you’ll configure the emulator to closely resemble the devices on which you propose to deploy your application here i:e selenium online training .
The emulator window consists of a tool screen on the left and phone controls/keyboard on the proper . The device screen initially displays ‘ANDROID‘, then displays the graphical logo, while the Android platform related to the AVD is initializing.
What is AVD Manager?
AVD Manager may be a tool to make and manage Android Virtual Devices(AVDs), which define device configuration for the Android Emulator. Before you’ll actually run an emulator, you would like to put in the Android SDK on your machine and define an AVD, which defines the hardware characteristics of the emulator. You can define things just like the device RAM, whether there’s touch screen and/or keyboard, camera support, audio playback support, etc. You can create several AVDs to check your device on several virtual devices.
How to Create an Android Virtual Device?
Once installation of all the prerequisites are done, we’d like to launch the SDK Manager to download relevant files to make an emulator and run the virtual device.
o In command line(cmd), type in android sdk. It would open the SDK Manager for you to download the relevant files
o In the SDK Manager select the files as shown below. This will help you create a virtual device
There are two ways to make Android Virtual Devices for mobile testing:
o Using Command Line
o Using AVD Manager
Creating a New Android Virtual Device using AVD Manager
The first step is to launch the AVD Manager and for that, there are variety of options you’ll follow:
o Launch AVD Manager using Program Menu : Go to Start → All Program → Android SDK Tools → AVD Manager
o Launch AVD Manager using Command Line : Go to Run and type cmd to open command prompt window. Type: android avd
o Launch AVD Manager from folder location : Browse to Android SDK folder and Double-click on AVD Manager.
Either of the above ways, it might open the Android Virtual Device Manager, which might assist you create the virtual devices. The AVD Manager main screen shows one default virtual device, which is Nexus 5.
- Click on Create button to make a replacement AVD
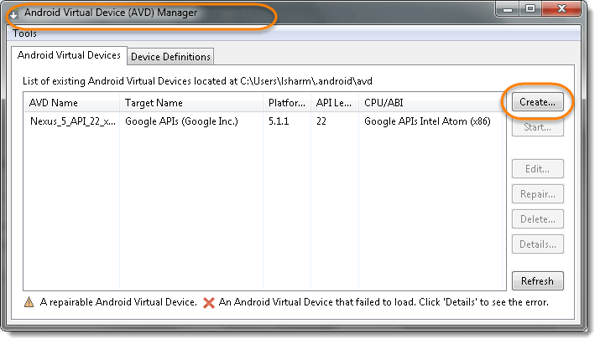
- A crop up will open, follow the below screenshot for the values. In case you’re simulating a selected device, you would possibly want to call it intrinsically. For example NexusSix-4.4 refers to an AVD that simulate Nexus-SIx which runs on Android 4.4.2 version.
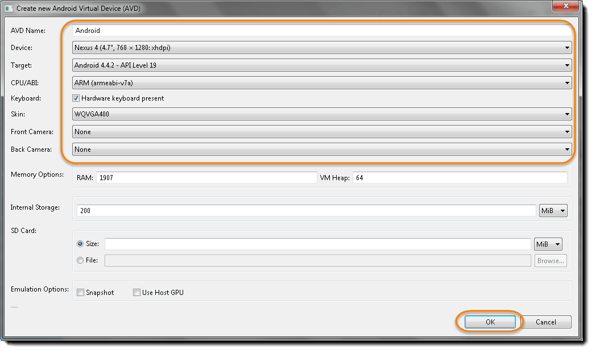
In this test i select a really generic name Android to stay it simple.
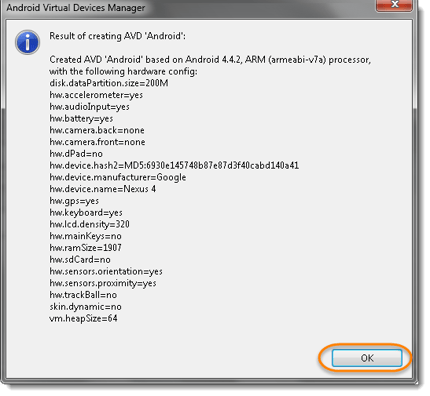
Note: you’ll fiddle with different configurations for your virtual device. - Click on OK to proceed with the save changes.
