Python Variables: Declare, Concatenate, Global & Local
What is a Variable in Python?
A Python variable is a reserved memory location to store values. In other words, a variable in a python program gives data to the computer for processing.
Every value in Python has a datatype. Different data types in Python are Numbers, List, Tuple, Strings, Dictionary, etc. Variables can be declared by any name or even alphabets like a, aa, abc, etc.
In this tutorial, we will learn,
- How to Declare and use a Variable
- Re-declare a Variable
- Concatenate Variables
- Local & Global Variables
- Delete a variable
How to Declare and use a Variable
Let see an example. We will declare variable “a” and print it.
a=100
print (a)
Re-declare a Variable
You can re-declare the variable even after you have declared it once.
Here we have variable initialized to f=0.
Later, we re-assign the variable f to value “guru99”
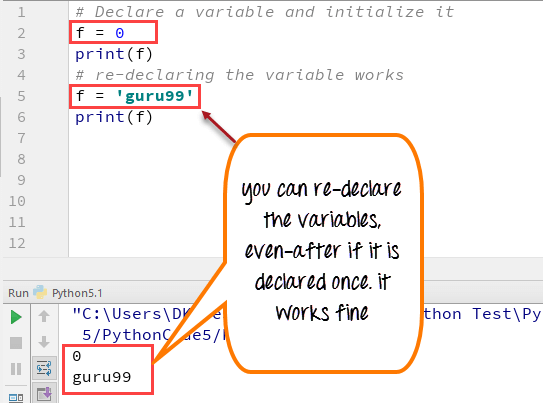
Python 2 Example
# Declare a variable and initialize it
f = 0
print f
# re-declaring the variable works
f = 'guru99'
print f
Python 3 Example
# Declare a variable and initialize it
f = 0
print(f)
# re-declaring the variable works
f = 'guru99'
print(f)
Concatenate Variables
Let’s see whether you can concatenate different data types like string and number together. For example, we will concatenate “Guru” with the number “99”.
Unlike Java, which concatenates number with string without declaring number as string, Python requires declaring the number as string otherwise it will show a TypeError
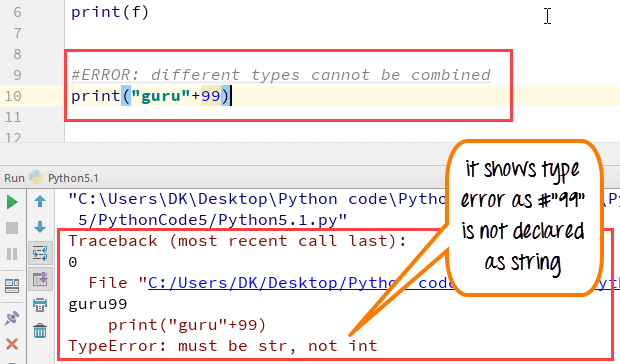
For the following code, you will get undefined output -
a="Guru"
b = 99
print a+b
Once the integer is declared as string, it can concatenate both “Guru” + str(“99”)= “Guru99” in the output.
a="Guru"
b = 99
print(a+str(b))
Local & Global Variables
In Python when you want to use the same variable for rest of your program or module you declare it a global variable, while if you want to use the variable in a specific function or method, you use a local variable.
Let’s understand this difference between local and global variable with the below program.
