Speaking of graph data processing, we have had experience in using various graph databases. In the beginning, we used the stand-alone edition of AgensGraph. Later, due to its performance limitations, we switched to JanusGraph, a distributed graph database. I introduced details on how to migrate data in my article “Migrate tens of billions of graph data into JanusGraph (only in Chinese)”. As the data size and the number of business calls grew, a new problem appeared: Each query consumed too much time. In some business scenarios, a single query took up to 10 seconds, and with increase of the data size, a more complicated single query needed two or three seconds. These problems had seriously affected the performance of the entire business process and the development of related businesses.
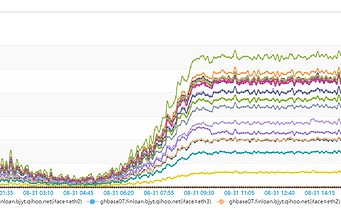
The architecture design of JanusGraph determines that a single query is time-consuming. The core reason is that its storage depends on the external storage, and JanusGraph cannot control the external storage well. In our production environment, an HBase cluster is used, which makes it impossible for all queries to be pushed down to the storage layer for processing. Instead, data can only be queried from HBase to the JanusGraph Server memory and then filtered accordingly.
#database #tutorial #graph database #database performance #nebula graph #graph database adoption