- After you complete above steps, the emulator are going to be displayed under the Android Virtual Devices tab, configured on the AVD Manager. Now select the AVD name and click on on Start on the proper .
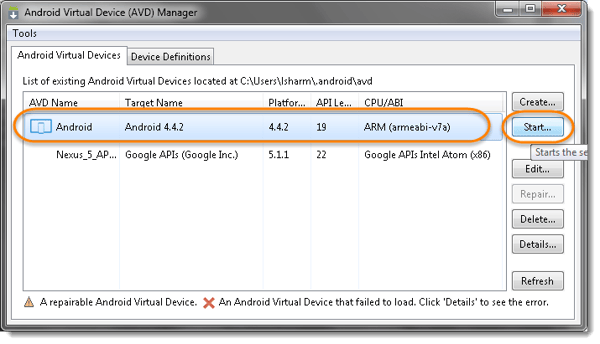
- this is able to launch the crop up with few options, you’ll choose as you would like . Once done, click on Launch, this may launch the emulator.
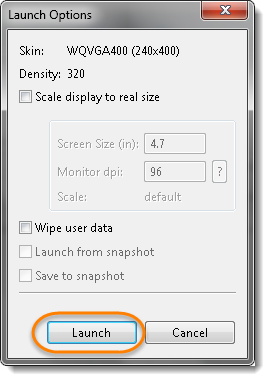
Scale display to real size: This causes the resolution of the emulator’s display to be scaled to match the screen size
Wipe user data: This would wipe any previous app installation you have done and would launch a plain fresh emulator
Launch from snapshot: This causes the emulated device to start from a previously saved snapshot of the device’s state. The emulator launches much faster when launched from a snapshot.
Save to snapshot: This causes the emulated device’s state to be saved to a snapshot upon device exit - Emulator will launch, it might take jiffy to display the house Screen of the virtual android device. The time taken is really adequate to the turn on time on the important mobile device.
Note:
- You can use the command ‘adb devices‘ to see if the adb is detecting the emulator. This basically completes the Android SDK installation part.
- If ANDROID logo appears for more than 15-30 minutes, something has probably gone wrong. Reboot your computer, start AVD Manager, delete our created ‘Android’ AVD, recreate this AVD, and relaunch new AVD.
The emulator window launched with 5554: Android in its title bar. Value 5554 identifies a console port that you simply can use to question and control the AVD’s environment. Android supports a maximum of 16 concurrently executing AVDs, where each AVD is assigned an even-numbered port number that starts at 5554. It means we will initialize quite one AVD at an equivalent time and may test the app with parallel execution.
Creating an Android Emulator using Command Line
Android Emulator is often configured differently for simulating different android devices. With the assistance of AVD configuration, Android Emulator can simulate:
o Target platforms versions
o Screen sizes
o Solutions
o Input methods
o Hardware configurations
o External storage sizes for SD card
Although there are an honest number of default device configurations present in AVD Manager, if you’ve got any particular device in mind that you simply want to emulate, you would like to create an AVD that resembles the features of your target device. For example, you would like to understand the screen size and determination then on.
Creating Default Device Definition
- Attend Device Definitions tab and choose one among the presets and click on ‘Create AVD’
- Every default device will provide you some preset AVD which are often changed consistent with your need
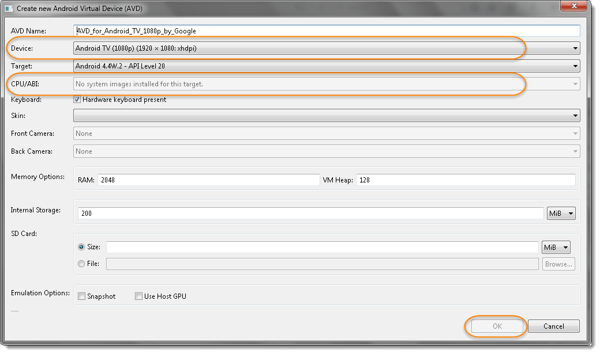
Note: Notice that the OK button is disabled, simply because under CPU/ABI it says that “No system Images installed for this target“. To avoid this, select different Device configuration from Device & select any skin or select none for skin and proceed.