- Variable “f” is global in scope and is assigned value 101 which is printed in output
- Variable f is again declared in function and assumes local scope. It is assigned value “I am learning Python.” which is printed out as an output. This variable is different from the global variable “f” define earlier
- Once the function call is over, the local variable f is destroyed. At line 12, when we again, print the value of “f” is it displays the value of global variable f=101
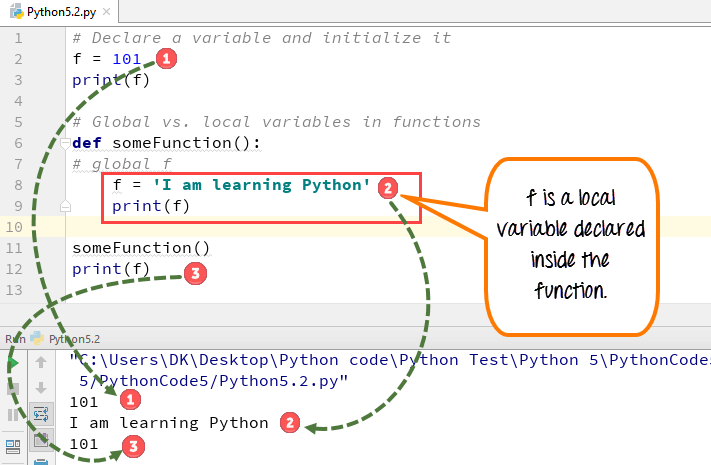
Python 2 Example
# Declare a variable and initialize it
f = 101
print f
# Global vs. local variables in functions
def someFunction():
# global f
f = 'I am learning Python'
print f
someFunction()
print f
Python 3 Example
# Declare a variable and initialize it
f = 101
print(f)
# Global vs. local variables in functions
def someFunction():
# global f
f = 'I am learning Python'
print(f)
someFunction()
print(f)
Using the keyword global, you can reference the global variable inside a function.
- Variable “f” is global in scope and is assigned value 101 which is printed in output
- Variable f is declared using the keyword global. This is NOT a local variable, but the same global variable declared earlier. Hence when we print its value, the output is 101
-
We changed the value of "f" inside the function. Once the function call is over, the changed value of the variable "f" persists. At line 12, when we again, print the value of "f" is it displays the value "changing global variable"

Python 2 Example
f = 101;
print f
# Global vs.local variables in functions
def someFunction():
global f
print f
f = "changing global variable"
someFunction()
print f
Python 3 Example
f = 101;
print(f)
# Global vs.local variables in functions
def someFunction():
global f
print(f)
f = "changing global variable"
someFunction()
print(f)
Delete a variable
You can also delete variable using the command del “variable name”.
In the example below, we deleted variable f, and when we proceed to print it, we get error “variable name is not defined” which means you have deleted the variable.
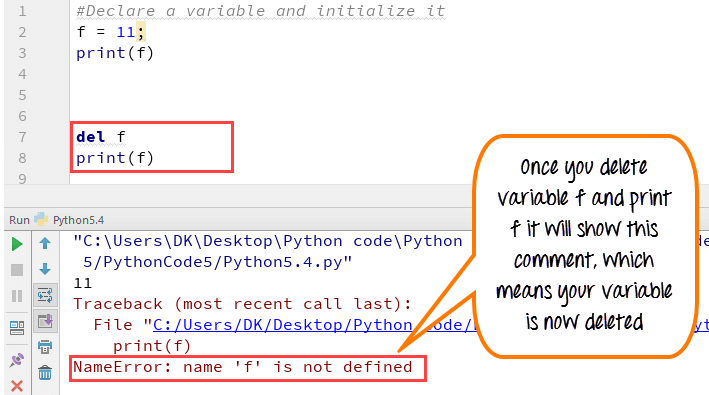
f = 11;
print(f)
del f
print(f)
Summary:
- Variables are referred to “envelop” or “buckets” where information can be maintained and referenced. Like any other programming language Python also uses a variable to store the information.
- Variables can be declared by any name or even alphabets like a, aa, abc, etc.
- Variables can be re-declared even after you have declared them for once
- In Python you cannot concatenate string with number directly, you need to declare them as a separate variable, and after that, you can concatenate number with string
- Declare local variable when you want to use it for current function
- Declare Global variable when you want to use the same variable for rest of the program
- To delete a variable, it uses keyword “del”.
Python Tutorial for Absolute Beginners - What Are Variables?
#python #web-development #machine-learning