Below are the lists of optional and mandatory settings:
o AVD NAME: Choose a name for the AVD like NexusSix-4.4 that refer to your device configuration
o Device: Select the AVD resolution as per the device options
o Target: Select the Android version / Test Environment or Target Platform
o CPU/ABI: Select Intel Atom (x86) for 32-bit and ARM (armeabi-v7) for 64-bit.
o Keyboard: Select this box to use the keyboard in the AVD
o Skin: Select this box to get the hardware buttons
o Front Camera: If the system have a webcam, that can be used with AVD
o Back Camera: If the system have a webcam, that can be used with AVD
o Memory Options: Set RAM & VM Heap for the device according to your need
o Internal Storage: Set this as per your need and Select GiB/MiB from the drop down
o SD Card: Set this as per your need and Select GiB/MiB from the drop down
o Emulation Options
- Snapshot: Select this to persist, it allows you to quickly start the emulator after the primary startup.
- Use Host GPU: Select this to use the pc graphics
- After you complete the above steps, the emulator are going to be displayed under the Android Virtual Devices tab, configured on the AVD Manager. Now Select the newly added AVD name and click on on Start on the proper.
- This is able to launch the crop up with few options, you’ll choose as you would like . here selenium online training Hyderabad Once done click on Launch, this may launch the emulator.
o Scale display to real size: This causes the resolution of the emulator’s display to be scaled to match the screen size
o Wipe user data: This would wipe any previous app installation you have done and would launch a plain fresh emulator
o Launch from snapshot: This causes the emulated device to be started from a previously saved snapshot of the device’s state. The emulator launches much faster when launched from a snapshot
o Save to snapshot: This causes the emulated device’s state to be saved to a snapshot upon device exit
Once done, Emulator will launch. It would take jiffy to display the house Screen of the virtual Android device.
Creating a Custom Device Definition
In case the available device definitions don’t match the device type you’d wish to emulate, you’ll create a custom device
definition for your AVD:
- If the AVD manager is opened, attend Device Definitions
- Click on Create Devices.
- The Configure Hardware Profile window will display and it’ll allow you to specify various configurations like the screen size, memory options, input type, and sensors.
Note: Once all the knowledge is filled properly, Create Device button will get enabled and you’ll proceed then. - After you complete above steps, the emulator are going to be displayed under the Device Definition tab, configured on the AVD Manager. selenium training Now Select the newly created AVD name and click on on Create AVD on the proper.
Automation using Android emulator
o Get Emulator Platform Version
o Unlock Android emulator screen
o Go to Settings. You will find About Phone under settings.
o Go to About Phone. It will show you Android version
o Verify calculator App Is Available In Emulator
We are getting to run an Appium test for calculator application so it should be there in emulator. Generally, calculator app are going to be already installed in emulator. To check if it is installed or not,
- Unlock emulator
- Verify if there’s an application with name Calculator
- Get app activity and package name. We need launcher activity and package name of calculator app. Activity and package name of calculator app on behalf of me are:
o Package name : com.android.calculator2
o Activity name : com.android.calculator2.Calculator - Create Appium Test Script In Eclipse. Now we are able to create and run our first Appium test on Android emulator for calculator application. I have prepared Appium test script as below. I have used RemoteWebDriver of Selenium Webdriver to launch app with required capabilities.
- to start out an instance of the emulator from the instruction , navigate to the tools/ folder of the SDK. Enter emulator command like this: emulator -avd []
So that was all about performing Appium testing on emulator.
#selenium #webdriver #api #automation #tools
